Spheres of the Earth
advertisement

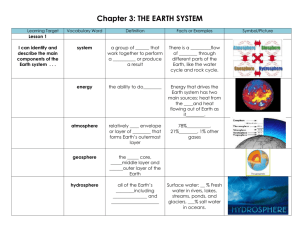
Name: ______________________________________ Period: ____ The Structure of Earth System- a group of parts that work together Energy- the _______________ do work. Earth gets its this ability to work (energy) _________________ and from the center of the earth as it cools. Earth itself is a _____________________, but on earth there are open systems or spheres that influence one another. The Spheres of the Earth System: Atmosphere: the relatively thin layer of _____________that forms earth’s outermost layer o Mostly ____________________ &______________________ o Dust particles o Cloud droplets o ___________________________ Geosphere: nearly all of earth’s ______________ o __________________ o Metal & other __________________ o Has three layers _____sphere: contains all of Earth’s ______________ o Oceans, glaciers, rivers, lakes, ground water, & water vapor o Covers ¾ of the Earth o Mostly salt. Only a tiny portion is _________________. _____sphere: the part of Earth where ___________________________. Feedback = the ________________________ between the spheres Inside Earth _______________ is the study of what’s on and in the Earth. Geologists are scientists who study the processes that create Earth’s features and search for clues about Earth’s ________________. o They study the ________________ and ________________ characteristics of rock, the material that forms Earth’s hard surface. o They map where different types of rocks are found and describe __________________, the features sculptured in rock and soil by water, wind, and waves. o They study how ____________ (waves caused by earthquakes) ______________ through earth. Two forces Change Earth’s Surface: o o __________________ forces – shape the surface by building up mountains and landmasses. Destructive forces - slowly wear away __________________ What’s inside? Three main layers: o ____________________ o ____________________ o ____________________ THE CRUST The layer of rock that forms Earth’s __________________ skin. o Includes dry land and the ________________________. o Approx. ____________________ thick. o ___________________ – oxygen, silicon, aluminum, calcium, iron, sodium, potassium, magnesium o Temperature ___________________ Two Types Oceanic crust - the crust beneath the ___________________ o The ___________________ crust is under the ocean. (Basalt – dark, fine-grained rock) ___________________ crust – the crust that forms the continents and some major islands. (Granite – coarse grained rock) The deeper down into Earth, the greater the ______________ and ___________________. (just below earth the rock is cool, but after about 20meters down the temperature increases nearly 1oC/40m) THE MANTLE The layer of ___________________ below the crust Starts ___________________beneath the surface (40-3040km) down o Approx. ___________________ thick o ___________________ – silicon, oxygen, iron, magnesium o Temperature – ___________________ THREE mantle layers o Lithosphere – brittle rock o Asthenosphere – less rigid rock (___________________) o Mesosphere – hot but more ___________ due to pressure THE CORE Makes up 1/3 of Earth’s _________________, but only 15% of its volume. o Composition – ___________________ and _________________ Outer core – layer of ______________________ that surrounds the inner core o The liquid metal causes ___________________ o Temperature – ___________________ o Approx. ___________________ thick Inner core – dense ball of __________ _____________ under extreme pressure. o The solid inner core spins at a slightly ________________ rate than the spinning of the whole Earth. Earth’s ___________________ field is created by this movement (and convection currents) Causes the planet to act like a giant bar ________________ o Temperature – ___________________ o Approx. ___________________ thick BACK TO THOSE CURRENTS. . . Heat Transfer (from warm to cool): Conduction-by _____________ Convection – by the ________________________ Radiation- by ___________ Density = mass/volume So. . . Heat from the core (and the mantle itself) act like a stove top heating soup. . . this causes convection _______________ (hot to cold- rising & sinking)