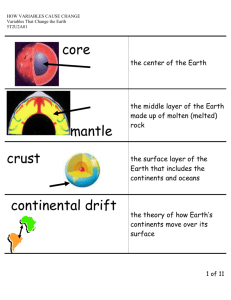
Grade 6 Vocabulary List
advertisement
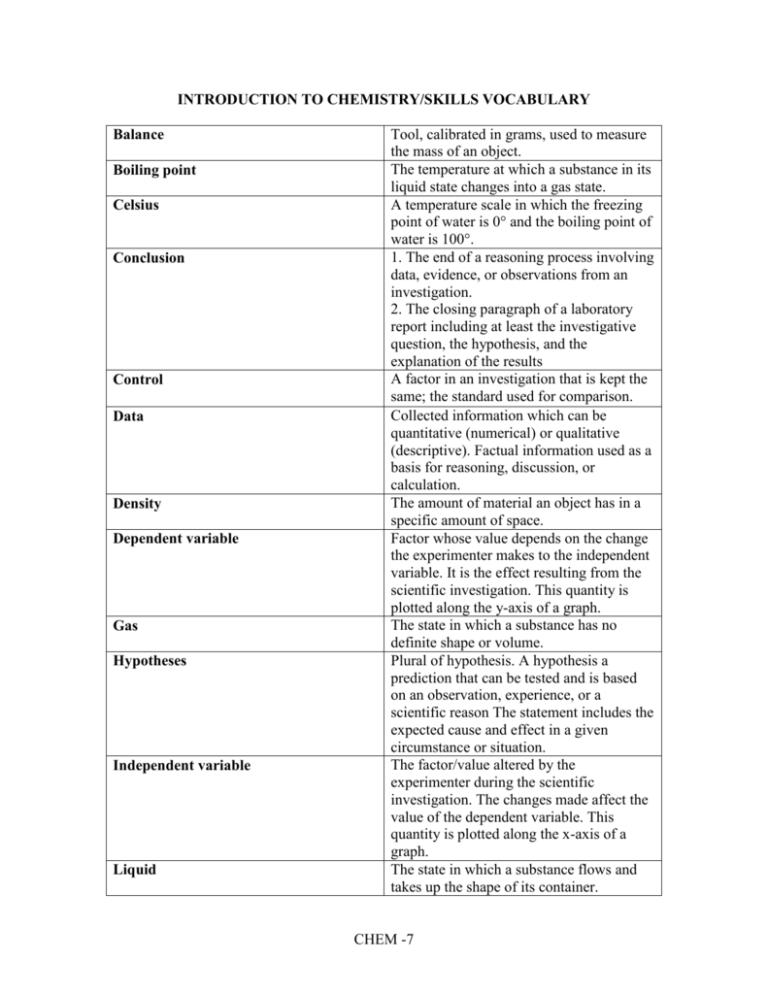
INTRODUCTION TO CHEMISTRY/SKILLS VOCABULARY Balance Boiling point Celsius Conclusion Control Data Density Dependent variable Gas Hypotheses Independent variable Liquid Tool, calibrated in grams, used to measure the mass of an object. The temperature at which a substance in its liquid state changes into a gas state. A temperature scale in which the freezing point of water is 0° and the boiling point of water is 100°. 1. The end of a reasoning process involving data, evidence, or observations from an investigation. 2. The closing paragraph of a laboratory report including at least the investigative question, the hypothesis, and the explanation of the results A factor in an investigation that is kept the same; the standard used for comparison. Collected information which can be quantitative (numerical) or qualitative (descriptive). Factual information used as a basis for reasoning, discussion, or calculation. The amount of material an object has in a specific amount of space. Factor whose value depends on the change the experimenter makes to the independent variable. It is the effect resulting from the scientific investigation. This quantity is plotted along the y-axis of a graph. The state in which a substance has no definite shape or volume. Plural of hypothesis. A hypothesis a prediction that can be tested and is based on an observation, experience, or a scientific reason The statement includes the expected cause and effect in a given circumstance or situation. The factor/value altered by the experimenter during the scientific investigation. The changes made affect the value of the dependent variable. This quantity is plotted along the x-axis of a graph. The state in which a substance flows and takes up the shape of its container. CHEM -7 Magnetism Mass Matter Model Observe Physical properties Qualitative Solid Solubility Standard unit State of matter Substance Trend Variable Volume Weight The field of force produced by a magnet or an electric current. A measure of the amount of matter in an object. Anything that has volume and mass. An illustration, description, small reproduction, or other representation that is used to explain an object, system, or concept. To gather information and direct evidence by using senses and/or scientific instruments. Any property of matter that can be observed by your senses. Data that is related to the quality of observations. The state in which a substance has a definite volume and shape and resists forces which try to change these. Ability of a substance to dissolve in another substance. Inches, feet, yards, centimeters, meters, grams, ounces, pounds, Celsius degrees, Fahrenheit degrees, hours and minutes and non-standard units (i.e. paper clips). The forms matter can take, as in liquid, solid, or gas. Matter of a particular kind, or chemical makeup. The general drift, tendency, or direction of a set of data. Any factor in an investigation that could affect the results. Amount of space an object or substance takes up; measured in liters or cubic centimeters. The measure of the gravitational force acting on an object. CHEM -8 Well-designed investigation A detailed inquiry or systematic examination which includes the following criteria: • only one variable is tested • testing conditions such as time, temperature, and surfaces are controlled • multiple trials are completed • appropriate materials and equipment are selected • clear, logical directions are included Note: Vocabulary terms in regular font indicate terms from the Maryland State Voluntary Curriculum Glossary. Those terms in italics indicate vocabulary within the Baltimore County Curriculum. All appropriate vocabulary must be included in daily instruction. CHEM -9 ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM VOCABULARY Armature Atom Battery Brush Chemical energy Commutator Conduct Conduction Electric circuit Electric current Electrical conductivity Electrical energy Electricity Electrochemical cell Electrode Electrolyte Electromagnet Electromagnetic energy Electron Energy Energy conversion The moving part of an electric motor, consisting of dozens or hundreds of loops of wire wrapped around an iron core. The smallest part of a substance that can exist and still retain the properties of that substance. A combination of two or more electrochemical cells in series. The contact point connected to a current source and the commutator of a motor. Energy stored in the chemical bonds of molecules (Form of Energy). A device that controls the direction of the flow of current through an electric motor. Allow energy to flow through a material. The transfer of heat (or electrical) energy through a substance or from one substance to another by direct contact of atoms or molecules. Continuous path that can be followed by charged particles. The flow of charged particles from one place to another. A property of a mineral to transmit electricity. Energy of electrical charges as a result of their position or motion (Form of Energy). A general term for the physical phenomena that arise from the interaction of electric charges. A device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy. A metal part of an electrochemical cell, which gains or loses electrons. A liquid or paste that conducts electricity. A strong magnet that can be turned on and off; a solenoid with a ferromagnetic core. The energy of light and other forms of radiation. The negatively charged particle that moves around the nucleus of an atom. The ability to cause matter to move or change (Ability to do work). See energy transformation. CHEM -10 Energy transformation Friction Gravitational Gravitational Potential Energy Gravity Heat energy Induction Kinetic energy Law of Conservation of Energy Law of Electrostatics Light Magnetic Magnetic domain Magnetic field Magnetic field lines (Magnetic lines of force) Magnetic pole Magnetism Mechanical Energy Neutral atom When energy changes from one type to another. The force that acts between materials that touch as they move past each other. Friction is caused by irregularities in the surface of objects that are touching. The mutual force of attraction between particles of matter. The magnitude depends on the masses of the particle and the distance between them. Potential energy that depends on the height of an object. The force of gravitational attraction on or near the surface of a celestial body. The energy of a material due to the random motion of its particles. Also called thermal energy. The word "heat" is used when energy is transferred from one substance to another (Form of Energy). A method of electrically charging an object by means of the electric field of another object. Energy of motion/Action (Form of Energy). Energy cannot be created or destroyed only changed from one form to another. Law that states like charges repel; unlike charges attract. Electromagnetic radiation or electromagnetic waves which are visible to the human eye. Having the properties of a magnet. A region in which the magnetic fields of all atoms are lined up in the same direction. A region of space around a magnet in which objects are affected by the magnetic force. Lines that map out the magnetic field around a magnet. The ends of a magnetic object, where the magnetic force is strongest. The field of force produced by a magnet or an electric current. Energy an object has because of its motion or position (Form of Energy). An atom with an equal number of protons and electrons is electrically neutral. CHEM -11 Particle with a neutral charge located in the nucleus of an atom. Energy that is released either by splitting Nuclear energy atomic nuclei or by forcing the nuclei of atoms together. The core at the center of every atom. Nucleus Electrical circuit arranged so that current Parallel circuit passes through more than one pathway simultaneously. A body suspended from a fixed point so as Pendulum to swing freely to and fro under the action of gravity. The stored energy of a body because of its Potential energy position (Type of Energy). Positively charged particle in the nucleus Proton of an atom. A device in an electric circuit that uses Resistor electrical energy as it interferes with the flow of electric charge. An electric circuit in which the current Series circuit passes through only one pathway. An electrical connection that allows Short circuit current to take an unintended path. Energy from the Sun in the form of light Solar energy and heat energy. A current- carrying coil of wire with many Solenoid loops that acts as a magnet. Potential energy in the form of a stationary Static electric charge electric charge. A build up of charges on an object. Static Electricity The part of an electrode above the surface Terminal of the electrolyte. Note: Vocabulary terms in regular font indicate terms from the Maryland State Voluntary Curriculum Glossary. Those terms in italics indicate vocabulary within the Baltimore County Curriculum. All appropriate vocabulary must be included in daily instruction Neutron CHEM -12 Earth Space Science Vocabulary Absolute Magnitude Apparent Magnitude Asteroid Asteroid Belt Athenosphere Atmosphere Batholith Caldera Canyon Celestial Cinder Cone Chromosphere Comet Composite volcano Compression Continental Drift Convection Convection current The brightness of a star if it were a standard distance from Earth The brightness of a star as seen from Earth Enormous rocks or boulders that revolve around the sun, usually between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter The region of the solar system between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, where many asteroids are found The soft layer of the mantle on which the lithosphere floats The layers of gases that surround Earth or another planet A mass of rock formed when a large body of magma cooled inside the crust The large hole at the top of a volcano formed when the roof of a volcano’s magma chamber collapses A deep, narrow valley with steep sides Pertaining to the sky or visible bodies in the sky A steep, cone-shaped hill or mountain made of volcanic ash, cinders, and bombs piled up around a volcano’s opening The middle layer of the sun’s atmosphere Small frozen masses of ice, dust, and gases that travel a definite path through the solar system A tall, cone-shaped mountain in which layers of lava alternate with layers of ash and other volcanic materials Stress that squeezes rock until it folds or breaks The hypothesis that the continents slowly move across the Earth’s surface A method of transferring heat energy by the movement of the heated substance itself A circular current in a fluid like air, water, or molten rock. The process occurs when the fluid is unevenly heated so that part of the fluid rises, cools, and then sinks producing the circular movement CHEM -13 Convergent Boundary Core Corona Crater Creep Crust Crustal plate Deformation Density Deposition Divergent Boundary Dome Mountain Earthquake Elliptical galaxy Erosion Epicenter Faulting Flooding Focus Folding Fossil Galaxy A plate boundary where two plates move toward each other The center of Earth or other celestial body The outer layer of the sun’s atmosphere A round pit on the moon’s surface Slow downhill movement of weathered rock material The thin rocky outer layer of the Earth (also known as Earth's surface) Any of the huge moving segments of the Earth's crust which travel over the Earth's mantle A change in the volume or shape of Earth’s crust The amount of material an object has in a specific amount of space Process by which sediments are deposited in a new location A plate boundary where two plates move away from each other Landform created when molten rock pushes up rock layers on the earth’s surface and the layers then are worn away in places, leaving separate high peaks The moving and shaking of part of Earth's crust A galaxy shaped like a flattened ball, containing only old stars The carrying away of weathered soil, rock, and other materials on the Earth's surface by gravity, water, and wind The point on Earth’s surface directly above an earthquake’s focus The process of movement along a break or crack in Earth's crust An overflowing of a body of water onto normally dry land Area along a fault at which slippage first occurs, initiating an earthquake The process of bending rock layers in Earth's crust The remains or imprint of a prehistoric plant or animal A large collection of stars, gas, and dust held together by mutual gravitation CHEM -14 Gas Giant Glacier Gravity Groundwater Gulley Irregular Galaxy Land form Landslide Lava Light Year Lithosphere Magma Mantle Maria Mass movement Meander Meteor Meteorite Meteoroid Mineral Moment Magnitude Scale Moon Moraine The name given to the first four outer planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune A large mass of snow and ice moving along Earth's surface The force of gravitational attraction on or near the surface of a celestial body Water that is in the porous parts of Earth's crust A large channel in soil formed by erosion A galaxy that does not have a regular shape Physical feature of the earth’s surface Sudden movement of loose rock and soil down a slope Liquid magma that reaches the surface; also the rock formed when liquid lava hardens The distance that light travels in one year A rigid layer made up of the uppermost part of the mantle and the crust The molten mixture of rock-forming substances, gases, and water from the mantle The middle layer of the Earth between the crust and the core Dark, flat regions on the moon’s surface Any one of several processes by which gravity moves sediment downhill A looplike bend in the course of a river A meteoroid that burns as it travels through Earth's atmosphere leaving a streak of light made of hot gases A meteoroid that has hit the Earth’s surface A chunk of rock or dust in space A naturally occurring, nonliving solid with a characteristic crystal, structure and definite chemical makeup A scale that rates earthquakes by estimating the total energy released by an earthquake A natural satellite revolving around a planet A ridge formed by the till deposited at the edge of a glacier CHEM -15 Mountain Mud flow Nuclear fusion Orbit Oxbow lake Photosphere Planet Plate tectonics Plucking Regolith Retrograde Rotation Revolution Richter Scale Rill River Rock Rock slide Rotation Runoff Sand dune Satellite Sea floor spreading A landform with a high elevation A downhill movement of mud which usually occurs after a heavy rainfall The process by which hydrogen atoms join together to form helium, releasing energy A path of one body in its revolution about another body A meander cut off from a river The inner layer of the sun’s atmosphere A major body (not a comet or asteroid) orbiting around a star Large crustal plates moving on the Earth's surface and resulting in changes in the Earth's surface The process by which a glacier picks up rocks as it flows over the land Layer of weathered rock fragments covering much of the moon’s surface The spinning of a planet from east to west, opposite to the direction of rotation of most planets and moons The movement of a celestial body in an orbit around another celestial body A scale that rates seismic waves as measured by a particular type of mechanical seismograph A tiny groove in soil make by flowing water A natural stream of water with a large volume The material that forms Earth’s hard surface A mass of rock sliding down a hill or mountainside The spinning motion of a planet or other object on its axis Water that flows over the ground surface rather than soaking into the ground A mound of sand that is deposited by the wind An object that moves around Earth or some other object rather than falling onto it Process by which new ocean floor is formed by lava erupting from a rift valley, pushing the existent floor outward from the rift CHEM -16 Sediment Seismic Wave Seismometer Shearing Shield volcano Slump Spiral Galaxy Solar Flare Solar System Star Subduction Sun Sun Spot Tension Terrestrial planet Transform Boundary Tributary Tsunami Uplift Universe Small pieces of rock, shell, and plant and animal matter that is moved and deposited by water, wind, or ice A vibration that travels through Earth carrying the energy released during an earthquake A device that measures the actual movements of the ground Stress that pushes a mass of rock in opposite directions A wide, gently sloping mountain made of layers of lava and formed by quiet eruptions Downhill movement of a large block of soil under the influence of gravity A galaxy whose arms curve outward in a pinwheel pattern. (Milky Way is an example) An explosion of hydrogen gas from the sun’s surface that occurs when loops in sunspot regions suddenly connect The Sun with the group of celestial bodies that revolve around it A natural, luminous, celestial body The process by which oceanic crust sinks beneath a deep-ocean trench and back into the mantle at a convergent plate boundary The star around which Earth and the other planets revolve that provides the main source of energy for living things on Earth A dark area of gas on the sun that is cooler than surroundings gases Stress that stretches rock so that it becomes thinner in the middle The name given to the four inner planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars A plate boundary where two plates move past each other in opposite directions A stream that flows into a larger stream Large sea wave produced by submarine earth movement or volcanic eruption The raising of an area of land due to horizontal forces that slowly push on the area All of space and everything in it CHEM -17 Valley Volcanic eruption: Volcano Weathering A depression on Earth's surface between ranges of hills or mountains Process by which lava reaches Earth's surface A weak spot in the crust where magma has come to the surface A chemical or physical process in which rocks exposed to the weather are worn down by water, wind, or ice. Note: Vocabulary terms in regular font indicate terms from the Maryland State Voluntary Curriculum Glossary. Those terms in italics indicate vocabulary within the Baltimore County Curriculum. All appropriate vocabulary must be included in daily instruction. CHEM -18 ECOLOGY VOCABULARY Abiotic Biome Biotic Carrying Capacity Community Competition Consumer Decomposer Ecosystem Environment Food Chain Food Web Habitat Natural resource Organism Population Predator Prey Producer Species Nonliving features of an ecosystem such as climate, light, soil chemistry, and water availability A large, relatively distinct terrestrial region, encompassing many interacting ecosystems, and characterized by similar climate, soil, plants, and animals, regardless of where it occurs on Earth. A biome is commonly named for its plant cover Features of the environment of an organism arising from the activities of other living organisms, as distinct from abiotic factors The largest population that an area can support An association of different species living together at the same time in a defined habitat with some degree of mutual dependence. It can be of various sizes from lake sediments to rainforests The result of a common demand by two or more organisms or types of organisms for limited resources Organism that eats other organisms for food An organism that obtains energy from decaying organic material A group/community of organisms interacting with their environment The physical surroundings of an organism which includes the living and nonliving components The feeding relationship of species that transfer energy through the organisms in a community The complex interconnection of food chains in an ecosystem The local environment in which a specified organism, population, or species lives, characterized by physical and chemical features, and the presence of certain other species (Compare ecosystem, biome, environment) Something from the natural environment (water, air, trees, fuels) that is used to meet one's needs and wants A living thing A group of the same species that live in the same area at the same time An organism that is killed and eaten by another organism (prey); includes animals eating other animals, and animals eating plants An organism that is killed and eaten by another organism An organism that makes its own food Organisms whose members are alike and successfully reproduce among themselves CHEM -19