Name: Genetics Review Directions: For each genetics problem
advertisement

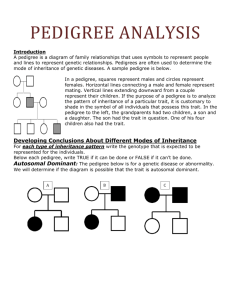
Name: ___________________________ Genetics Review Directions: For each genetics problem make sure you identify your alleles (single letters), the cross, and the Punnett square. Answer any other questions that the problem then asks of you. 1. Snowmen with carrot noses are dominant over snowman with button noses. Cross a hybrid snowman with a carrot nose with a snowwoman with a button nose. What are the genotypes and phenotypes of their children? What type of dominance is this and why? 2. When a red haired elf mates with a blue haired elf, you get a purple haired elf. Mate a red haired elf with a purple haired elf. What type of dominance is this and why? What are the genotypes and phenotypes of the possible offspring? 3. A peanut butter sandwich and a jelly sandwich mate to make a peanut butter & jelly sandwich. Cross a PB&J sandwich and a jelly sandwich. What kind of dominance is this and why? What are the chances of getting three PB&J sandwiches in a row? 4. In dinosaurs, having long arms is dominant over having short arms. Also, having sharp teeth is dominant over having round teeth. A dinosaur that is heterozygous for both traits mates with a dinosaur that has short arms and round teeth. What is the probability that they will have 3, short armed and sharp teeth female dinosaurs in a row? 5. A man with type B blood has two children, one with type O and one with type A. What is the genotype of the father? What is the genotype and phenotype of the mother? Why? 6. In clouds, a sunny cloud mates with a snowy cloud to make a rainy cloud. What type of dominance is this and why? If two rainy clouds meet over Mt. Olive, what is the probability of Mt. Olive having 3 snow days in a row? 7. Duchene Muscular Dystrophy is a sex linked recessive trait. If a woman is homozygous dominant and married a normal man, what is the chance that their offspring will have Duchene? Provide your alleles and cross. 8. When a cow with triangle spots is crossed with a cow that has circle spots, you get some circle spots and some triangle spots. Cross a circle cow with a triangle cow. What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring. What type of dominance is this? Why? 9. In unicorns, long horns are dominant over short horns. Also, white pelts are dominant to rainbow pelts. Cross a unicorn with a purebred long horn and rainbow pelt with a unicorn that is hybrid for both traits. What are the possible phenotypes of their offspring? 10. In piglets, begin normal sized is dominant to being a teacup piglet. A normal sized piglet is to be bred and the breeder wants to get as many normal sized piglets as possible, but he is not sure what the genotype of the normal sized pig is. What would he need to do to figure it out? What is the name of this process called? 11. A man with Type B blood is named the father of a child with Type A blood. The mother of the child has Type AB blood. Can he be the father of the child? Why or why not? Prove with a Punnett square. 12. In fruit flies, white eyes are sex linked recessive. If a male with white eyes was to mate with a female that was heterozygous for red eyes, what is the chance that they would produce three red eyed females in a row? Provide your alleles and cross. 13. Looking at the pedigree above, what type of inheritance is depicted? (Dominant or recessive? Autosomal or sex linked?) Use certain individuals in the pedigree to support both of your answers. 16. Looking at the pedigree above, what type of inheritance is depicted? (Dominant or recessive? Autosomal or sex linked?) Use certain individuals in the pedigree to support both of your answers. 16. Kelly married George and had two children, Sue and Tom. Kelly’s best friend Tina got married at the same time to Kevin and they had two children as well, David and Rachel. Tina and Kelly were so happy when Rachel and Tom grew up and decided to marry. Rachel and Tom ended up giving them six grandchildren, Matt, Joe, Steph, Jen, Ryan, and Molly. Kelly, Kevin, Steph, and Jen all have green skin. Why type of inheritance is this trait? How do you know? List each individual in the pedigree and provide their genotype. Provide the alleles that you are using. 17. Explain why males can be carriers in autosomal traits but not in sex linked traits. 18. What types of Rh are compatible? Why? What would happen if there was Rh incompatibility? 19. Explain Mendel’s work and results. You may want to choose one characteristics that he looked at in particular. Reference the P generation, F1 generation, and F2 generation. 20. What is the difference between an autosomal trait and a sex linked trait? 21. What is the difference between a sex linked trait and a sex influenced trait? 22. What are complex characteristics? What are some examples? 23. Do only your genes determine what you look like? Why or why not?


![Biology Chapter 3 Study Guide Heredity [12/10/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006638861_1-0d9e410b8030ad1b7ef4ddd4e479e8f1-300x300.png)