Gallery 5: Architecture
advertisement

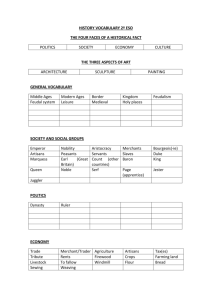
Gallery 1: Astronomy The holiest month for Muslims is Ramadan. Ramadan occurs during the 9th lunar month of the Muslim calendar, and is based off of the cycle of the moon. Muslim’s believe that it was during this month that Muhammad had his first revelation. During the month of Ramadan, Muslims fast from sun rise to sunset. This means that they do not eat or drink all day. In order to celebrate this holy month at the correct time, early Muslims had to be expert astronomers. Tools like the Astrolabe, development of the Lunar Calendar, and the Armillary Sphere came out of the Islamic Empires. Gallery 5: Architecture The architects of the Islamic Empire preserved Greco-Roman architecture. They utilized architectural techniques such as the dome and the arch. Mosques, or Islamic holy buildings, were built using these architectural features. The Islamic empire has left buildings such as public baths, the Mosque of Damascus, and the Dome of the Rock. Gallery 6: Medicine Scholars of the Islamic Empire were well versed in Greco-Roman and Persian education. They preserved the discoveries made by these mighty empires of the past. Scientists and doctors of the Islamic Empire built upon the knowledge of the past, and revolutionized the science of the practice of medicine. Al-Razi was the most successful physician in the Islamic world. He wrote a work titled, The Comprehensive Book, which was an encyclopedia for medicine. In this work he discussed the nature of illness, looking beyond the symptoms, and attempting to discover the cause of illness. Astrolabe: The Astrolabe was an instrument used for astronomical measurements. It measured the altitudes of celestial bodies (moon/stars/sun/planets) and could calculate the latitude of a fixed point. It was used to measure the position of the celestial bodies in the sky in order to determine time of day, and well as time of year. The Lunar Calendar: It was very important for Islamic astronomers to be able to track the phases of the moon over the year. The holiest month of the year is Ramadan. This month commemorates the first revelation that Muhammad had. During Ramadan, Muslims fast from sunrise to sunset. The fasting lasts one month, or one lunar cycle. Because of this, it was important that astronomers were able to track the phases of the moon in order to recognize Ramadan at the appropriate time. Astronomers developed a calendar that predicted when each phase of the moon would occur. This allowed them to plan when Ramadan would occur. Armillary sphere The armillary sphere is a model of celestial bodies in the sky (Sun, moon, stars, and planets). It is a metal sphere made with a framework of rings that represent the latitude and longitude of different celestial bodies. The device allows the user to locate where any celestial body will appear in the sky at any point in the year. The machine shows the user the real motion of the Earth in relation to the other planets, the sun, starts, and the moon. Gallery 2: Calligraphy Muslims believed that drawing representations of holy figures was considered icon worship, and therefore against the teachings of God. Religious artwork could not contain any images depicting Muhammad, Allah, or other theological figures. Rather than creating artwork with images of people, they used an artist form of writing, called calligraphy, to bring sophistication to the copies of the Koran. Arabic calligraphy is based off of Arabic lettering. Islamic calligraphy can be found in the pages of the Koran, and adorning walls and ceilings of Mosques across the Islamic world. Gallery 4: Advances in Geometry Muslims believed that drawing pictures of religious figures was considered icon worship, and therefore against the teachings of God. Religious artwork could not contain any images depicting Muhammad, Allah, or other theological figures. Rather than adorning the walls of Mosques with images of religious figures, mathematicians and artists adorned the walls with intricate geometric patterns. Muslim artists had to be skilled in geometry in order to create these masterpieces. The geometric works of art depict the Muslim view of the world. These forms create infinite patterns to represent Allah’s infinite nature. Artists were able to convey spirituality without having to depict icons in the artwork. Frequently, artists would purposefully create a mistake in the art to represent the imperfect nature of humans. The Mosque of Damascus The Mosque of Damascus was built during the Umayyad Empire, which is why it is also sometimes referred to as the Umayyad Mosque. It is the earliest surviving stone mosque, built between 705 and 715 AD. The site is holy to Muslims and Christians, because it stands on the site where the Church of St. John the Baptist, who Christians believed was the man to baptize Jesus, once stood. The Mosque has a huge open courtyard surrounded by slender columns. There are massive isles held up with columns and archways. The walls of the Mosque were once covered with over an acre of mosaics depicting a landscape believed to be paradise, as described in the Qur’an. The original Mosque was destroyed in 1401, however was later rebuilt. The Dome of the Rock The Dome of the Rock is located on the Temple Mount in Jerusalem. This site is a holy site for the three Abrahamic Religions. It is the site of the Second Jewish Temple, and Wailing Wall, which was destroyed by the Romans in 70 AD. The structure also stands at the location where believers of Judaism and Christianity believe Abraham offered his son as a sacrifice to God. Muslims believe that this was also the location of Muhammad’s “Night Journey,” in which he ascended into the Heavens and had his revelations with the Angel Gabriel. The structure enshrines a rock, which Muslims believe is the location where Muhammad ascended into Heaven. It was built by the Umayyad Caliphate, and is the first work of true Islamic Architecture. The Dome of The Rock displays a massive Dome structure atop an octagonal building structure. In 1561, Suleiman the Magnificent commissioned geometric tiles to be placed around the entire structure. Optics Ibn al-Haytham (965-1039 AD) is known as the “father of optics.” He, accurately, explained how human vision works. He used physical, mathematical, experimental, and psychological experimentation in order to come to his conclusions. He disproved the Greek belief that light comes out of the eye, and bounces off the object, and comes back to the eye to produce an image. Instead, he discovered that light enters the eye, is focused, and then is project to the back of the eye. This will later lead to the invention of the pinhole camera. Circulation Ibn al-Nafis was another scientist who left a mark on modern medicine, making major advances in the knowledge of blood flow and circulation in the human body. He discovered that the heart was divided into two halves, and that they pumped blood independently around the body. He understood that blood could only travel from one side of the heart to the other by first traveling through the body. Canon on Medicine Ibn Sina (980-1037 AD) was a scientist of the Islamic Empire. He compiled Aristotelian and Greek theories about medicine with his own views. He wrote The Canon on Medicine, which became the most famous medical book in around the world and was translated over 87 times. Gallery 7: Arabic number During the Roman Empire mathematicians and traders utilized Roman numerals to represent values. Roman numerals were a system in which combinations of Latin letters represented numeric values. During the Arabic Empire, a new method to keep track of values was adopted; the Hindu-Arabic number system. This system was originally created in India, however, during Muslim expansion it was adopted by the Muslim empire. The Hindu-Arabic number system uses a combination of the numerals, 0-9, to represent different values. Interestingly, this is one of the earliest systems to have a concept of 0 as a numeral. The Muslim Empire adopted this system from India, and through expansion and trade, the system soon spread through Europe. This is the modern number system that we use today. Gallery 3: literature Arabia has a rich literary history. Bedouins living in Arabia have left behind works that pre-date the spread of Islam and the Muslim empire. Poets wrote poems discussing the spirit of life in the desert and celebrating the ideas of bravery, love, generosity, and hospitality. These were all values that would keep a person alive in the harsh deserts of the Arabian Peninsula. Early Muslims wrote poetry that praised Muhammad. Later, Caliphs would commission writers to create works praising their successes. Literature expanded during the Abbasid Caliphate to include themes of the pleasures of life, love, and nature. A famous Muslim work is called The Thousand and One Nights. It is a collection of fairy tales, parables, and legends. The ideas for some of the pieces were most likely adapted from Persian and Indian folk lore. The story follows a Persian king who discovers that his wife has cheated on him. He has her killed, and decides that all women are the same. He marries a succession of young women, only to have them executed the day after their wedding. In order to preserve her life, one young woman begins to tell the king a story on their wedding night, but does not finish it. The king does not kill her because he wants to hear the ending. The next night, she finishes the first story, but starts a new one. She continues this for 1001 nights. Stories such as Aladdin, The Voyages of Sinbad, and Ali-Baba and the Forty-Thieves all originated in this work. Name:___________________________________ Block:________ Directions: Visit each of the galleries with your group. As you visit each gallery describe what innovation is being described, and how that innovation has impacted the Western World. This will remain in your note section of your binders. Islamic Empire Legacies Gallery 1. Astronomy 2. Writing 3. Literature Innovation (s) Impact of Western World 4. Geometry 5. Architecture 6. Medicine 7. Numbers Part 2: Use the galleries you just visit to answer the following writing prompt. Answers should be written with an introduction, body, and conclusion. "What were the most important Islamic achievements? Why were the Muslims able to make such great contributions, and how did these contributions impact the world?" _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________