Chap 16 notes

Chap 16
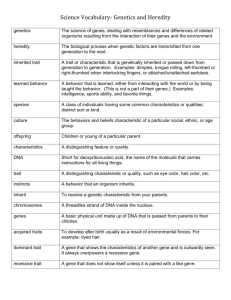
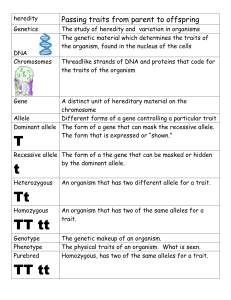
Allele – an option for a trait
EX: trait = eye color brown, blue, green, hazel, gray
Allele frequency - # of times an allele occurs in a population compared to other alleles
Our class = 8 brown, 5 blue, 4 green, 5 hazel, 1 gray
8/23, 5/23, 4/24, 5/23, 1/23
Gene pool – all different genes & alleles present in a population
Evolution – change of allele frequency of a population’s gene pool
Gene variation in population sources = mutation & gene shuffling
Mutation – a gene or a chromosome (DNA) changes; usually happens randomly
only mutation that occur in sperm/egg affect offspring
each of us are born with about 300 mutations already
Recombination in sexual reproduction –
when making sperm or eggs (meiosis)
independent assortment - this is why no 2 siblings are identical – because each sperm & egg are different
crossing over – shuffle your parents DNA when you produce sperm or eggs
Lateral gene traits – bacteria swap DNA with each other
same or different species
can lead to DNA plasmid, or antibiotic resistance
Single gene traits – one dimple, 2 dimples, no dimples, widow’s peak hairline, hitchhikers thumb- trait controlled by one gene, usually have 2 to 3 distinct options - lead to changes in allele frequency, dramatic shifts or no change at all
Polygenetic gene traits – are controlled by 2 or more genes, many different variations – height (controlled by 160 genes), eye color, hair color, hair texture
Polygenetic traits represented by a bell curve –
Directional – one end of curve has higher fitness than in the middle
Stabilizing – near the center of the curve have higher fitness than at either end, average becomes more common
Disruptive – at the upper & lower ends of the curve have higher fitness than near the middle
Genetic drift –
Bottleneck effect – disaster or disease can kill off a population except for a few, and now their genes are more frequent Ex: papayas
Biogeography – a science that attempts to describe the changing distributions & geographical patterns of living and fossil species of plants and animals.
2 important factors Darwin was unable to explain without heredity –
source of variation
how inheritable traits were passed from one generation to the next
Evidence of evolution –
fossil records
geographic distribution
homologous body structure
early development
DNA & protein analysis
Major concept of Lamark’s work – inheritance of acquired traits, selective use & disuse of organisms acquired or lost certain traits during your lifetime
Hutton & Lyell’s work – Earth was millions of years old, Earth was formed by natural forces, geological features could be built up or torn down over long periods of time
Malthus suggested overwhelming majority of a species offspring die