Cells have 3 main jobs - Littlemiamischools.org
advertisement

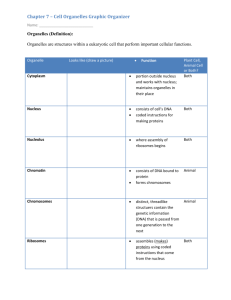
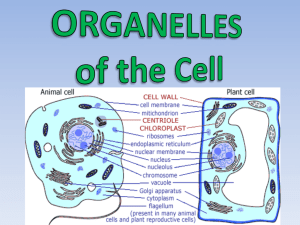
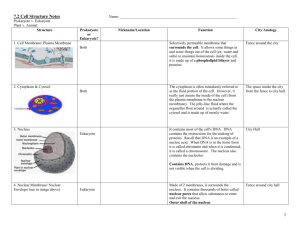
Cells have 3 main jobs 1. make energy need energy for all activities need to clean up waste produced while making energy 2. make proteins proteins do all the work in a cell, so we need lots of them 3. make more cells for growth to replace damaged or diseased cells The Parts of the Cell—Organelles Organelles do the work of cells each structure has a job to do keeps the cell alive; keeps you alive 1. Energy Related Organelles Mitochondria - The Cell's Chemical Furnaces --singular is "mitochondrion” Found in all eukaryotic cells (yes, plants have mitochondria). --function—to change glucose (food) into energy. This is called cellular respiration. Energy is stored in the form of ATP --2 membranes, one smooth outer membrane, and an inner membrane folded into layers which provides the site for a metabolic pathway (the series of enzyme catalyzed chemical reactions that make ATP). Chloroplasts - Where Photosynthesis Takes Place --only found in plant cells --function—to convert light energy to glucose through photosynthesis --carbohydrates (glucose) is then broken down in mitochondria --2 membranes, one outermembrane, and an inner membrane that forms thylakoids (chlorophyll inside) which are stacked into granum. The space between the granum is called Pthe stroma (where glucose is made). 2. Organelles involved in the production of proteins—which do the work of the cells (reproduction, growth, enzymes, transportation of materials, etc.) The Nucleus—main office directing all activities --nuclear envelope contains nuclear pores for some things to enter and exit -- chromatin is DNA and proteins, when the cell begins to divide, chromatin condenses and forms chromosomes. The Chromosomes contain the instructions for forming new cells/proteins. --DNA remains in the nucleus, it sends instructions to the cytoplasm via messenger RNA --RNA directs the synthesis of proteins on ribosomes in the cytoplasm --Nucleolus assembles ribosomes within the nucleus. Endoplasmic Reticulum -- Transport System --divides cell into compartments --function--moves molecules through the cell's interior, like a highway or conveyor belt (notice the ER is attached to the nucleus so RNA can send the instructions out to the ribosomes) Rough ER --has ribosomes which give it its "rough" appearance --functions in protein synthesis --ER transports newly assembled proteins to the Golgi Apparatus Smooth ER --contains enzymes that aid in forming lipids (such as hormones like estrogen and testosterone) Ribosomes – Product Production --function—to carryout the instructions for making new proteins from the nucleus. Works like a machine on an assembly line attaching one amino acid at a time --mRNA is "read" by the ribosomes and amino acids are assembled into proteins --ribosomes are made in the nucleolus inside the nucleus --ribosomes can be attached to the ER or free in the cytoplasm. Golgi Apparatus – Packaging and delivery System --flattened stacks of membranes --function—to collect, package and distribute molecules made in the cell and used elsewhere Jobs of the Golgi Apparatus (aka Golgi Complex) 1. separates proteins according to their destinations 2. modifies proteins (adds sugar and makes glycoproteins) 3. packages materials into vesicles which are exported outside the cell secretion 3. Other Organelles Lysosomes - Digestion Centers and Garbage Disposal --function—to break down molecules that are waste products or for use in other organelles. --contains high levels of digesting enzymes (to "lyse" means to dissolve) --recycle old and worn out cell parts "suicide sac" - apoptosis --digest other particles taken in by phagocytosis --this "food" is stored in food vacuoles, the lysosomes fuse with the vacuoles and release digestive enzymes --found in animal cells TAY-SACHS disease – missing an enzyme of the lysosomes that breaks down a fatty substance. Over time this fat builds up in the brain and nervous tissue, smothering the cells. Results in degeneration and death. Vacuole: storage facility -- function--mainly storage of water, salts, food, proteins and carbohydrates. --some have a specific function (contractile vacuole which maintains homeostasis in unicellular organisms by pumping out excess water) -- Plant cells have a CENTRAL VACUOLE - used for storage and help to maintain hydrostatic pressure contractile vacuole Cytoskeleton - Support System—the framework of the building Microfilaments– occur in bundles, form tracks within the cell for the movement of organelles, used to form pseudopod, and provide support for the cell membrane, or to make connections between cells. Microtubules - help maintain cell shape and helps separate chromosomes during dell division Centrioles – used during cell division to move and separate chromosomes, only found in animal cell Related to Movement Pseudopod – extensions of the cell that allow for movement (ameba), depend on actin filaments Cilia (hair) & Flagella (whip) --function in movement -- 9+ 2 Arrangement of microtubules For more information: www.thelifewire.com click on the photo of the Mandrill primate for the 8th edition, scroll down to View Content by Chapter---select Chapter 4. AWESOME RESOURCE! To be continued…cell membrane and cell wall