C1_atoms_and_limestone
advertisement

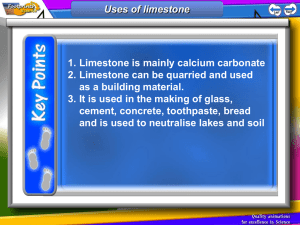
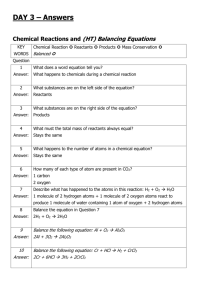
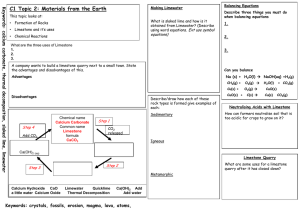
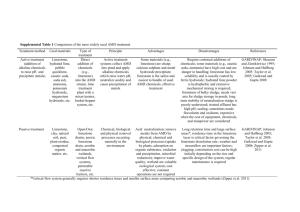
C1 The fundamental ideas in chemistry ATOMS PERIODIC TABLE AND CHEMICAL REACTIONS A Explain why an atom is electrically neutral. B Describe and explain the electronic arrangement of different atoms in the periodic table. C Describe the structure of an atom and explain the terms Atomic No. and mass no. C Draw the electronic structure of the first 20 elements C Draw and fully label an atom and its structure. C Calculate the no. of subatomic particles from atomic no. and mass no. of elements D Recognise names, symbols and diagrams of elements or compounds. E State a definition for elements. A* Write word and balanced symbol equations for reactions of Grp 1 elements with oxygen and water. B Explain why noble gases are unreactive giving examples C Explain the common properties associated with elements from groups 1 and 0. A* Write a balanced symbol equation to represent combustion, identifying elements &. compounds. A* Write and balance chemical equations, showing that atoms are not gained or lost. A Explain what is conservation of mass and calculate the mass of reactants or products from given information about the other substances in a reaction B Explain why elements in the same group have similar chemical properties. B Write the formula of some common compounds and molecular elements. C State the difference between an atom, ion and a molecule C Explain the difference between an element and compound C Describe how metal and non-metal atoms can join together to form compounds. C Describe how metals and non- metals form ions with examples from grp 1 and grp 7 elements D Understand that the Periodic Table can tell us about the properties of elements. D Use the formula of a compound to find out the number and type of elements in it. D State the electrical charge on each subatomic particle E State what an element is and write the symbol of the common elements from the periodic table E State what atoms are and what do they contain and label them in an atom Limestone and building materials Calcium carbonate A* Explain in detail the 'Limestone Cycle' using balanced symbol equations for each stage. A* Devise a viable, detailed experiment to test the strength of concrete as building materials due to variation of its contents A Write a balanced symbol equation for the production of slaked lime and quick lime and explain their uses A Distinguish between rocks, ores and minerals. B Explain the advantages and disadvantages of quarrying in a specific location. B Explain how metal carbonates reacts with acid, including Mg, Cu, Zn, Ca and Na B Explain what is limelight and complete a word equation for the thermal decomposition of limestone. B Discuss the trends in the thermal decomposition of metal carbonates. B/C Explain why limewater turns cloudy when CO2 is bubbled through it using WE / BSE B Compare the advantages and disadvantages of using timber, stone, glass steel and concrete as building materials. B Explain how acid rain might affect limestone buildings B Draw a flow chart to show how limestone can be turned into cement, concrete, mortar and glass. C Describe how limestone quarrying can damage the environment. C Describe and explain how some metal carbonates, including calcium carbonate, can be thermally decomposed. C Describe the production of slaked lime in word equations. D Write the formula of limestone, quick lime and slaked lime E List some uses of limestone as a material on its own and as a raw material.