Lecture 03.05.09 Entrance Slip: Draw the Bohr model for Helium
advertisement

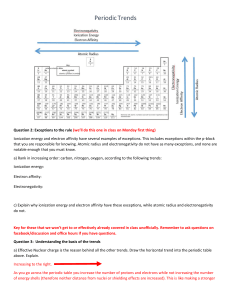
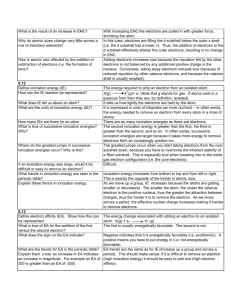
Lecture 03.05.09 Entrance Slip: Draw the Bohr model for Helium, Carbon, Neon, and Phosphorus. State Standard: Given the number of electrons and energy level, students should be able to identify the atom. Big Idea: Periods on the periodic table correspond to the number of electron clouds. Chemical groups determine the number of electrons in the outer electron cloud. Fun Fact: Some worms will eat themselves when they can’t find food. Your ribs move over 5 million times a year, when you breathe. Bohr’s Model What do you think: How do you think an increase in the number of electrons would impact the spectrum of an atom? What modifications in Bohr’s model would need to take place to accommodate the extra electrons Goals: View the spectrum of hydrogen Chapter 7 Activity #6 o Step 1, 2, 3a-c, 4, 5, 6 o Students work in pairs o Take turns looking at light and compare what you see o Draw the colors in your notebook with the proper spacing and order Read and Outline Chem Talk Pg. 400 – 401 o Periodic Table Revealed Ions and Ionization Energy Ionization Energy: the energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom at ground state Ion: an electrically charged atom or group of atoms that has acquired a net chare, either positive or negative o Atoms are neutral and have the same number of protons and neutrons, but they can gain or lose electrons 1st Ionization Energy is the energy to remove the 1st electron 2nd Ionization Energy is the energy to remove the 2nd electron Electron Configuration and Energy Levels Electron Configuration: the distribution of electrons in an atom’s energy levels The energy level, written En, corresponds to the number of different type of orbitals Orbitals are either s, p, d, or f o S contains 2 electrons o P contains 6 electrons o D contains 10 electrons o F contains 14 electrons o The superscript tells you how many electrons are in that particular orbital The Periodic Table Period: a horizontal row of elements in the periodic table Chemical Group: a family of elements in the periodic table that have similar electron configurations o Elements in a group share similar physical and chemical properties