Notes: Overview of DNA and Genetics 3/9 A human (Eukaryotic) cell
advertisement
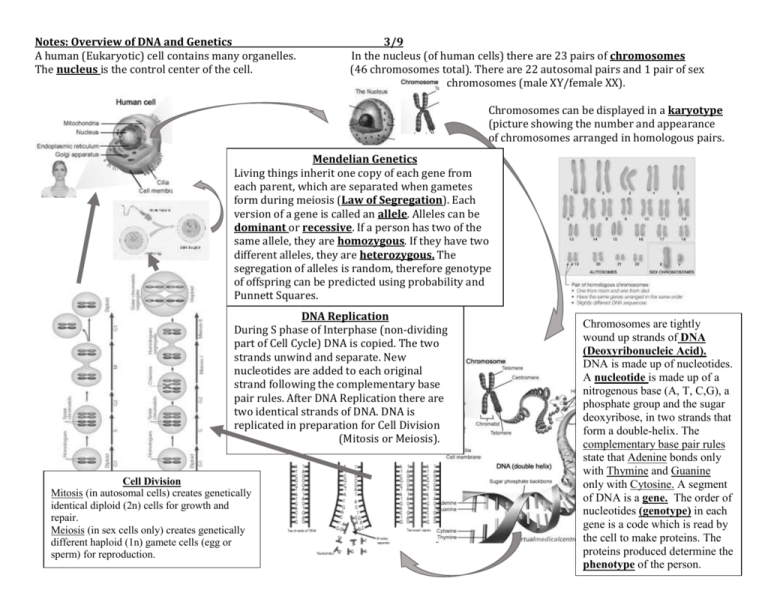
Notes: Overview of DNA and Genetics A human (Eukaryotic) cell contains many organelles. The nucleus is the control center of the cell. 3/9 In the nucleus (of human cells) there are 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 chromosomes total). There are 22 autosomal pairs and 1 pair of sex chromosomes (male XY/female XX). Chromosomes can be displayed in a karyotype (picture showing the number and appearance of chromosomes arranged in homologous pairs. Mendelian Genetics Living things inherit one copy of each gene from each parent, which are separated when gametes form during meiosis (Law of Segregation). Each version of a gene is called an allele. Alleles can be dominant or recessive. If a person has two of the same allele, they are homozygous. If they have two different alleles, they are heterozygous. The segregation of alleles is random, therefore genotype of offspring can be predicted using probability and Punnett Squares. DNA Replication During S phase of Interphase (non-dividing part of Cell Cycle) DNA is copied. The two strands unwind and separate. New nucleotides are added to each original strand following the complementary base pair rules. After DNA Replication there are two identical strands of DNA. DNA is replicated in preparation for Cell Division (Mitosis or Meiosis). Cell Division Mitosis (in autosomal cells) creates genetically identical diploid (2n) cells for growth and repair. Meiosis (in sex cells only) creates genetically different haploid (1n) gamete cells (egg or sperm) for reproduction. Chromosomes are tightly wound up strands of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid). DNA is made up of nucleotides. A nucleotide is made up of a nitrogenous base (A, T, C,G), a phosphate group and the sugar deoxyribose, in two strands that form a double-helix. The complementary base pair rules state that Adenine bonds only with Thymine and Guanine only with Cytosine. A segment of DNA is a gene. The order of nucleotides (genotype) in each gene is a code which is read by the cell to make proteins. The proteins produced determine the phenotype of the person.