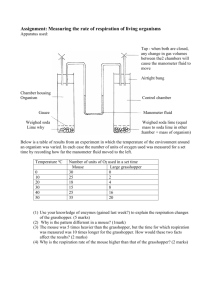
Cell Structure & Infectious cells Provides energy for the cell by

Cell Structure & Infectious cells
1.
Provides energy for the cell by breaking down sugar molecules in cellular respiration
Mitochondria
2.
Provides food for a plant cell by collecting energy from the sun during photosynthesis
chloroplast
3.
Allows material to enter or exit the cell & protects the contents of the cell cell membra
4.
What type of cell attaches to a cell membrane, injects genetic material, duplicates until the cell burst & dies virus
5.
How does mold most often infect your body? breath in spores to infect the lungs
6.
How does a cold virus most often get in your body? breath in through the mouth or nose
7.
How would a parasite in the intestines most likely affect the digestive system? keep you from absorbing nutrients
8.
What process helps organisms use oxygen to get energy from food?
Cellular respiration
9.
An organism that carries a disease that can be passed to humans. vector
10.
Control center of the cell nucleus
11.
Tiny particle with nucleic acid surrounded by a protein coat that can only reproduce inside a living cell by injecting its
DNA & causes an infection virus
12.
List 3 Differences in plant and animal cells large central vacuole, chloroplasts, cell wall
13.
Why is cellular respiration important to a cell? provides energy
14.
How are the cell wall & cell membrane similar?
Both protect
Identify the cell on the right as a plant or animal cell
Animal
15.
Identify the type of cell being used in a positive way to help in the environment or in industries?
A) healthy digestive systems, production of dairy products (cheese, yogurt), Oxygen for the environment, insulin production for diabetic patients bacteria
B) used to make certain antibiotics mold
C) use to make breads rise and alcohol from fermentation by producing CO2 fungus (yeast)
Heredity
17 .Use a punnett square to cross one heterozygous parent with one homozygous recessive parent parents: (use the letter E)
18. What percent is pure recessive? 50%
19. What is the genotype and phenotype for the offspring in percentages for two heterozygous parents (R = round & r = wrinkled)
25% RR round, 50% Rr round, 25% rr wrinkled
20. Number the following in order form smallest to largest:: Chromosome, allele, nucleus, DNA allele, DNA, chromosomes, nucleus
21.
Use the pedigree to answer the following questions a.
How many females express the trait of color-blindness? 1 b.
If the female from generation IV-6 marries a dominant male
(non-color blind), what is the chance of having a daughter with the disorder? 0% A son with the disorder? 50%
X
n
= color blind
X
N
= not color blind
22.What is it called when the actual DNA is altered in some way by inserting a needed gene directly into a cell to help cure a disease or improve a crop ? genetic engineering
23.What is it called when specific traits are selected in the parents in order to ensure they are passed to the offspring & the genes are not actually altered?
selective breeding
24. Incomplete dominance: If a Red flower (RR) is crossed with a white flower (WW) What percent of the offspring are pink (RW)
100%
25.
Based on the pedigree below, what can we determine about the phenotype of the offspring in the 3 rd generation?
Ee
Ee all offspring will have attached ears ee
EE
Ee
E
e
E = Attached Ears e = unattached
?
3
rd
Ecology and Adaptations
generation
26.. What type of biome would the following adaptations help an organism survive best?
A. Nocturnal & storing water: desert
B. white fur, layer of fat, hibernation: tundra
C. bright colors (attract a mate), camouflage (hide from predators), poison: rainforest
D. large leaves to collect more sunlight: rainforest
E. do not lose their needle shaped leaves: tundra/taiga
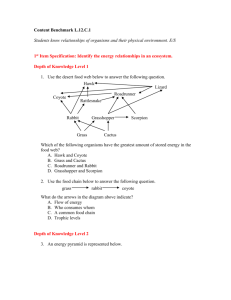
Grass grasshopper lizard Hawk
Hawk lizard grasshopper grass
27. What would happen to the herbivore population if the number of hawks increased? decrease
28. If the disease mouse-scratch fever wipes out the mouse population, what would happen to the snake population? decrease
29. What do the arrows represent in the food web? the flow of energy from one organism to another
30. Which organism in the pyramid is the tertiary consumer? hawk
31. Which organism in the pyramid has the most energy available?
Grass
32. Why is the pyramid used to show energy flow in an ecosystem?
there is less energy available at each trophic level
33. Why does the amount of energy available decrease in the pyramid?
Lost as heat
34. Circle the primary consumers in the web. grasshopper, rabbit, mouse
35. What would happen to this ecosystem if the producers were to decrease? all organisms would decrease
36. What would happen to this ecosystem if the producers were to increase? , more herbivores, then more carnivores