Investigation 3 “Aquatic Environments” Vocabulary Homework for
advertisement

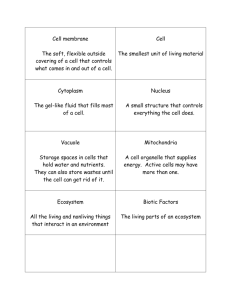
Investigation 3 “Aquatic Environments” Vocabulary Homework for Week of October 1-5, 2012 1. Aquarium: a tank for keeping live water plants and animals. 2. Aquatic Environment: water is the most important nonliving factor in an aquatic environment. An aquatic environment is different from a terrestrial environment because it is a water environment, not a land environment. 3. Algae: microscopic organisms. The green color in the aquarium water is from many, many green algae. Snails and scuds eat algae for food. 4. Freshwater environment: a pond, lake, stream, pool, or aquarium. The water is not salty like the ocean. 5. Elodea: a common aquatic plant. 6. Lemma (duckweed): an aquatic plant. It floats on the surface of the water. 7. Ecosystem: the interactions of the living and nonliving components of an environment. Homework for Week of October 8-12, 2012 8. Producer: an organism that makes its own food. Plants and algae are producers. 9. Consumer: an animal that eats other organisms. 10. Decomposer: an organism that eats dead plants and animals. The most important decomposers are bacteria and fungi. Earthworms can be decomposers. 11. Food Chain: describes the path that food takes from one organism to another. 12. Food Web: more complex than a food chain and shows where there may be competition for food resources. 13. Competition: competition for food is when two animals eat the same food. 14. Resource: Food is a resource, something that an organism needs. Homework for Week October 15-19, 2012 15. Marine Ecosystem: an ocean or saltwater bay environment. 16. Plankton: microscopic aquatic organisms that drift in the water. Some of them are plantlike, and some are animal-like. They are very important to food webs in freshwater and marine ecosystems. 17. Phytoplankton: are tiny plantlike organisms. They are producers in freshwater and marine ecosystems. 18. Zooplankton: are microscopic animals. They are consumers in freshwater and marine ecosystems. 4th Grade Environments Investigation 3