Growth, function and division Interphase, mitosis and cytokinesis
advertisement

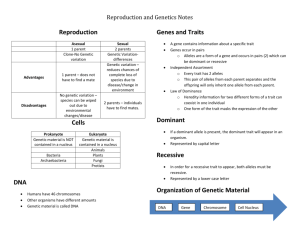
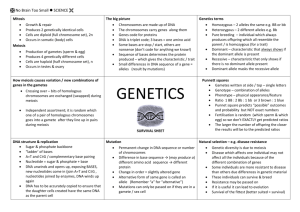
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. Growth, function and division Interphase, mitosis and cytokinesis Drawing The division of cells to form new ones The period of growth, function and copying of DNA The stage in which chromosomes become visible The chromosomes line up on equator Sister chromatids separate Two new nuclei form Cytoplasm splits in two Division of gametes/haploid cells into diploid ones. Prophase, Metaphase , Anaphase and Telophase (Meiosis I and II) Any physical characteristic of organism that can be inherited. Eye color, height, hair color, etc. The field which studies how traits are inherited. Mendel Homozygous or two of the same alleles for a trait. The selective mating of two organisms P F1 (1) organisms inherit two copies of each gene, one from each parent (2)the two copies of each gene segregate during gamete formation A specific region of DNA A particular form of a gene Two or more Pure or two of the same alleles Two different forms of alleles The pair of genes/alleles (two letters) The physical feature expressed The allele that is expressed when two different forms are present. The allele that is masked but only expressed if two copies are present. All offspring will be homozygous if the parents are the same or heterozygous if mixed. 32. 75% express dominant allele and 25% express the recessive allele. 33. 50%/50% 34. Traits are inherited separately 35. Increases genetic variation 36. Inheritance of recessive alleles 37. A person who carries one recessive allele but does not express the trait or disorder. 38. Genes on the sex chromosomes 39. They can donate an X or Y 40. X: because it has more genes and is bigger 41. Neither allele expressed: red +white=pink 42. Both alleles are expressed: red+white= red & white spotted 43. Controlled by many genes: skin, hair and eye color 44. Has one normal and one affected allele, but the normal masks the other 45. A male has only one X so he will express the trait 46. Circles=female square=male ; shaded=expresses the trait; unshaded=does not express the trait; and halfshaded=carrier 47. A map of all the chromosomes in a cell 48. The subunits of DNA/RNA 49. Sugar, phosphate and nitrogen base 50. Double Helix 51. Covalent bonds 52. Molecule is unzipped , new nucleotides added and two new strands form 53. DNARNAProtein 54. The process of copying DNA 55. Making mRNA from DNA template 56. Going from mRNA to a protein 57. Replication and transcription occur in the nucleus, translation occurs in cytoplasm on ribosomes. 58. A nucleic acid which transmits genetic information 59. DNA is double stranded, RNA is single; DNA has thymine, RNA has uracil; DNA has deoxyribose sugar, RNA has ribose 60. Similar to replication but only on strand is formed. 61. Ribosomal, messenger and transfer 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. Three Ribosomes A change or mistake in DNA A change in species over time Charles Darwin Mechanism in which individuals who adapt to their environment survive and reproduce and pass traits to offspring. A trait that allows an organism to better survive in its environment. Genetic comparisons=DNA/amino acid sequences; embryology=similar embryos at early stages of development; homologous structure=look similar but different functions; analogous= function similar but different structure; vestigial= used to have a function in ancestors; and fossils=traces of early organisms Collection of all alleles in a population Population not evolving. No natural selection or movement or change in allele frequency. Convergent= two unrelated species appear similar divergent= one common ancestor branches off to two or more species. Same as # 70 Genetic drift; gene flow; mutations; sexual selection; and natural selection Geographic= separates populations by area Reproductive= separates by sex or prevents mating. 76-79 was bonus and will not be on final exam