Study Guide 2.1 and 2.2
advertisement

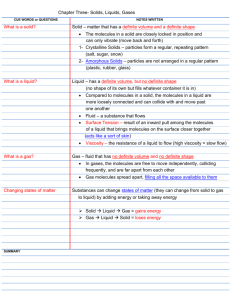
Study Guide 2.1 and 2.2 – States of Matter & Changes of State KEY 1. Solid – has a definite shape, definite volume keeps its shape in any container, any position particles packed closely together particles tightly fixed in one position they move, only slightly, vibrate in place 2. Crystalline solid – particles form in regular, repeating patterns patterns create crystals salt, sugar, snow are examples melts at a distinct temperature 3. Amorphous solid – particles not arranged in regular pattern doesn’t melt at distinct temp. – becomes soft, might change into another substance examples: glass, plastic, rubber 4. Liquid – has a definite volume but no shape of its own shape changes with container particles almost as close as those in solid BUT, they move around freely (like marbles in your hand) is a “fluid” – substance that flows 5. Surface tension – characteristic property of a liquid inward force or pull among molecules in a liquid brings surface molecules closer together (acts like a “skin”) ex: needle and bugs floating on water 6. Viscosity – characteristic property of a liquid it’s a liquid’s resistance to flowing depends on size, shape, and attraction between molecules High viscosity (LOTS of resistance) = SLOW FLOW (ex: honey, mayonnaise, molasses) Low viscosity (VERY LITTLE resistance) = FAST FLOW (ex: water, vinegar) 7. Gas – gas is a fluid, can flow has neither shape, nor volume particles spread to fill their container 8. Volume – the amount of space that matter fills 9. The relationship between gasses and the volume of a container – gas particles fill their container, so the volume of a gas is the same as the volume of its container 10. Temperature (and how it relates to the motion of particles of matter) the measure of the energy of the motion of matter particles more energy means higher temps. less energy means lower temps. 11. Melting – the change in state from solid to liquid ice to water o Thermal Energy (TE) around ice increases - makes water molecules move faster o increase TE means increase in temp o particles break free from their fixed positions – become liquid 0 degrees Celsius is water’s freezing and melting point 12. Melting point – specific temp at which a solid melts 13. Freezing – the change in state from liquid to solid water to ice o Thermal Energy (TE) around water decreases - makes water molecules move slower o decrease in TE means decrease in water’s temp o particles move so slowly that they take on fixed positions – become solid 14. Vaporizing – the change in state from liquid to gas water to water vapor o Thermal Energy (TE) around water increases - makes water molecules move faster o increase TE means increase in temp o particles gain enough energy to move independently – become a gas (water vapor) 100 degrees Celsius is water’s boiling point 15. Evaporation – vaporization that takes place only on the surface of a liquid ex: a puddle drying up slowly 16. Boiling (and boiling point) – vaporization that takes place below and at the surface of a liquid ex: pot of boiling water (the bubbles that rise are water that has turned from a liquid state to a gas state) boiling point – temp at which a liquid boils (vaporizes) 17. Condensation – the change in state from a gas to a liquid water vapor to water o Thermal Energy (TE) around water vapor decreases - makes water molecules move slower o decrease TE means decrease in temp o particles lose enough energy to form a liquid o ex: fog, clouds, your breath in the winter time water vapor – a colorless gas that cannot be seen – clouds, fog, breath are NOT water vapor 18. Sublimation – change in state from a solid directly to a gas (no liquid state) dry ice (solid carbon dioxide – can’t exist as a liquid at our atmospheric pressure) o Thermal Energy (TE) around the solid dry ice increases - makes DI molecules move faster o increase in TE means increase in temp o particles lose enough energy to break free of their fixed positions and turn directly into a gas