physical properties
advertisement
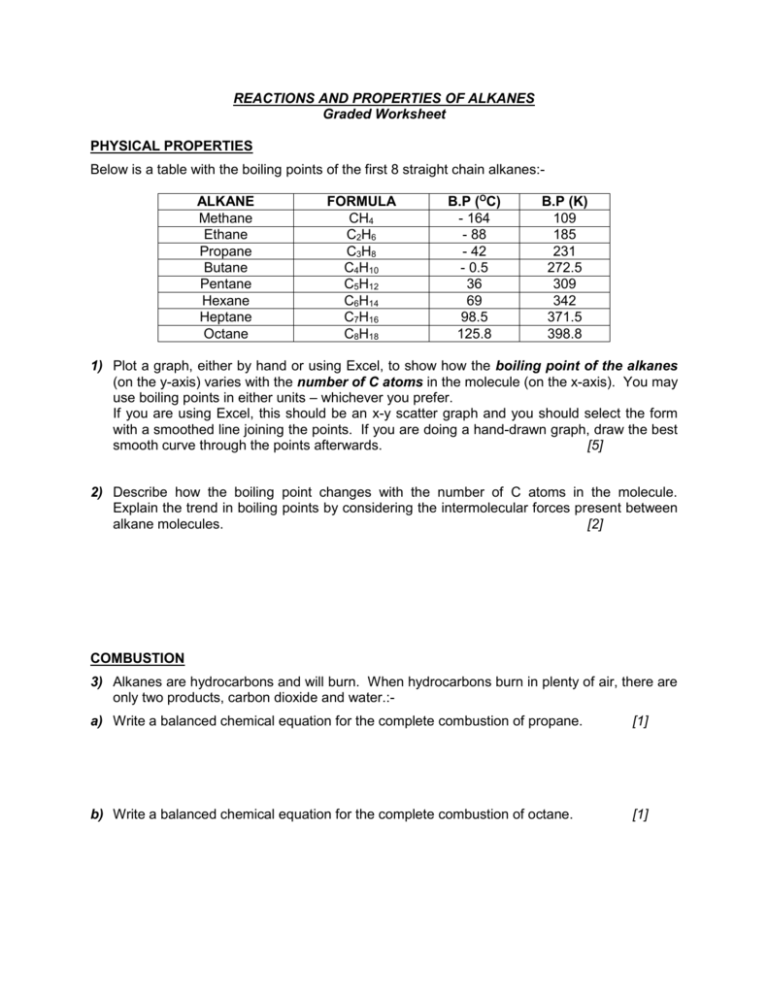
REACTIONS AND PROPERTIES OF ALKANES Graded Worksheet PHYSICAL PROPERTIES Below is a table with the boiling points of the first 8 straight chain alkanes:ALKANE Methane Ethane Propane Butane Pentane Hexane Heptane Octane FORMULA CH4 C2H6 C3H8 C4H10 C5H12 C6H14 C7H16 C8H18 B.P (OC) - 164 - 88 - 42 - 0.5 36 69 98.5 125.8 B.P (K) 109 185 231 272.5 309 342 371.5 398.8 1) Plot a graph, either by hand or using Excel, to show how the boiling point of the alkanes (on the y-axis) varies with the number of C atoms in the molecule (on the x-axis). You may use boiling points in either units – whichever you prefer. If you are using Excel, this should be an x-y scatter graph and you should select the form with a smoothed line joining the points. If you are doing a hand-drawn graph, draw the best smooth curve through the points afterwards. [5] 2) Describe how the boiling point changes with the number of C atoms in the molecule. Explain the trend in boiling points by considering the intermolecular forces present between alkane molecules. [2] COMBUSTION 3) Alkanes are hydrocarbons and will burn. When hydrocarbons burn in plenty of air, there are only two products, carbon dioxide and water.:a) Write a balanced chemical equation for the complete combustion of propane. [1] b) Write a balanced chemical equation for the complete combustion of octane. [1] c) What environmental problem arises from the carbon dioxide formed from the burning of fossil fuels? [1] 4) 1 mole of an alkane requires 11 moles of oxygen for complete combustion. Deduce which alkane this is and write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction. [2] 5) When there is a limited oxygen supply, then the hydrocarbons are incompletely burnt. Soot and carbon monoxide form instead of carbon dioxide. Describe the problems associated with these two products of incomplete combustion. [2] SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS 6) When chlorine reacts with an excess of methane in ultraviolet light, chloromethane is formed as the main organic product. a) Write a balanced equation for the reaction forming chloromethane. [1] b) Give the name of the mechanism for the formation of chloromethane and then outline it, including the name for each of the three stages in the reaction. [4] 7) Although chloromethane is the main organic product in the reaction above, there are other products formed. Give the names and formula of two other organic compounds, one containing chlorine and one not containing chlorine, which might be present in the mixture at the end of the reaction. Explain how each of these products has been formed. [3]