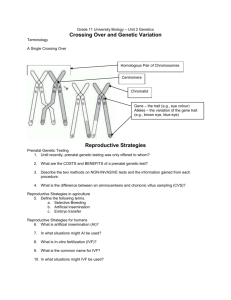
Reproduction and Genetics Notes
advertisement
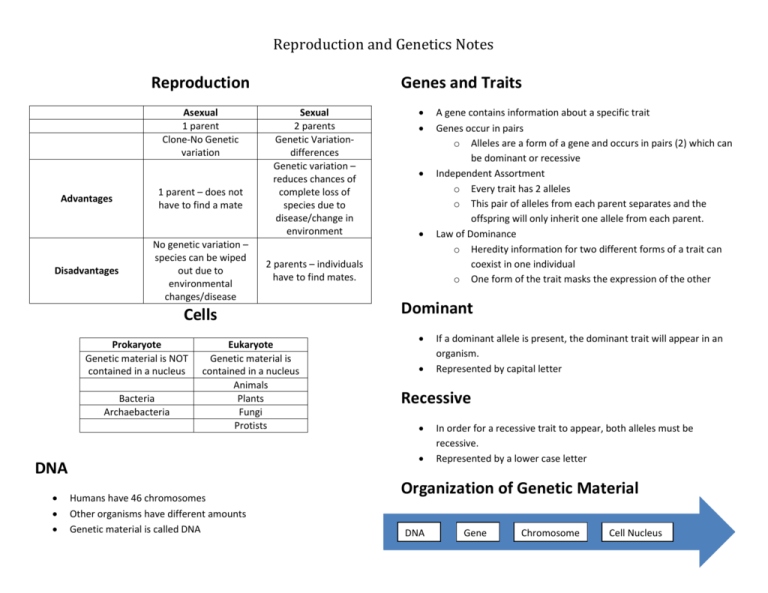
Reproduction and Genetics Notes Reproduction Asexual 1 parent Clone-No Genetic variation Advantages 1 parent – does not have to find a mate Disadvantages No genetic variation – species can be wiped out due to environmental changes/disease Genes and Traits Sexual 2 parents Genetic Variationdifferences Genetic variation – reduces chances of complete loss of species due to disease/change in environment Bacteria Archaebacteria Eukaryote Genetic material is contained in a nucleus Animals Plants Fungi Protists Humans have 46 chromosomes Other organisms have different amounts Genetic material is called DNA A gene contains information about a specific trait Genes occur in pairs o Alleles are a form of a gene and occurs in pairs (2) which can be dominant or recessive Independent Assortment o Every trait has 2 alleles o This pair of alleles from each parent separates and the offspring will only inherit one allele from each parent. Law of Dominance o Heredity information for two different forms of a trait can coexist in one individual o One form of the trait masks the expression of the other Dominant If a dominant allele is present, the dominant trait will appear in an organism. Represented by capital letter Recessive DNA 2 parents – individuals have to find mates. Cells Prokaryote Genetic material is NOT contained in a nucleus In order for a recessive trait to appear, both alleles must be recessive. Represented by a lower case letter Organization of Genetic Material DNA Gene Chromosome Cell Nucleus Reproduction and Genetics Notes Vocabulary Gene Allele Dominant Recessive Phenotype Genotype Heterozygous Homozygous Heredity Chromosomes Basic unit of heredity One of two alternate forms of a gene An allele whose trait always shows up in the organism when it is present An allele that is masked/covered up when a dominant allele is present Physical characteristics – what is seen Set of alleles (ex: bb) – allele combination A combination of alleles that are different A combination of alleles that are the same the passage of genetic instructions from one generation to the next found INSIDE the nucleus/A structure in all living cells that consists of a single molecule of DNA bonded to various proteins and that carries the genes determining heredity.