Spring2015FinalExamReview

BIOLOGY SPRING SEMESTER FINAL EXAM REVIEW 2015
Matching: Match the word with its correct definition
_____1) Changing slowly and constantly over long periods of time
_____2) Preserved or mineralized remains of an organism that lived long ago
_____3) A scientist that uses radiometric dating to determine the age of fossils
A. Gradualism
B. Extinction
C. Fossil
_____4) The death of all members of a species D. Paleontologist
5) Explain the difference between behavioral isolation, geographic isolation, and reproductive isolation.
6) Explain how the above terms (in question #5) can be related to the term “speciation.”
7) Define “natural selection” AND explain how it could cause competition.
8) Define “vestigial structure” and give an example.
9) The similarity of homologous structures suggests that two or more species
______________________________________________________________________________________________.
10) How is embryological evidence important to the theory of evolution?
11) Strong evidence for evolution comes from the fossil record. Circle: True or False
12) Explain the difference between the following terms: a. Mutation _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ b. Genetic Drift ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ c. Gene Flow ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
13) Immigrants move _________________ a population and emigrants move ________________ a population.
14) All mutations are lethal. Circle: True or False
Matching: Match the word with its correct definition.
_____15) One species benefits, the other gets killed A. Commensalism
_____16) One species benefits, the other gets harmed
_____17) One species benefits, the other gets neither harmed nor benefited
_____18) Both species benefit
19) Explain why white furred mice would not benefit in the desert.
B. Parasitism
C. Mutualism
D. Predation
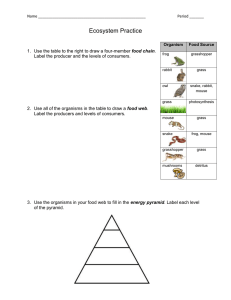
20) How are food chains and food webs related?
21) A "primary consumer" can also be called a(n) ______________________________.
22) An example of an abiotic factor is _____________________ and an example of a biotic factor is ____________________.
23) Why are decomposers important to the success of an ecosystem?
24) An example of a food chain is… a. Lizard b. Grass c. Mouse
Grasshopper
Mouse
Hawk
Hawk
Grass
Rabbit d. Grass Tree Lizard
25) What do the arrows represent in a food chain?
26) Give two examples of organisms that would be considered “producers.”
27) Explain why the top of the food chain does NOT receive 100% of the stored energy from the organisms they are eating.
28) Which of the following would be considered an example of a population?
a. all insects in a desert c. all plants in the rainforest
b. all silver maple trees in a forest d. all trees in the taiga
*Explain why that answer is correct and the others are not.
29) Put the following terms in the correct order from smallest (left) to largest (right).
Population Organism Ecosystem Community
30) Which part of a stable ecosystem cannot be recycled since it is either used up or lost as heat? ________________
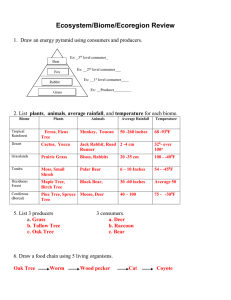
The diagram to the right/below represents an energy pyramid. Use it to answer questions #31 & #32.
31) If level A produces 1000 J of energy, how much energy is available to level B? ___________
32) On the energy pyramid to the right, which level represents primary consumers? _______
33) The first plants to grow after a fire are called the ____________________________________.
34) In ecology, what does the term “succession” mean?
35) Explain why the deer population may increase over time. Explain a few factors that may lead to the increase in the deer population within a given area.
* Explain why the deer population may decrease over time. Explain a few factors that may lead to the decrease in the deer population within a given area.
36) An organism’s interactions with other organisms is referred to as its _________________________.
37) The specific place where an organism lives out its life is a _______________________________.
Matching: Match the correct word with its description.
_____38) A group of ecosystems that have the same climate and climax community A. Desert
_____39) Most amount of species and precipitation
_____40) Fires, grazing animals, and drought keep this biome free of many trees
_____41) Made up of coniferous evergreen forest
B. Fresh Water
C. Tundra
D. Tropical Rainforest
_____42) Composed mostly of trees that lose their leaves
_____43) Has a layer of permafrost below the soil surface
_____44) Lowest amount of annual precipitation
_____45) Less than 1% salt content
_____46) Source of most of the world’s rainfall
E. Marine
F. Temp. Deciduous Forest
G. Biome
H. Taiga
I. Grassland
47) If the human population is growing “exponentially,” what shape will the curve follow in the population graph?
___________________
48) The picture to the right is called a __________________________________.
49) Using the figure to the right, which cohort has the least amount of people?
____________________________________
50) What does it mean to have “arable” land?
51) Explain how a region’s “carrying capacity” can affect the population.
52) Using the “Population Growth” graph below, explain what is happening to the population at (B), (C), and (D).
53) What helped slow down the population growth in 1962?
54) What is the world’s population? ___________________________________
55) If a country has a large number of individuals on the bottom of their population pyramid, what does that indicate about the population?
56) The pyramid for the United States is nearly straight up and down creating a rectangle-shape. Explain what this may indicate about our population.
57) If a country is using more resources than the biocapacity allows, what will eventually happen?
58) When you calculated your “ecological footprint,” what were you calculating?
59) Explain the difference between an ecological deficit and an ecological reserve.
60) Ecological Sustainability is when a resource cannot be renewed and will eventually run out.
Circle: True or False