C3 Vocabulary and Learning Target packet
advertisement
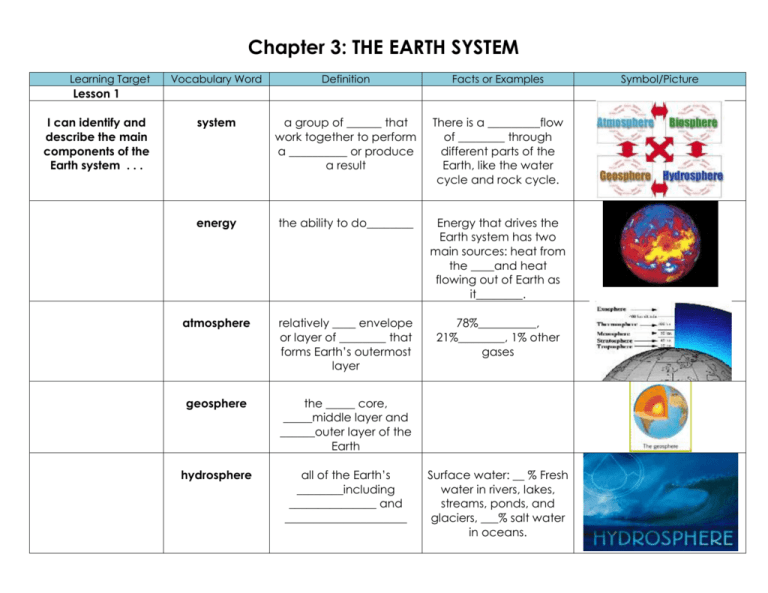
Chapter 3: THE EARTH SYSTEM Learning Target Vocabulary Word Definition Facts or Examples system a group of ______ that work together to perform a __________ or produce a result There is a _________flow of ________ through different parts of the Earth, like the water cycle and rock cycle. energy the ability to do________ Energy that drives the Earth system has two main sources: heat from the ____and heat flowing out of Earth as it________. atmosphere relatively ____ envelope or layer of ________ that forms Earth’s outermost layer 78%__________, 21%________, 1% other gases geosphere the _____ core, _____middle layer and ______outer layer of the Earth hydrosphere all of the Earth’s ________including _______________ and _____________________ Lesson 1 I can identify and describe the main components of the Earth system . . . Surface water: __ % Fresh water in rivers, lakes, streams, ponds, and glaciers, ___% salt water in oceans. Symbol/Picture I can summarize the effects of constructive and destructive forces . . . biosphere the parts of Earth that contain _________ ______________ constructive forces forces that shape the land’s surface by ____________ mountains and other land masses. Ex. __________ spew lava that hardens into rock; ___________ can lift up mountains and rocks. Destructive forces forces that __________ and _________away landmasses by ___________ or _________. Ex. ________ – wearing down and carrying away of land by water, _____ or ________. Lesson 2 I can explain how geologists learn about Earth’s inner structures . . . rock samples seismic waves samples of rock brought up from _______holes 12.3 km deep or from volcanoes blasting ____ from 100 km deep. waves produced by___________, the speed & __________ they take give clues about Earth’s ______________ This is ________ evidence. This is ________ evidence. I can identify the characteristics of Earth’s crust, mantle, and core, & describe how temperature and pressure change inside Earth. . . pressure a __________ pressing down on an area The deeper down inside Earth, the __________ the pressure. (Temperature also increases) crust layer of rock that forms Earth’s ___________ skin basalt _______, ________-grained rock __________ crust is much like basalt granite _______, ________-grained rock _________ crust is much like granite mantle a layer of hot, ________ rock found under the crust. About __________ km thick, made up of layers. lithosphere _________ and uppermost part of the __________ Strong, hard, rigid rock. Main elements are ___________ & __________, varies from 5-40 km for most areas, up to 80 km for mountains, __________on ocean floor. asthenosphere below the ________, hotter and more ___________ Less rigid area of rock, can bend mesosphere below the________________, includes the lower __________ Hot and more rigid outer core layer of molten (melted) _________ surrounding the inner core, below the mantle. Liquid - 2,558 km thick inner core __________ ball of solid metal (________ & ________) Radius of ball is 1,222 km thick. radiation transfer of energy that is carried in ______________rays like light Ex. Outside of car gets hot from sun’s rays conduction heat transfer between materials that are __________ each other Lesson 3 I can explain how heat is transferred . . . Ex. When you touch the door handle of the car, the heat is felt by your hand. I can describe convection currents in Earth’s mantle . . . convection heat transfer by the movement of a ________ (liquid or ______) convection currents The flow that transfers ________within a fluid. Heating and cooling a fluid changed the __________ and the force of gravity to cause a convection current to have __________. Ex. When you open the car door, hot air rushes out to warm you. Heat from the core and mantle cause ___________ currents in the mantle. Warm rock ______ (____ density) & cool rock _____ (________ density) Learning Targets Chapter 3 Lesson 1 I can identify and describe the main components of the Earth system. . . The Earth system has four main spheres: the _________________________, the _________________, the ______________________m and the _____________________________. As a major source of energy for Earth processes, the _______ can be considered part of the Earth system as well. I can summarize the effects of constructive and destructive forces . . . Lands are constantly being created and ______________ by competing forces. _________________________ forces shape the land’s surface by building up ________________________ and other landmasses. _________________________ forces destroy and wear away landmasses through processes like ___________________ and ________________________. Lesson 2 I can explain how geologists learn about Earth’s inner structures . . . Geologists have used two main types of evidence to learn about Earth’s interior: direct evidence from _________________________________ and indirect evidence from _______________________________. I can identify the characteristics of Earth’s crust, mantle, and core, and describe how temperature and pressure change inside Earth . . . The deeper down inside Earth, the ________________ the pressure. The ______________________ inside Earth _______________ as depth increases. The three main layers of the Earth are the ______________________, _____________________ and ____________________. The ________________ is a layer of solid rock that includes dry ______________ and ocean ________________. The ________________ is about 3,000 km thick and is made of very _________, _____________ rock. The ________________ is mostly _______________ and nickel. It consists of a _________________ outer core and a _________________ inner core. Lesson 3 I can explain how heat is transferred . . . There are three types of heat transfer, _________________________, ___________________________ and __________________________. I can describe convection currents in Earth’s mantle . . . Heating and cooling of a fluid, changes the fluid’s _________________________ and the force of _________________ combine to set ______________________ ____________________ in motion Heat from the _____________ and the ________________ itself causes convection currents in the mantle.