Human Genetics Study Guide What are autosomes? What are sex
advertisement

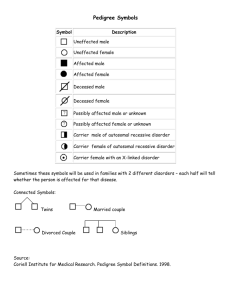
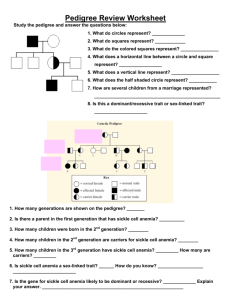
Human Genetics Study Guide 1. What are autosomes? 2. What are sex chromosomes? 3. Which sex chromosomes are found in a female? In a male? 4. How many autosomes are in a normal human body cell? 5. How many sex chromosomes are in a normal human body cell? 6. Which parent’s gamete determines a baby’s gender and why? 7. What is a sex-linked trait? 8. Who is more likely to inherit a sex-linked trait & why? 9. List the examples for sex-linked disorders that we covered in class. 10. What is a karyotype? 11. How is a karyotype made? 12. What does a pedigree show? 13. In a pedigree, what does a circle represent? A square? 14. In a pedigree, how do you show: a. a carrier: b. an individual that has the trait: c. an individual that does not have the trait: 15. Mutations can cause genetic disorders. Differentiate between gene mutations and chromosomal mutations. 16. Define the two types of GENE mutations: a. Point mutation: b. Frameshift mutation: 17. Define the following CHROMOSOMAL mutations: a. Deletion: b. Duplication: c. Inversion: d. Translocation: e. Nondisjunction: 18. What term means one few chromosomes? One too many? 19. List the examples of autosomal dominant disorders. 20. List the examples of autosomal recessive disorders. 21. What is an example of a disorder that shows codominance? 22. What would the blood cells look like for an individual that is heterozygous for sickle-cell anemia? 23. What type of mutation causes sickle cell anemia? 24. If a disorder is caused by an autosomal recessive allele, how many copies of the recessive allele must a person inherit to have the disorder? *Be able to identify the genetic disorder depicted in a karyotype *Be able to determine the genotype of individuals in a pedigree *Know the information given in your Genetic Disorders Graphic Organizer!