Name Period ______ Earth and Space Science Fall Final Review
advertisement

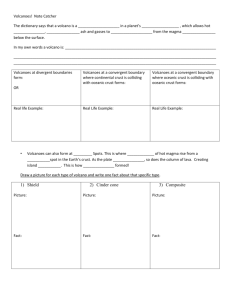
Name ________________ Period _________ Earth and Space Science Fall Final Review Chemistry 1. Draw and atom and label each of the 3 subatomic particles. 2. The protons and neutrons added together equals the ___________________________ number. 3. The number of protons is the _______________________ number. 4. A tiny particle that has no mass and has a negative charge is called an ___________________. 5. _______________ are the smallest particle of an element that retains that element’s characteristics. 6. What is the definition of element? 7. What is the definition of matter? 8. What are the 4 states of matter? 9. Using the periodic table below, determine which element is in period 3, Group 2?_____________ 10. Using the periodic table below, determine which element is in period 5, Group 14? ____________ 11. Using the periodic table below, how many elements are in the period 3? ______________ 12. Color the metals yellow. 13. Color the non-metals blue. Minerals Define the following terms: 1. Mineral3. Inorganic4. What are the 4 characteristics of minerals? (Hint: think sinc!) Describe these tests used to identify minerals: 5. Color6. Cleavage/Fracture7. Hardness8. Texture9. Luster10. Streak11.Density12.Which is the most reliable test? why? 13.Which is the least reliable test? why? 21. According to Mohs Hardness Scale, which of these groups of minerals is the hardest? 22. According to Mohs Hardness Scale, which of these groups of minerals has a hardness of 4? 23. According to Mohs Hardness Scale, which of these groups of minerals can scratch Quartz? Rock Cycle 1. What are the three common rock types and how are they formed? 2. There are two types of igneous rock. Describe where they are formed and what crystal size they have. 3. What are the two things needed to create a metamorphic rock? 4.Define weathering5. Define erosion6. Define deposition- 7. Draw the rock cycle and label each component. Geologic Time 1. List the 4 eras of geologic time, in order from past to present. 2. In what era did dinosaurs exist? 3. Define the Law of Superposition. 4. Faults are always younger/older the rocks they cut through. 5. Intrusive igneous rock helps us get a relative age of rock strata because it is younger/older than the rock it cuts through. 6. Scientists use radioactive elements in samples to determine the _________ age of a substance. 7. Radioactive elements in rocks decay at _________ rates, allowing for accurate dating. 8. ______ is the oldest rock strata layer in the diagram to the left. 9. ---------- Is the youngest rock strata layer in the diagram to the left. 10. Letters E and F above the other strata because they were deposited ______________ the other layers. 11. Using the diagram to the right, list the layers from youngest to oldest. 12. Formation “A” in the diagram to the right is younger than which letters? 13. Define relative age- 14. Define absolute age- Plate Tectonics 1. List here and label the 3 main layers of the Earth: 2. List here and label the 5 physical layers of the Earth: 1. What percentage of the Earth does the core comprise? ______________ 2. What percentage of the Earth does the mantle comprise? ______________ 3. What percentage of the Earth does the crust comprise? ________________ 4. How thick is the Earth’s continental crust? _________________ oceanic crust? ______________ 5. What two layers of earth’s interior make up the lithosphere? ___________________________ 6. Why is the earth’s interior so hot? 7. How do we know what the inside of the Earth looks like if we have never drilled past the mantle? 8. Why was Wegener’s hypothesis originally rejected by scientists? 9. Where is new oceanic crust created? 10. Where is old oceanic crust destroyed? 11. Draw a picture of a convection current, and explain what is happening at each arrow (use the words dense, hotter, colder, etc.) 12. Use arrows to show the difference between convergent, divergent, and transform plate boundaries: 13. What two elements are the inner core composed of? ______________________________ 14. Which part of Earth’s interior is a liquid? ______________________________ 15. What happens to the age of the oceanic crust as you get farther away from the mid-ocean ridge? 16. List two pieces of evidence that the plates move? 17. What structures form at convergent boundaries? 18. What structures form at divergent boundaries? 19. Label the following diagram with these vocabulary terms, please use the numbers associated with the term: (mid-ocean ridge, volcano, subduction zone, trench, newest oceanic crust, oldest oceanic crust, continental crust, divergent boundary, convergent boundary, melting, convection current (draw it), and friction) Earthquakes 1. Where do most earthquakes occur along the edges of? 2. Define plastic deformation- 3. Define elastic rebound- 4. What is the difference between focus and epicenter? 5. Describe each of the three types of seismic waves. 6. The strength of an earthquake based on the Richter scale is determined by what? 7. The strength of an earthquake based on the Modified-Mercalli scale is determined by what? 8. W hat is the process called that allows us to locate the epicenter using at least 3 seismograph’s information? 9. Identify what each of the diagrams are below. _________________________________ _________________________________ 10. Put a star on the diagram to the right where the epicenter of the earthquake is. Volcanoes 1. What are the three different shapes of volcanoes? Describe them. 2. What is the difference between magma and lava? 3. Diagram a volcano and label it’s different structures. 4. At what types of plate boundaries do most volcanoes occur? 5. How do hot-spot volcanoes form? 6. What is the “Ring of Fire”?