Exam 4 Review Part 2 - Iowa State University
advertisement

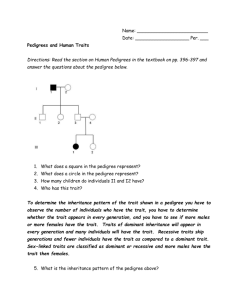
Exam Review Week 16.3 Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Leader: Natalie Course: BIOL/GEN 313 Date: 12/12 Chapter: 16, 17, 2.3, 3.1-3.3, 4.1-4.3, 6.1-6.2 1. What reaction is catalyzed by beta-galactosidase? A. Regulatory protein into an active repressor B. Active activator into an inactive activator C. Lactose into glucose and galactose 2. Which of these is correctly paired as Cis or trans acting? A. Lac I+ can cis act to restore control on a different DNA molecule B. Lac I+ can trans act to restore control on a different DNA molecule C. Lac O+ can trans act to restore control to a lac O^C 3. What is NOT an example of histone remodeling? A. DNA methylation B. Histone acetylation C. Control of flowering in Arabidopsis 4. How does acetylation stimulate transcription? A. Acetylation leads to a decondensed state B. Acetylation promotes the formation of a 30nm chromatin fiber C. Acetylation prevents its conformation to be hypersensitive to DNase 1 5. Transcription factors and regulatory proteins that alter chromatin structure without changing the chemical structure of histones are called? A. DNA methylation B. Chromatin-remodeling complexes C. DNase 1 hypersensitive sites 6. If a rat acquired a mutation in its base sequence so that it would look different than its twin, would this be an example of epigenetic change? A. No, changes in the base sequence are not an example of epigenetic change B. Yes, any change that changes expression in a twin is epigenetic change C. No, because since they are twins the other twin would soon acquire the same base mutation 7. What is the functional definition of a silencer? A. a regulatory sequence that when bound activates transcription, can be distant from the regulated gene, and is it independent of position and orientation B. a regulatory sequence that when bound to an insulator inhibits transcription, can be distant from the regulated gene, and is it independent of position and orientation C. a regulatory sequence that when bound to a repressor inhibits transcription, can be distant from the regulated gene, and is it independent of position and orientation 8. Which of these statements is INCORRECT about meiosis? A. Meiosis 1 undergoes equational division B. Meiosis 2 is similar to mitosis C. There are two mechanisms that produce genetic variation 9. A cell at G1 of interphase has 8 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will is have in anaphase of meiosis 1? A. 4 B. 8 C. 16 10. Which is true of Mendel’s laws? A. Mendel’s first law is the principle of independent assortment B. Mendel’s principle of segregation allows for genetic variation C. Independent assortment occurs in Anaphase 1 11. What is NOT a two way to predict progeny for multiple traits? A. Punnett square B. Branching method C. The 2^n formula 12. Which of these syndromes is INCORRECTLY paired? A. Turner’s syndrome- XYY B. Poly X- XXX C. Klinefelter’s- XXY 13. Which of these statements is correct? A. maleness and femaleness is determined solely by genes B. The SRY gene is needed and it can transpose onto an X chromosome, so a Y chromosome isn’t needed for maleness C. The SRY gene is needed and it can transpose onto any chromosome, so a Y chromosome isn’t needed for maleness 14. Which of these would appear female? A. XXY B. XX with the SRY gene C. XY with androgen insensitivity 15. Which of these is INNCORRECT regarding the Lyon hypothesis A. In an human with XXXY it would inactivate 2 of the X chromosomes in every cell B. It inactivates one of the X chromosomes in females so only the same X chromosome would be in every cell of the body C. is a hypothesis about dosage compensation 16. Which is correct about inheritance? A. X-linked recessive traits will affect females predominantly B. X-linked dominant traits will be affect males predominantly C. Autosomal recessive traits will skip generations and have equal ratios of affected males to females 17. How does the pedigree of a Y-linked trait differ from the pedigree of an autosomal dominant trait? A. A Y-linked dominant trait is passed from a father to all of his sons, an autosomal dominant trait would be passed to only half of his sons. B. A Y-linked dominant trait is passed from a father to all of his sons, an autosomal dominant trait would be passed to ¼ of his sons. C. An autosomal dominant will affect only males, a Y-linked dominant trait will affect an equal ratio of males to females 18. If Joe, who is color blind, marries a woman who is a carrier of the color-blind allele, what is the probability that their first child will be a color-blind boy? Color blindness is X-linked recessive. A. 1/2 B. 1/4 C. 1/8