Eukaryotic Cell Structure Notes
advertisement

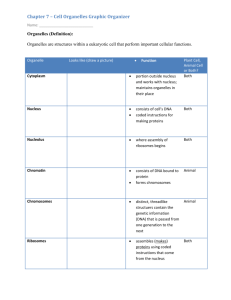
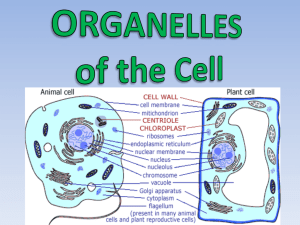
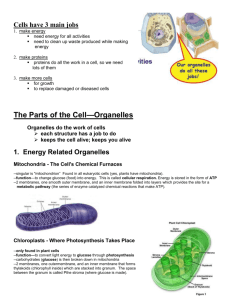
7.2 Cell Structure Notes Prokaryote v. Eukaryote Plant v. Animal Structure Name: ______________________________________________________________ Prokaryote or Eukaryote? 1. Cell Membrane/ Plasma Membrane Both 2. Cytoplasm & Cytosol Both 3. Nucleus Eukaryote Nickname/Location Function City Analogy Selectively permeable membrane that surrounds the cell. It allows some things in and some things out of the cell (ex: water and salts) to maintain homeostasis inside the cell. it is made up of a phospholipid bilayer and proteins. Fence around the city The cytoplasm is often mistakenly referred to as the fluid portion of the cell. However, it really just means the inside of the cell (from the plasma membrane to the nuclear membrane). The jelly-like fluid where the organelles float around is actually called the cytosol and is made up of mostly water. The space inside the city from the fence to city hall. It contains most of the cell's DNA. DNA contains the instructions for the making of proteins. Recall that DNA is an example of a nucleic acid. When DNA is in the loose form it is called chromatin and when it is condensed, it is called a chromosome. The nucleus also contains the nucleolus. City Hall Contains DNA, protects it from damage and is not visible when the cell is dividing. 4. Nuclear Membrane/ Nuclear Envelope (see in image above) Eukaryote Made of 2 membranes, it surrounds the nucleus. It contains thousands of holes called nuclear pores that allow substances to enter and exit the nucleus. Outer shell of the nucleus Fence around city hall 1 Structure Prokaryote or Eukaryote? 5. Chromosomes/ DNA/ Chromatin Both Nickname/Location Function Chromosomes are made up of DNA and proteins. They have bands on them called genes. DNA is found primarily inside the nucleus and it carries the instructions for the making of proteins. City Analogy The instructions to run the city Genetic blueprint for protein. Is known as a double helix due to its twisted ladder shape. 6. Nucleolus Found inside the nucleus, this is where ribosomes are created. Eukaryote 7. Ribosomes (the black dots on the rough endoplasmic reticulum shown at the right) 8. Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth and Rough) Both Proteins (like enzymes) are assembled on ribosomes. Ribosomes are small particles made up of RNA and proteins. They are either attached to the ER or free floating in the cytosol. Protein factory that is made up of RNA. Eukaryotes Found throughout the cell and made up of sacs filled with fluid and enzymes. Smooth ER does not have ribosomes. Lipids are assembled, carbohydrates are metabolized, and drugs are detoxified on the smooth ER. Fluid filled tunnel. Smooth ER- River that runs through the city- no boats on the river. Rough ER- River with boats. Rough ER has ribosomes. Proteins are assembled and folded on the rough ERProtein production. 2 Structure 9. Golgi Bodies/ Golgi Apparatus/ Golgi Complex Prokaryote or Eukaryote? Eukaryotes 10. Mitochondria Eukaryotes Nickname/Location Function City Analogy Looks like a stack of pita bread. Proteins leave the rough ER and arrive at the Golgi. The Golgi modifies the proteins, sorts them, and ships to a location either inside the cell or outside the cell using the cell vesicles. Post office- proteins sent off to where they belong Makes energy for the cell called ATP by taking in O2. They are surrounded by 2 membranes and contain their own DNA. Mitochondria are inherited from your mom (maternal side). A generator, sending out energy Cell powerhouse where cellular respiration takes place (releases energy stored in food). 11. Cytoskeleton (Microtubules and Microfilaments) Eukaryotes Maintains the cell's shape and is involved in moving organelles and the entire cell. Keeps organelles in place. It is used during cell division. Microtubules are large, hollow, and made of a protein called tubulin. Microfilaments are think, flexible and made of protein called actin. 12. Vacuole Both Stores materials like water, salts, and proteins. Plants have a large central vacuole with mostly water, dissolved minerals, and wastes inside it. Unicellular organisms (like amoeba) contain contractile vacuoles that pump excess water from the cell. Animals have food vacuoles that fuse with a lysosome. The small organelles that are used to store water, waste, or food in the cell. Water tower 3 Structures Found ONLY in Animal Cells: Structure Nickname/Location Function City Analogy 13. Lysosomes Organelle that is filled with hydrolytic/digestive enzymes that is used to speed up the breakdown of large food particles, macromolecules, waste, and even cells if need be. They recycle organelles so they can be used by the rest of the cell. Recycling center, garbage truck 14. Centrioles Made of microtubules, centrioles are involved in cell division. They are always at a right, 90 degree angle. Large bundle of proteins that help with cell division and organize the cell. They look like twizzlers! 15. Flagella or Cilia Made of microtubules these projections enable cells to move through a liquid. This is called motility or locomotion. Paddles (how to row a boat) Flagella- Long, hair-like projections located on the outside of the cell. They move in a wave-like motion. Cilia- Short projections located on the outside of the cell. Moves in a whip-like motion. Structures Found ONLY in Plant Cells: Structure Nickname/Location 16. Chloroplasts (Plastids) Function City Analogy Captures solar energy to make food for the plant in the process of photosynthesis. They are made of three membranes, contain its own DNA and also contains the green pigment called chlorophyll. Solar panel Traps solar energy turning it into glucose. 4 17. Cell Wall Supports, shapes, and protects the cell. Porous (has holes) enough to allow water, oxygen, and carbon dioxide to pass through easily. In plants, the cell wall is made of the complex carbohydrate called cellulose. An additional fence It is a rigid structure. It keeps extra water out of the cell, provides protection, and helps to keep the cells' shape. Path of a Protein Step 1: ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Step 2: ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Step 3: ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Step 4: ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Step 5: ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Step 6: ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 5