Ch 10-Genetics Vocabulary
advertisement

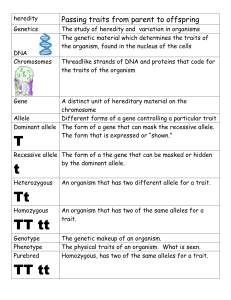
Ch 10-Genetics Vocabulary 1. Genetics- the study of heredity. 2. Heredity-the passing of traits from parent to offspring. 3. Allele-one of two or more slightly different molecular forms of a gene that arise through mutation and that code for different versions of the same trait. 4. Heterozygous-having a pair of nonidentical alleles at a gen locus. 5. Homozygous dominant-having a pair of dominant alleles at a gene locus. 6. Homozygous recessive-having a pair of recessive alleles at a gene locus. 7. Monohybrid cross-experimental cross between two parents that are homozygous for different versions of the same trait. 8. Probability-the chance that each outcome of a given event will occur is proportional to the number of ways the outcome can be reached. 9. Genotype-genetic constitution of an individual. 10. Phenotype-observable trait or traits of an individual that arise from gene interactions and geneenvironment interactions. 11. Punnett square method-construction of a diagram of a genetic cross that is a simple way to predict the probable outcomes. 12. Dihybrid cross-experimental cross between true-breeding parents that differ in two traits. 13. Law of Independent Assortment-Mendelian theory that by the end of meiosis, each pair of homologous chromosomes are sorted out and shipped to gametes without effecting other pairs. 14. Incomplete dominance-condition in which one allele of a pair is not fully dominant over the other. 15. Codominance-in heterozygotes, simultaneous expression of a pair of nonidentical alleles that specify different phenotypes. 16. Multiple allele system-three or more slightly different molecular forms of a gene that occur among individuals of a population.