Chapter 7.1 Chemistry Notes: Describing Reactions
advertisement

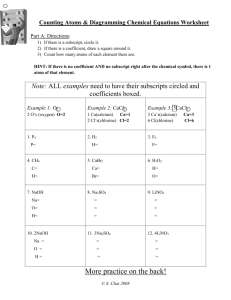
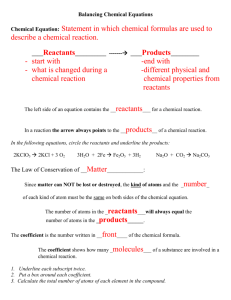
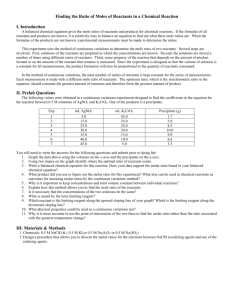
Name: ____________________________________ Date: ___________________ Period: _____ Chapter 7.1 Notes: Describing Reactions A. Physical VS Chemical Properties a. Physical Change – A change that occurs when some of the _____________________ of a material change, but the substances in the material remain the _________. b. Chemical Change – A change that occurs when a substance ________ and forms one or more ______ substances. i. Signs of a chemical change include _________ change, _______________ change, _______ produced, ______ formed, ____________________ formed. c. When __________ undergoes a chemical change, the ____________________ of the matter changes. When matter undergoes a ______________ change, the composition of the _______________ remains the same. B. Chemical Reactions a. A useful ________________ of a chemical reaction tells you the ______________ present ___________ and __________ the reaction. b. Reactants – The substances that undergo __________ and are present ___________ the reaction takes place. c. Products – The ______ substances formed as a result of that change and are present ___________ the reaction takes place. d. A chemical _____________ is a representation of a chemical _______________ in which the reactants and products are expressed as _________________. e. Reactants Products Ex. 1) Burning Charcoal Word Equation: Carbon + ______________ = ___________________ Dioxide Chemical Formula: ____ + ______ = ______ C. Conservation of Mass a. The Law of Conservation of Mass states that mass is neither ____________ nor ______________ in a chemical reaction. b. Therefore the ______ of the products is always ______ to the mass of the __________________. c. While _____________ charcoal you actually see the ___________ burn and _________________. The same __________ of charcoal that appears to have __________________ is actually converted into _______ dioxide _______. Name: ____________________________________ Date: ___________________ Period: _____ D. Balancing Equations a. In order to show that mass is __________________ during a reaction, a chemical equation must be __________________. b. ______________ equations can be balanced by changing the _______________ (the numbers that appear before symbols.) c. When balancing a chemical equations _________ change the ____________________ in the formula. E. Steps to Balancing a Chemical Formula a. Step 1: Count the number of atoms of each element on each side of the equation. b. Step 2: change one or more coefficients until the equation is balanced. (Only change the coefficients that need to be changed.) Ex. 1) Write a balanced equation for the reaction between copper and oxygen to produce copper(II) and oxide, CuO. What do you Know? - Reactants: _______________________ - Product: ________________________ Plan and Solve: - Write a chemical equation with the reactants on the left side and the product on the right side - _____________________________ - Change the coefficient of CuO in order to balance the number of O atoms. - _____________________________ - Change the coefficient of Cu. - ___________________________________ What do you need to know? - Balanced Equation Answer: Ex. 2) Balance the equation H2O2 H2O + O2 What do you Know? What do you need to know? - Reactants: - Balanced Equation _______________________ - Product: ________________________ Plan and Solve: Answer: - Write a chemical equation with the reactants on the left side and the product on the right side - _____________________________ - Change the coefficient of H2O2 and H2O in order to balance the number of H and O atoms. - _____________________________ Name: ____________________________________ Date: ___________________ Period: _____ Ex. 3) Balance the equation Mg + HCl H2 + MgCl2 What do you Know? What do you need to know? - Reactants: _______________________ - Balanced Equation - Product: ________________________ Plan and Solve: - Write a chemical equation with the reactants on the left side and the product on the right side - _____________________________ - Change the coefficient of HCl in order to balance the number of H and Cl atoms. - _____________________________ Answer: F. Counting With Moles a. A _______ is an amount of a ______________________ that contains approximately ________________ particles of that substance. This number is known as ____________________ number b. Because chemical reactions often involve large numbers of small ____________, chemists use a counting unit called the __________ to measure amounts of a substance. G. Molar Mass a. Molar mass is the ______ of one _________ of a substance. b. In the same way that a dozen _____ has a different mass than a dozen _________, a mole of _____________ would have a different mass than a mole of _______________. c. The molar mass is the same as the ________ mass expressed in __________. d. For a _______________ you can calculate the _______ mass by adding up the atomic masses of its component _________, and then expressing the sum in _________. Ex. 4) Find the molar mass of a molecule of CO2. Name: ____________________________________ Date: ___________________ Period: _____ H. Mole-Mass Conversion a. Once you know the molar mass of a substance, you can convert moles of that substance into mass, or a mass of that substance into moles. Ex. 5) Convert 55.0 g of CO2 to moles. What do you know? What do you want to know? Plan and Solve: Use a conversion factor. Answer: Ex. 6) Convert 144g of H2O to moles. What do you know? What do you want to know? Plan and Solve: Use a conversion factor. Answer: