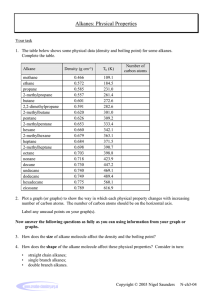
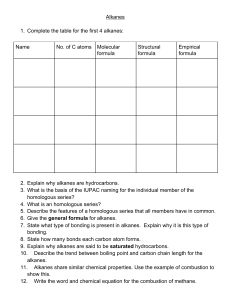
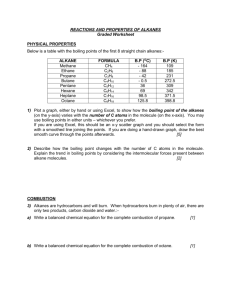
Alkane Reactions Worksheet - Chemistry II
advertisement

Honors Chemistry II REACTIONS OF ALKANES Reactions of Alkanes Are alkanes and cycloalkanes generally reactive or unreactive? 1. Alkane molecules usually assume the most _______________ conformations. 2. The bonding of alkanes is considered “_______________” bonding, which means that the electron pairs are shared directly _______________ the atoms, so it is _______________ for reagents to get to these electrons. 3. There are __________ non-bonded electrons (lone pairs) to participate in reactions. Therefore, alkanes are _______________ to normal chemical reactions. 1. Combustion What types of fuels do we burn in our homes, in our BBQ grills, and gas camping stoves? What do we call a reaction in which something is burned? What is needed to burn something? Examples: o Write a balanced equation for the combustion of propane. o Write a balanced equation for the combustion of 2,3-dimethylhexane. o Predict the products of the following reaction: 2 C3H8 (g) + 7 O2 (g) o If alkanes are burned with insufficient oxygen, _______________ _______________ is produced instead of carbon dioxide. Biological Combustion of Hydrocarbons What types of biomolecules contain long chains of hydrocarbons, with a carboxyl group at the end? What are the by-products of the burning of these fats and lipids in our bodies? o o o 2. Halogenation Alkane halogenation is the substitution of a _______________ with a _______________. Fluorination is strongly exothermic and difficult to control, while iodination is endothermic and nonspontaneous. Chlorination and bromination are the most widely used halogenation reactions. Chlorination and bromination follow radical halogenation mechanisms (see handout), and need visible or UV light to get started (h). A similar mechanism can be used to explain the reaction of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) with ozone (O3) in the atmosphere (see handout). Examples: Cl2 h Br2 h Chlorine will replace any hydrogen on the hydrocarbon, where bromine will replace the hydrogen that is bonded to the carbon that has the most carbons bonded to it. This is called _______________. Examples: Cl2 h Br2 h