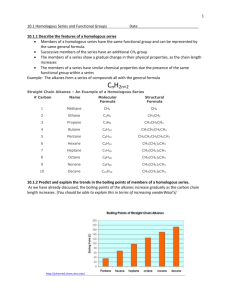
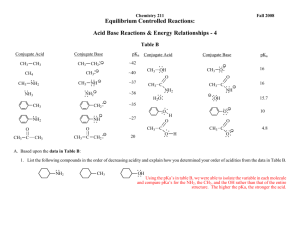
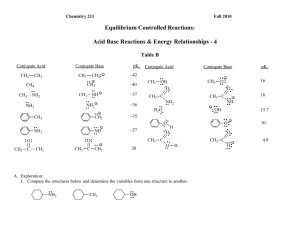
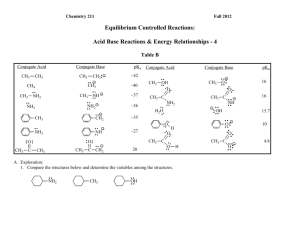
c. Using pKa`s of Acids and Bases to Investigate the Stabilities of
advertisement
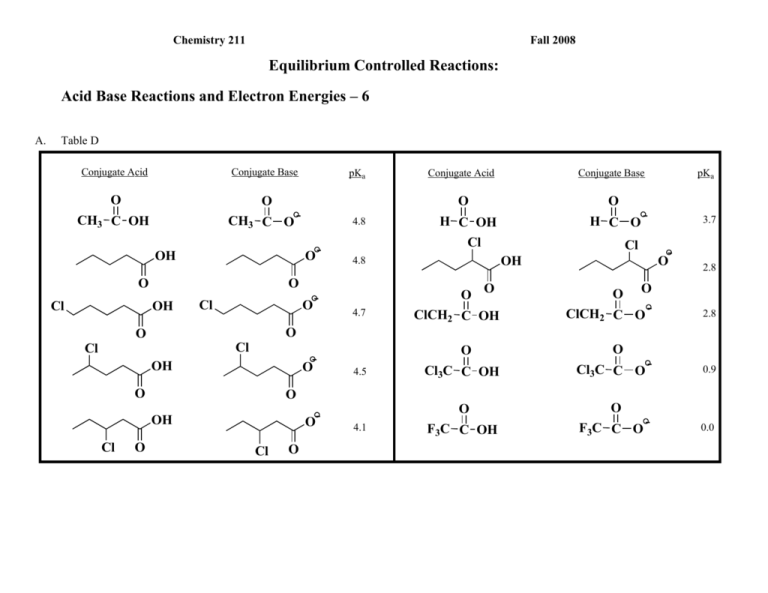
Chemistry 211 Fall 2008 Equilibrium Controlled Reactions: Acid Base Reactions and Electron Energies – 6 A. Table D Conjugate Acid Conjugate Base O O CH3 C O - CH3 C OH O O OH Cl Cl Cl O OH O Conjugate Base O O O O 4.7 Cl ClCH2 C OH 3.7 - OH 4.8 pKa H C O- H C OH Cl O 4.5 O O- OH O O- Conjugate Acid O O 2.8 O ClCH2 C O - 2.8 O O Cl 4.8 O- OH Cl pKa Cl O 4.1 O Cl3C C OH Cl3C C O - O O F3C C OH F3C C O - 0.9 0.0 Acid-Base Rxns & Electron Energy-6 B. 2 Based upon the data in Table D, Indicate the site of the highest energy electrons on each of the following ions. Then list the ions in order of decreasing energy of their highest energy electrons. (Highest Energy to Lowest Energy) - CH3 CH NH Cl - Cl CH2 CH2 NH - CH3 CH NH - CH3 CH2 NH F Identify the structural changes in the above structures. From the first one and the second one, the structural difference is the placement of the Cl, which makes those two isomers. The difference between the first and the third is the substituent halogen, which changes between Cl and F. Explain how you determined your order of energy. Cite specific data from Table D and indicate how it was used to support your conclusions. By observing trends among structures in Table D, we decided that the placement of the substituent halogen is the determinant of the energy for each of the above structures. Within groups of structures where everything except the location of the halogen remains constant, one can see that as a halogen is placed closer in the structure to the HEE, the energy increases (as is shown quite well in the first five structures and their pKa), and the lowest energy will occur when the halgen is not even present in the structure. As far as the difference in the halogen is concerned, when using the same method as above, looking at the last two structures (pKa 0.9 and 0.0) that Cl will increase overall energy more than F. C. Suggest theoretical explanations for the effects illustrated In B. above. Acid-Base Rxns & Electron Energy-6 3 Out of Class Applications for Class Group Activity # 11 A. Reading: CGWW pp. 196-7 Electron-donating groups decrease acidity B. Activities: 1. Indicate the site of the highest energy electrons on each ion. Then use the theory that you developed in class to predict the relative energies (lowest to highest) of the highest energy electrons of following anions. CH3 O CH3NH F O O O Explain how your predictions were made. 2. For each of the following compounds, circle the most acidic proton or group of protons and explain your choice on the basis of an appropriate theory. O F CH3 CH3 H N O H CH O CH3 CH3 CH3 C CH3 H O CH3 CH3 H O H 3. Predict which of the following reactions should produce more product at equilibrium. Explain your choice on the basis of an appropriate theory. O CH2 C CH 3 O - C + C Cl O - C CH 3 C C H CH2 Cl O CH2 -O H Cl C C CH C 3 -O CH2 Cl H C C CH 3 O H C O Acid-Base Rxns & Electron Energy-6 4 C. Nomenclature of Alkenes and Alkynes References: 1. CGWW: Ch. 2 pp. 31-32 2. Tutorials: a. http://chemistry.boisestate.edu/people/richardbanks/organic/nomenclature/organicnomenclature1.htm Sections Alkenes Alkynes Developed by Richard C. Banks, Professor of Chemistry, Boise State University Provides questions with answers b. http://www.molecularmodels.ca/nomenclature/index-2.htm Developed by Professor Dave Woodcock, Okanagan University College, British Columbia, Canada (Contains many examples.) Sections: 4. Functional Groups with Suffixes Only. I. Introduction II. Alkynes III. Alkenes (i) Naming Alkenes. Note: Your browser must have the chemscape chime plug-in for these pages to work. Select "1. Introduction to these pages", then click on "Nomenclature Index - Chemscape Chime" and begin with the "How and Why". If you have problems, go to the http://www.sci.ouc.bc.ca/chem/nomenclature/nom1.htm and click on "chemscape chime" and follow directions to download the "chemscape chime plug-in." If you have problems contact me. b. http://www.acdlabs.com/iupac/nomenclature Developed by Advanced Chemistry Development Laboratories (Gives detailed rules for nomenclature.) Recommendations 1993 R-3 Characteristic (Functional) Groups R-3.1 Unsaturation R-3.1.1 Suffixes denoting multiple bonds Acid-Base Rxns & Electron Energy-6 5 3. Applications a. Name the following: Br b. Draw structural formulas for the following compounds: 5-chloro-1-cyclopentyl-1-pentyne 2,3,5-trimethylcycloheptene 4-bromo-3-ethoxy-2-methyl-2-pentene 8-butoxy-6-ethyl-3-iodo-4-nonyne