Supplemental Table 1 Comparison of the most widely used AMD
advertisement
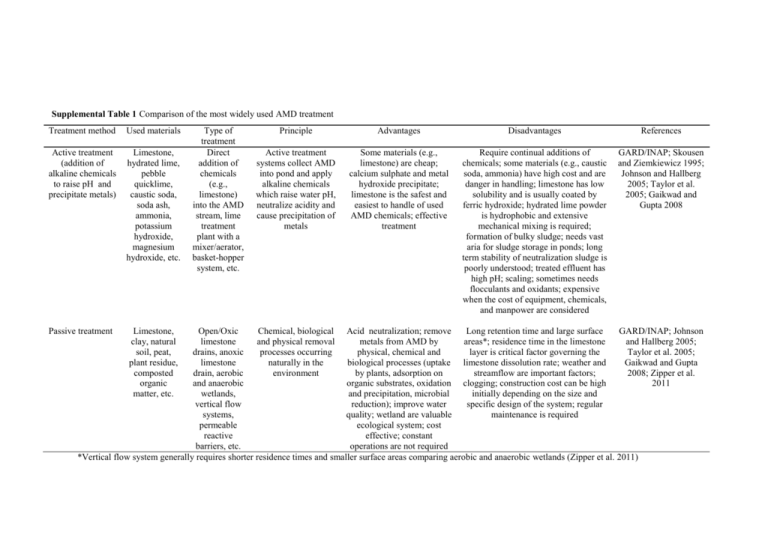
Supplemental Table 1 Comparison of the most widely used AMD treatment Treatment method Used materials Active treatment (addition of alkaline chemicals to raise pH and precipitate metals) Limestone, hydrated lime, pebble quicklime, caustic soda, soda ash, ammonia, potassium hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide, etc. Passive treatment Limestone, clay, natural soil, peat, plant residue, composted organic matter, etc. Type of treatment Direct addition of chemicals (e.g., limestone) into the AMD stream, lime treatment plant with a mixer/aerator, basket-hopper system, etc. Principle Advantages Disadvantages References Active treatment systems collect AMD into pond and apply alkaline chemicals which raise water pH, neutralize acidity and cause precipitation of metals Some materials (e.g., limestone) are cheap; calcium sulphate and metal hydroxide precipitate; limestone is the safest and easiest to handle of used AMD chemicals; effective treatment Require continual additions of chemicals; some materials (e.g., caustic soda, ammonia) have high cost and are danger in handling; limestone has low solubility and is usually coated by ferric hydroxide; hydrated lime powder is hydrophobic and extensive mechanical mixing is required; formation of bulky sludge; needs vast aria for sludge storage in ponds; long term stability of neutralization sludge is poorly understood; treated effluent has high pH; scaling; sometimes needs flocculants and oxidants; expensive when the cost of equipment, chemicals, and manpower are considered GARD/INAP; Skousen and Ziemkiewicz 1995; Johnson and Hallberg 2005; Taylor et al. 2005; Gaikwad and Gupta 2008 Open/Oxic Chemical, biological Acid neutralization; remove Long retention time and large surface GARD/INAP; Johnson limestone and physical removal metals from AMD by areas*; residence time in the limestone and Hallberg 2005; drains, anoxic processes occurring physical, chemical and layer is critical factor governing the Taylor et al. 2005; limestone naturally in the biological processes (uptake limestone dissolution rate; weather and Gaikwad and Gupta drain, aerobic environment by plants, adsorption on streamflow are important factors; 2008; Zipper et al. and anaerobic organic substrates, oxidation clogging; construction cost can be high 2011 wetlands, and precipitation, microbial initially depending on the size and vertical flow reduction); improve water specific design of the system; regular systems, quality; wetland are valuable maintenance is required permeable ecological system; cost reactive effective; constant barriers, etc. operations are not required *Vertical flow system generally requires shorter residence times and smaller surface areas comparing aerobic and anaerobic wetlands (Zipper et al. 2011)