Section 6.2 and 6.3 responses
advertisement

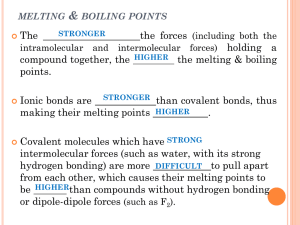
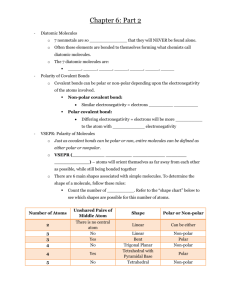
Section 6.2 Review Chemistry 11 1. An ionic compound dissolves in water because the attractions between the ions and the partials charges on the water molecules are strong enough to overcome the forces that bind the ions together. The attraction between an ion and a polar molecule is called an ion-dipole force. The negative ends of the polar water molecules are attracted to and surround the positive ions and pull them away from the solid crystal. The positive ends of the polar water molecules are attracted to and surround the negative ions and pull them away from the solid crystal. 2. The dispersion forces between larger molecules are stronger because as the number of electrons in a molecule increases, the chance that the vibration of electrons will create a transient, local dipole also increases. 4. For, hydrogen bonds to form between molecules, a hydrogen atom of one molecule must be bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen, fluorine or nitrogen. The positive nucleus of the hydrogen atom is exposed, giving the atom a partial positive charge. The second molecule must have a strongly electronegative atom that is in close proximity and will attract the partially positive hydrogen atom of the first molecule. 5. Intermolecular bonds are very weak compared with ionic bonds, covalent bonds and metallic bonds. Section 6.3 Review Chemistry 11 1. Chloroform, CHCl3, is polar since all dipoles are not equal, and do not cancel. In methane, CH4, the polarities of all bonds are equal and thus cancel. As a result, chloroform is slightly polar and the molecules will attract, giving it a higher boiling point than the non-polar methane. A second reason is that with the more massive chlorine atoms present in chloroform, there will be more attraction between the molecules regardless of polarity, e.g. CCl4 is still a liquid at room temperature. This is, in fact, the more significant effect. 2. The higher the bond energy of a substance, the higher the temperature must be to overcome the forces of attraction between the particles in the substances. High melting points and high boiling points indicate that the bond energies are strong. In molecular substances covalent bonds do not break when a substance melt or vaporizes. It is the intermolecular attractions that must be broken to cause melting or evaporation. 4. Ionic compounds are hard and brittle. When an object made up of ionic compounds is subjected to hammering or bending, the like charges of the particles can become aligned and reel each other. This will cause the crystal structure to break along the line where the charges are repelling. Therefore, ionic compounds are not practical compounds for tools. 5a. The melting point of the unknown solid is likely low. Since the compound does not conduct electricity as a liquid, it is a covalent compound. Covalent solids tend to have low melting point. b. The compound contains covalent bonds.