Pedigrees Powerpoint
advertisement

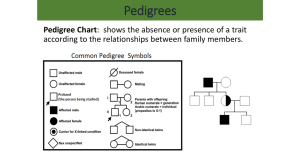
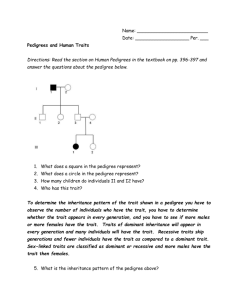
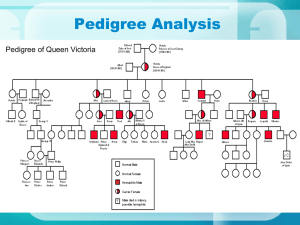
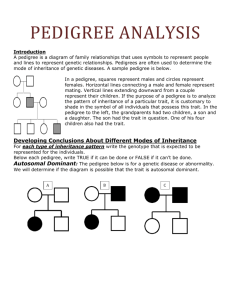
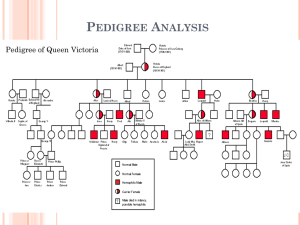
Pedigrees •What is a Pedigree? • A pedigree is a diagram of family relationships that uses symbols to represent people and lines to represent genetic relationships. These diagrams make it easier to visualize relationships within families, especially large extended families. • Pedigrees are often used to determine the mode of inheritance (dominant, recessive) of genetic diseases. • Squares represent males. • Circles represent females. • Horizontal lines linking a • male and female represent • mating. Vertical lines • extending downward from • a couple represent their children. • If the purpose of a pedigree is to analyze the pattern of inheritance of a particular trait, it is usual to shade in this trait. • Infected male In this pedigree: the grandparents had three children, two boys and one girl. The daughter married and Produced two grandchildren, both boys. The grandfather has the trait. The daughter is a carrier. One of the grandsons has the trait. •Types of Inheritance • There are four types of inheritance patterns that we will be analyzing: • 1. 2. 3. 4. • • • autosomal dominant autosomal recessive X – linked dominant X- linked recessive •Autosomal Dominant • • A – has the trait a – normal (no trait, recessive) • Autosomal Recessive • A – normal ( no trait, recessive) • a – has the trait • X – Linked Dominant • XA – has the trait • Xa – normal • Y – Y chromosome (males only) • X – Linked Recessive • XA – normal • Xa – has the trait • Y – Y chromosome (males only) •Locus • The location of a gene. • For example, the locus of the gene OCA1 (or Oculocutaneous Albanism Type 1, the gene associated with albinism) is on 11q1.4-2.1, which means it is on the long arm of chromosome 11, between sub-band 4 of band 1 to sub-band 1 of band 2.