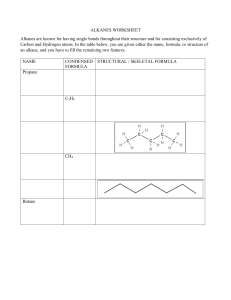
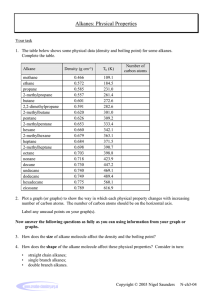
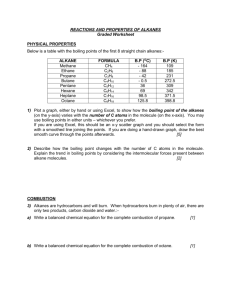
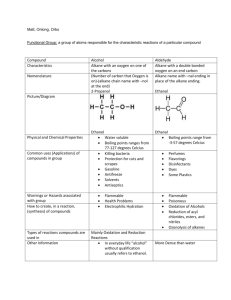
Alkanes properties and reaction
advertisement

Alkanes Uses Used as fuels Properties Boiling point increases with increasing size of alkane because intermolecular forces increase as a molecule gets bigger. Chemically quite unreactive SATURATED – only contain C-C single bonds Reactions Complete Combustion Burnt in excess oxygen to produce CO2 and H2O eg for methane: CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O (you need to be able to write and balance for any alkane given) Incomplete Combustion Burnt with insufficient oxygen to produce CO and H2O eg for methane: CH4 + 1½O2 → CO + 2H2O (you need to be able to write and balance for any alkane given) This reaction may also produce soot (C) Carbon monoxide, CO, is extremely toxic. People have died as a result of poorly serviced boilers (eg blocked vents) burning fuel incompletely. Reaction with Cl2 or Br2 Alkanes react with chlorine or bromine only in the presence of ultra violet light (UV light). The reaction is a SUBSTITUTION reaction (a hydrogen has been swapped for a bromine) CH4 + Br2 → CH3Br + HBr (in UV light)