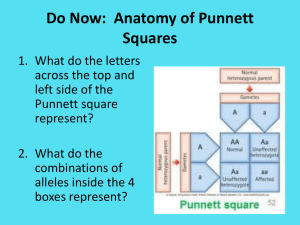
Step 1
advertisement
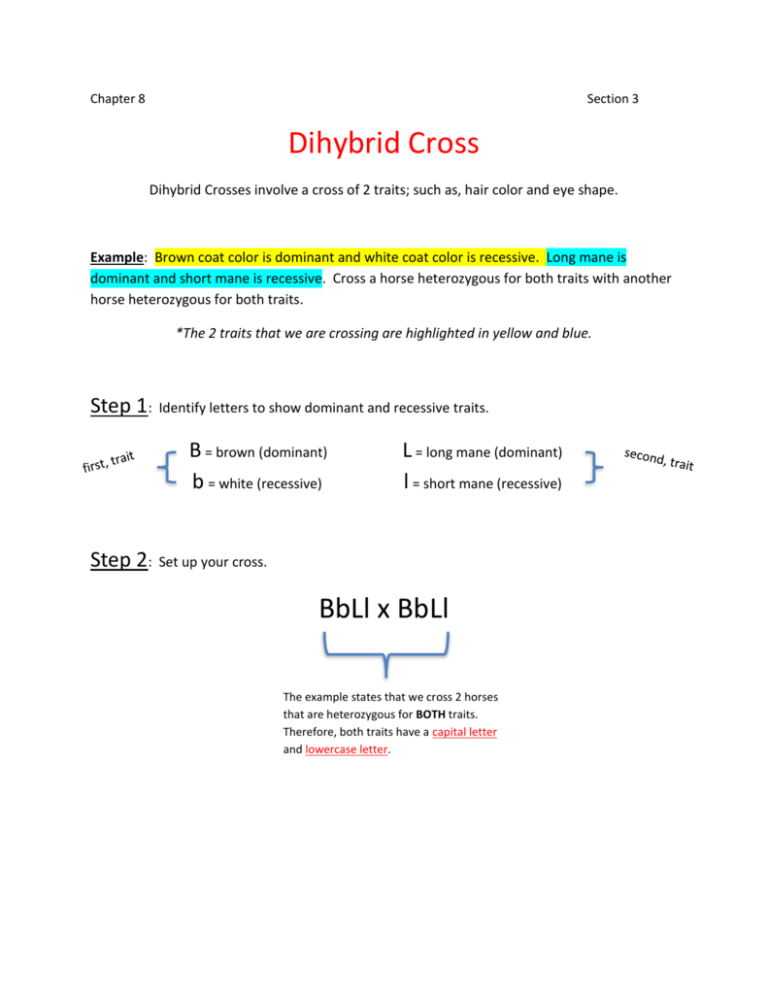
Chapter 8 Section 3 Dihybrid Cross Dihybrid Crosses involve a cross of 2 traits; such as, hair color and eye shape. Example: Brown coat color is dominant and white coat color is recessive. Long mane is dominant and short mane is recessive. Cross a horse heterozygous for both traits with another horse heterozygous for both traits. *The 2 traits that we are crossing are highlighted in yellow and blue. Step 1: Identify letters to show dominant and recessive traits. B = brown (dominant) b = white (recessive) Step 2: L = long mane (dominant) l = short mane (recessive) Set up your cross. BbLl x BbLl The example states that we cross 2 horses that are heterozygous for BOTH traits. Therefore, both traits have a capital letter and lowercase letter. Step 3: Set up the Punnett Square. For a dihybrid cross, the Punnett Square must have 16 boxes. Use the cross that we set up in step 2, to fill in the Punnett Square. To do this, we use the F.O.I.L. method. We do the F.O.I.L method for each parent. First Outside Inside Last BbLl x BbLl BL Bl Parent 1 bL Parent 2 bl BL Bl bL bl BL BL BL BL Bl BL bL BL bl Bl BL Bl Bl Bl Bl bL Bl bl bL BL bL bL Bl bL bL bL bl bl BL bl Bl bl bL bl bl bl Parent 2 Step 4: Phenotype Ratio. Your ratio should add up to 16 because there are 16 boxes. Use the Punnett Square to count the different combinations (color pencils will help) to cross out boxes. I also but the letter combos next to the physical traits, too so I know what I am looking for. Brown / Long (BL): 9 Brown / Short (Bl): 3 White / Long (bL): 3 White / Short (bl): 1 Parent 1