Script
advertisement

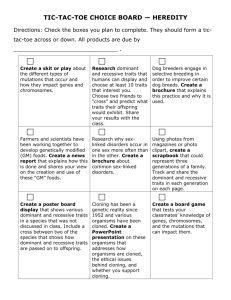
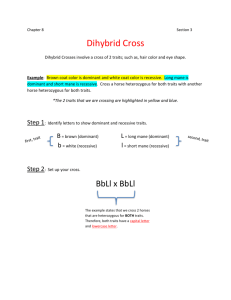
Standards: Standard 3.0 Life Science Topic C. Genetics Indicator * 1. Explain the ways that genetic information is passed from parent to offspring in different organisms. Objectives 1. Investigate and explain that in some kinds of organisms, all the genes come from a single parent, whereas in organisms that have sexes, typically half of the genes come from each parent. 2. Investigate and explain that in sexual reproduction, a single specialized cell from a female (egg) merges with a specialized cell from a male (sperm) and the fertilized egg now has genetic information from each parent, that multiplies to form the complete organism composed of about a trillion cells, each of which contains the same genetic information. Indicator * 3.3.2 The student will illustrate and explain how expressed traits are passed from parent to offspring. * Public Release * PDF Assessment limits: * phenotypes (expression of inherited characteristics) * dominant and recessive traits * sex-linked traits (X-linked only; recessive phenotypes are more often expressed in the male) * genotypes (represented by heterozygous and homozygous pairs of alleles) * punnett square (use to predict and/or interpret the results of a genetic cross; translate genotypes into phenotypes - monohybrid only) * Pedigree (use to interpret patterns of inheritance within a family) Script for My Digital Story: My name is Megan Phipps-Dickerson. Have you ever wondered how you ended up with certain traits? Characteristics such as eye color, hair color, hair texture, dimples, attached ear lobes, and freckles are just some of the genetic traits that we get from our parents. There are two types of traits, dominant and recessive. Dominant traits over-power recessive traits. Dominant traits are typically represented by a capital letter (B), where as the recessive trait is represented by a lower case letter (b). It is important to know that there are pure dominant traits, also called homozygous dominant traits, which are represented by two capital letter (BB), and there are hybrid or heterozygous dominant traits, which are represented by one capital letter and one lower case letter (Bb). The heterozygous trait, even though it is half dominant and half recessive, shows only the dominant trait because the dominant trait over powers the recessive trait. The only way for the recessive trait to show is for it to be homozygous recessive, which is represented by two lower case letters (bb). An easy way to remember this is to remember homo means same, like bb and BB, and hetero means different, like Bb. To determine the possibility of traits for the offspring, you cross the traits of the mother with the traits of the father in a punett square. I have blue eyes, which is a recessive trait. This means that blue eyes are represented my two lower case letters, let's say bb. Now figure out the probability of me getting blue eyes if my mom has blue eyes (recessive) and my dad has brown eyes (dominant). This means my mom, bb, is crossed with my dad, who is either BB or Bb. There are two ways to do this, BB X bb and Bb X bb. Let's do the first one, BB X bb. Fill in the sides of your punnett square. It doesn't matter which one you put up top or on the side, but I'm going to but BB on top and bb down the side. Now fill in the center of your punnett square. Start by pulling your top row down into the boxes below it; put a B in each box. Then pull the side row across into the boxes next to it, put a b in each box. You should end up with two letters in each box (4 boxes). In this case you end up with all Bb, this means that if my dad was homozygous dominant (BB) and my mom was homozygous recessive (bb) then they would have a 100% chance of having a child with brown eyes. But we know that I ended up with blue eyes, therefore my dad had to be heterozygous dominant (Bb). Let's try it, cross Bb with bb and see what you get. You should get Bb, and bb in the top row, and Bb and bb in the bottom row. That means there is a 50% chance of having a child with brown eyes, and a 50% chance of having a child with blue eyes. That explains why I have blue eyes, but my brother and sister have brown eyes. Now you can take this punnett square and use it to determine the probability of have different traits, like brown hair vs. blonde hair, dimples vs. no dimples, and the ability to roll your tongue vs. not being able to roll your tongue. You could also determine the possible traits of your children, but that's for another story. Possible sequence of pictures: *Picture of me- *Picture showing several different traits, like blonde and brown hair and freckles and no freckles- Try adding arrows pointing out different traits like eye color, hair color, and freckles. *Pictures of Letters: BB, Bb, and bb.*Punnett Square- *Filling in Punnett Square*Another picture of me- *Maybe a picture of my mom and dad... *Another Punnett Square*Another Punnett Square filled in... BB X bb *" "... Bb X bb *Picture of me and my sister and brother- *Picture of me and my bf... what would happen when blue eyes and green eyes mix?-