Earth`s Interior PowerPoint
advertisement

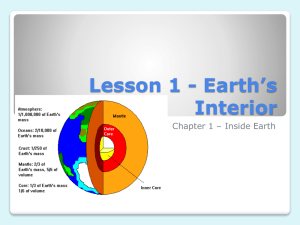
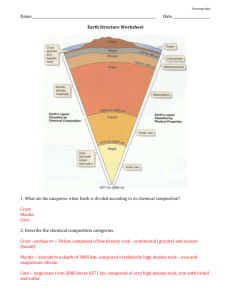
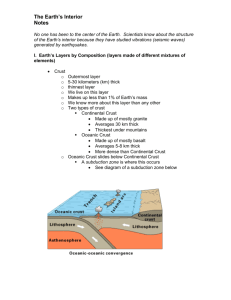
INSIDE EARTH CHAPTER 1: PLATE TECTONICS Section 1: Earths Interior GEOLOGY Geology: the study of planet Earth Geologists study the processes that create Earth’s features and search for clues about Earth’s history Geologists have to make predictions about what the Earth’s interior is made of by making indirect observations of seismic waves Forces beneath the Earth’s surface change the Earth’s appearance. There are two types of forces: CONSTRUCTIVE VS. DESTRUCTIVE FORCES Constructive: forces that build up mountains and landmasses Destructive: forces that destroy mountains and other features of land CONTINENTS Continents: the seven great landmasses surrounded by oceans the seven continents: 1. North America 2. South America 3. Africa 4. Europe 5. Asia 6. Australia 7. Antarctica GEOLOGISTS CANNOT OBSERVE EARTH’S INTERIOR DIRECTLY. Use seismic waves: vibrations that travels through Earth, carrying the energy released during an earthquake determine the speed and path of these waves to reveal the inner Earth’s structure TEMPERATURE AND PRESSURE As the depth of the Earth increases, so does the pressure and temperature. Pressure: amount of force pushing on a surface (huge amount of pressure on the core) EARTH IS MADE UP OF 3 MAIN LAYERS 1. CRUST Crust: Layer of rock that forms Earth’s outer skin (made of Oxygen, Silicon, Aluminum, Calcium, Iron, Sodium, Potassium and Magnesium) Includes soil and water 8-40 km thick Oceanic Crust: crust beneath the ocean Thin layer of crust Made of- basalt: dark dense rock with a fine texture Continental Crust: crust that forms the continents Thicker layer of crust Made of granite- rock that has larger crystals basalt and is not as dense; usually light in color 2. MANTLE Mantle: a layer of hot rock under the Earth’s crust (made of Iron, oxygen, Silicon and Magnesium) Lithosphere: a rigid layer made up of the uppermost part of the mantle and the crust; about 100km thick- (tectonic plates) Under the Lithosphere is a layer of hot rock Temperature and pressure in the mantle increase with depth Asthenosphere: thick, soft material that flows in the mantle; about 3,000km thick; moves in a convection current CORE 3. Core: innermost layer of Earth; consists of 2 parts (made of iron and nickel) Outer Core layer of molten metal that surround the inner core Behaves like a thick liquid Is under enormous pressure Inner Core Dense ball of solid metal Extreme pressure makes it a solid MAGNETIC FIELD The Earth has a magnetic field that is caused by the inner core spinning within the outer