Final Exam Review - June, 2003 (Chapters 7
advertisement

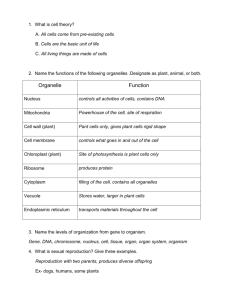
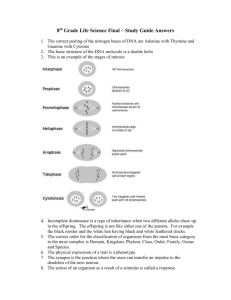
Final Exam Review (Honors Biology) – June, 2013 (Chapters - 8, 9, 12, 11, 14, 15, 16, 17, 3, 4, 5, 6) Chapters 8 & 9 1. What is the energy source in all cells? _________________ 2. When a phosphate group is removed from ATP, what is released? _____________________ Removing this phosphate group from ATP creates ____________ 3. Cellular respiration releases _______________ by breaking down food/glucose molecules. Cellular respiration occurs in all __________________ cells. 4. Write the balanced equation for cellular respiration below: _________________________________________________________________________________ 5. List the 3 stages of cellular respiration in order. a. ____________________ b. ____________________ c. ____________________ 6. What does glycolysis break down? ________________. What is glucose broken down into during cellular respiration? __________________, __________ and ______________. 7. Where does glycolysis take place in the cell? ________________. Where does cellular respiration take place in the cell? ___________________________ 8. How many ATP molecules does glycolysis YIELD? _________. How many ATP molecules are gotten from cellular respiration? __________. 9. Cellular respiration is considered an aerobic process because it requires presence of ______________. An anaerobic respiration does not. 10. What is the name of the anaerobic breakdown of glucose? __________________________. 11. What are the two main types of fermentation? _______________ and __________________. 12. Where does lactic acid fermentation occur in animals? ___________________. What does it cause? ______________________. 13. What type of fermentation occurs in bread dough? _______________________. 14. What is the balanced equation for photosynthesis? __________________________________________________________________________________. 15. What organelle captures sunlight in plants? _________________________. 16. What pigment gives green plants their color? ___________________. 17. Most plants appear green because chlorophyll does not absorb _______________ light. 18. What gas is produced as a by-product of photosynthesis? __________________. 19. Describe the light-dependent and light-independent reactions and know where they occur. The light dependent reaction uses __________ energy to produce ___________ and ________________ (as a waste product). It occurs in the ___________________________ of the chloroplast. The light-independent reactions use the ___________ from the light-dependent reactions, _____________ and ___________ to produce ___________. It occurs in the ______________ of the chloroplast. It is also known as the __________ ___________. 20. What structure is shown as G below in Figure 8-6 – ______________________. 21. Look at Figure 8-6. What are the products of the light-dependent reactions? _________________, ____________, ___________________. 22. In the picture below, A is water, E is O2, carbon dioxide is represented by the letter ___, glucose (sugars) are represented by the letter ___ and thylakoids are represented by the letter ___. Figure 8-6 2 23. The diagram below shows an example of interdependence among aquatic organisms. During the day, the organisms either use or give off substance A or B, as shown by the arrows. Which substances are represented by A and B? ________________________ & ____________________ Comparison of Photosynthesis and Respiration Raw Materials Products Purpose Photosynthesis water and CO2 glucose and oxygen store energy Respiration glucose and oxygen water and CO2 release energy 24. The process of photosynthesis and respiration can be thought of as a cycle because -___________________________________________________________________ 25. The graph below shows how dissolved O2 and CO2 levels changed in a pond over a 24-hour period. What caused the decrease in O2 concentration during the night? ____________________________________ Plants 26. The plants that have flowers are called as __________________________________ 27. The plants that do not have fruit that covers the seeds are called as _________________________ 28. The female reproductive part of the flower is called as _____________ and the male reproductive part of the flower is called as _______________ (it contains ______________) 29. What is the purpose of xylem? _________________________________________________________ 30. What is the purpose of phloem? _______________________________________________________ 31. Phototropism: Plants respond to ____________ by bending towards it. 32. Geotropism: Plants respond to _____________ (stem goes upwards & roots go downwards). 33. Thigmotropism: Plants respond to __________(Vines develop tendrils that coil around support). 3 Chapter 12 Figure 12-1 1. The structure labeled X in Figure 12-1 is a(an) ______________________ (monomer). Monomers connect to form _______________ ____________ which is a polymer. 2. What does DNA stand for? ________________________ __________. 3. The Watson and Crick model of DNA is a(an) ____________ __________, in which two strands are wound around each other. 4. In eukaryotes, DNA is located in the ________________. 5. During DNA replication, a DNA strand that has the bases CTAGGT produces a strand with the bases ______________________. 6. A change in a DNA sequence that affects genetic information is ________________. 7. What are the four main types of chromosomal mutations and what happens during each? ________________ – a piece breaks off and attaches in the ___________ order ________________ – a piece of a chromosome is _____________ ________________ – a piece of a chromosome is _____________ ________________ – a piece of a chromosome breaks off and ____________ to another chromosome Figure 12-3 8. In Figure 12-3, A, B, and C are three types of ___________. 4 9. What is molecule B in Figure 12-3, and what is its function? _____________ ________ (__________) – ____________________________________________________________________. 10. What are the three main parts of an RNA nucleotide? ___________ sugar, _____________ group, _________________ base 11. Unlike DNA, _________________ contains nitrogen base called uracil. Figure 12-2 12. According to Figure 12-2, what codons specify the amino acid arginine? ___________, ___________, ____________, _____________ 13. How many bases are needed to make each codon? ___________________ 14. How many codons are needed to specify one amino acids? ____________ 15. The order of nitrogenous bases in DNA determines the order of ___________ __________ in proteins. 16. Genes contain instructions for assembling __________________. 5 Chapters 11 & 14 1. The plants that Gregor Mendel crossed to produce the F1 generation made up the _______________(__) generation. 2. Chemical factors that determine traits are called as _____________. 3. The different forms of a gene are called __________________. 4. Organisms that have two identical alleles for a particular trait are said to be ___________________. 5. _____________________ is the likelihood that a particular event will occur. 6. The principles of probability can be used to predict the __________ of the offspring produced by genetic crosses. 7. When you flip a coin, what is the probability that it will come up tails? ________ 8. A __________ ___________ is a diagram that shows the genotypes of the offspring, the alleles in the gametes of each parent, all possible results of a genetic cross, but does not show the actual results of a genetic cross. 9. A phenotype is the _____________________ characteristic of an organism. Tt T T t TT Tt TT T TT T = tall t = short Tt Figure 11-1 10. In the Punnett square shown in Figure 11-1, the genotypes of the offspring are _____ and _____and phenotypes of all the offspring is __________. 11. Pea plants that are TT, Tt have same/different genotypes. 12. Crossing a pure-bred green-podded (dominant trait) plant with a pure-bred yellow-podded (recessive trait) plant is symbolized by: ______________ 6 13. When Gregor Mendel crossed true-breeding tall plants (TT) with true-breeding short plants (tt), the offspring were tall (Tt) because the allele for tallness is _________________________. 14. If you made a Punnett square showing Gregor Mendel’s cross between true-breeding tall plants and truebreeding short plants, the square would show that the offspring had a genotype that was same/different from that of both parents. 15. In the P generation, a heretozygous tall plant is crossed with a homozygous short plant. The probability that an F1 plant will be tall is ____________% 16. The principle of independent assortment states that genes for different traits can ________________ independently during the formation of gametes. 17. The principle of dominance states that _________________________________________________. 18. How many recessive alleles for a trait must an organism inherit in order to show that trait? ______ 19. How many different allele combinations would be found in the gametes produced by a pea plant whose genotype was RrYY? _________. 20. If a pea plant that is heterozygous for round, yellow peas (RrYy) is crossed with a pea plant that is homozygous for round peas but heterozygous for yellow peas (RRYy), how many different kinds of phenotypes are their offspring expected to show?________. 21. __________________ ___________________ is when one allele is not completely dominant over another. 22. _____________________ is when both alleles show up in the phenotype. 23. Multiple alleles - for e.g. _______________________________________. 24. Polygenic traits - for e.g. ___________________________________________ 25. What are Gametes? _____________________________________________; examples are _____, ______. 26. Gametes or sex cells have ______ complete set of chromosomes (one allele for each gene) that means gametes have only ________the number of chromosomes as compared to organism’s all other body cells. 27. All the regular body cells (somatic cells) are diploid (have ____ complete sets of chromosomes). The diploid number is indicated by ____). The _______ are haploid (haploid number is indicated by N or 1N). Mitosis All somatic cells result from mitosis Meiosis Only sex cells result from meiosis ______ daughter cells – exactly identical to each other and parent cell ________ daughter cells – genetically different from each other and parent cell # of chromosomes remains same Diploid Diploid 4 phases # of chromosomes is cut in half Diploidhaploid 8 phases 7 28. A chromosome consists of many ______________. 29. What are all the chromosomes except the sex chromosomes called? _________________. 30. What chromosomes are needed to produce a female? _______ male? ________ 31. Give three examples of sex-linked disorders. __________________________________ __________________________________ ___________________________________ 32. Three copies of chromosome 21 (Down’s Syndrome) is known as __________________. 33. What sex chromosomes do people with Turner syndrome have? _______________ 34. Males with Klinefelter syndrome have an extra ___________ chromosome (karyotype 47,XXY). 35. Sickle cell anemia is a disorder that involves ___________________ alleles and it results in production of abnormal ______ ______________ _________. 36. _________________________ may cause excessive bleeding. 37. What does the following picture show? ________________ _________. 38. The farther apart two genes are located on a chromosome, the more/less likely they are to be inherited together. RrYy RY Ry rY ry RY RRYY RRYy RrYY RrYy Ry RRYy RRyy RrYy Rryy RrYy rY RrYY RrYy rrYY rrYy ry RrYy Rryy X Y Seed Shape R – round r – wrinkled Seed Color Y – yellow y – green Figure 11-2 39. What is the phenotype ratio of the offspring in the Punnett square shown in Figure 11-2?______________ 8 40. Identify the phenotype of the offspring represented in the square labeled X in Figure 11-2? _____________________________ 41. How many of the offspring will be Round, Yellow? _____ 42. What will be genotype of the offspring represented in the square labeled Y in Figure 11-2? ____________ Figure 11-5 43. In Figure 11-5, what is the genotype of the pink-flowered snapdragons? ________. 44. What do the alleles in Figure 11-5 show? _______________ _____________. 45. According to Figure 11-5, if red-flowered snapdragons and ivory-flowered snapdragons are crossed, what percentage of their offspring would be expected to be pink-flowered? ___________. 46. According to Figure 11-5, if two pink-flowered snapdragons are crossed, what percentage of their offspring would be expected to be pink-flowered? _________. 9 Chapters 15, 16 and 17 1. Charles Darwin proposed the theory of _________________selection. 2. According to Darwin, early giraffes probably had necks of same/different lengths and the ones that were better adapted, survived. 3. What was Darwin’s ship named and what country was he from? __________________; ____________. 4. Whose theory was “use or lose.” ___________________. 5. According to Lamarck’s theory _____________ traits are passed on to offspring. 6. Structures that are reduced in size and have no apparent function are called as ________________structure 7. The appendix is an example of a _____________________ structure. 8. The wing of a bird and the wing of an insect are examples of _________________ structures because they have the same ____________________, but different ___________________. 9. The flipper of a dolphin and the leg of a dog are examples of ________________ structures because they have same ____________________ (have different mature forms but develop from same embryonic tissues) but different _____________________. 10. What is evolution? _______________________________________________________________. 11. What are fossils? __________________________________________________________________. 12. The scientists who study fossils and interpret the fossil record are known as _____________________. 13. The oldest/youngest fossils would normally be found in the lowest rock layers. 14. What are three types of evidence for the theory of evolution? a. _____________________________________ b. ____________________________________ c. ______________________________________ 15. The similarity between embryos indicates that some organisms have a common ___________________. 16. What is the half-life of an element? _______________________________________________________. 17. The half-life of Carbon-14 is 5,730 years. How much of the original C-14 in an organism would remain in a fossil that is 11,460 years old? ______________ 18. If the half life of an element is 2,000 years, and I started out with a sample that originally had 60 grams of that element in it and now I have 15 grams, how old is the sample? _______________years 10 19. _________________________ isolation is when populations are separated from each other by a mountain range, new river, etc. 20. Separation of populations by geographic barriers can lead to __________________. 21. Define “Species”. _____________________________________________________________________. 22. Members of the same species that live in the same area are called as _____________________________. 23. What is a gene pool? ___________________________________________________________________. 24. The __________________________________ Principle explains how often alleles occur in a population. 25. What is an organism’s fitness? ________________________________________________________. 26. The white or light colored peppered moth is the most “fit” in its environment when the trees were ____________ colored. 27. What turned the peppered moths from light to dark? _________________________________. 28. What is genetic drift? __________________________________________________________. 29. Earth’s first atmosphere contained little or no __________________________. 30. A mutation can change a __________________________. 31. What is needed for genetic equilibrium? 1. _______________________________________ 2. _______________________________________ 3. _______________________________________ 4. _______________________________________ 5. __________________________________________ 32. When genetic equilibrium is reached, the allele frequencies remain ____________________________. The _______________________ occurs when genetic equilibrium is disrupted. 33. When unrelated species begin to look alike because they occupy the same environment, this is _____________________ evolution. 34. Darwin’s finches were an example of _____________________ radiation, which is when many species evolve from a common _______________________ and one specific trait is improved in each species in order to adapt to the environment. 35. _________________________ is the death or disappearance of all members of a species in the wild. 36. An ________________ species is a group of organisms near extinction. 11 Chapters 3, 4, 5 and 6 1. Another word for producer is ______________________. 2. Green plants or algae are examples of _____________________. 3. In which way are green plants in a sunny mountain meadow and sulfur bacteria in a deep-sea volcanic vent alike? They both are ______________________ and produce ____________________________. 4. The organism which can not make their own food are known as _______________________. 5. What does a heterotrophic organism need to do in order to get the energy? _________________________. 6. A _______________________ obtains nutrients by breaking down dead and decaying matter. 7. A __________________feeds only on meat; a _______________feeds only on plants; an ______________ feeds on both. 8. Only 10% of the energy stored in an organism can be passed onto the next trophic level. Of the remaining energy, some is used for the organism’s life processes and the rest is _________________________. 9. A biomass pyramid shows the amount of ________________ ______________ at each trophic level. 10. Why can matter recycle through the biosphere? because matter is not used; it’s ____________________. 11. Of the following, water, nitrogen, carbon and energy, which one is not recycled in the biosphere? _______________-– it is used 12. Define: a. denitrification – _________________________________________________________________ b. nitrogen fixation – _______________________________________________________________ 13. Why do organisms need nutrients? ________________________________. 14. What are factors that contribute to Earth’s climate? a. ______________________ b. _______________________ c. _____________________________________ d. _____________________________________ e. __________________________ 15. Definitions: a. microclimate – the climate within a small area that _______________from the climate around it. b. demography – scientific study of ___________________. 12 c. niche - the range of _______________ and __________________ conditions in which an organism lives and the way it uses those conditions. d. immigration – moving ___________ a population e. soil erosion – the ______________ away of surface soil by wind and water f. abiotic- the ____________ elements of an ecosystem g. biotic – the _______________elements of an ecosystem h. photic zone – the region of the ocean that receives _____________. i. aphotic zone – the region of the ocean that does not receive ____________. j. deciduous – a tree that _____________ its leaves in the fall. 16. Sulfur and nitrogen compounds in smog combine with water to form ____________ _______________. 17. What happens as DDT moves up the trophic levels in a food chain or web? its levels _______________ 18. Which factor(s) increase the size of a population? 1.number of _________ 2.number of ______________ 3.number of individuals _______________ or ___________________. 19. When an environment has reached the maximum number of individuals it can support, it has reached its _______________________ ______________. 20. The types of Species Interaction (Symbiosis) Predation (+/-) – ____________________________________________________________________ Competition (-/-) – ___________________________________________________________________ Parasitism (+/-) – ____________________________________________________________________ Mutualism (+ / +) – __________________________________________________________________ Commensalism - (+ / 0) – _____________________________________________________________ Biomes 1. Which biome receives less than 25 cm of rain per year? __________________ 2. Which biome has permafrost? _________________ 3. Which biome receives at least 250 cm of rain per year? ___________________________ 4. Which aquatic Ecosystem includes rivers, ponds and lakes? ______________________ 5. Which aquatic Ecosystem has a mix of fresh and saltwater? ________________________ 13 6. In which aquatic Ecosystem the soil is wet part of the year? _______________________ 7. Which biome is found in the Pacific NW & also known as the Temperate Rain Forest? _________________________________________ 8. Which Biome has shrubs that contain flammable oil & catch fire easily? __________________________________________ 9. Which Biome has trees that lose leaves in fall? ____________________________________ 10. Which Biome is also known as also known as boreal forest? _______________ 11. Which biome has large herbivores, like rhinos, hippos, etc.? ______________________________ 12. Which biome is inland and has perennial grasses (e.g. Midwest U.S.)? ____________________________ 13. Which zone in the ocean extends from the low-tide mark to outer edge of continental shelf; has kelp forests? ______________________________ 14. Which zone in the ocean has warm, shallow water of coastal, tropical oceans and organisms that have symbiotic relationship with algae? ________________________________ 15. Which zone in the ocean is permanently dark? _____________________________ Genetic Engineering 1. What are restriction enzymes? ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. During Gel Electrophoresis, in which direction will the DNA fragments travel? _____________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Why do the DNA fragments travel in this direction? _____________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Where do the shorter DNA fragments (bands) end up reaching on a completed gel (at the completion of gel electrophoresis)? _____________________________________________________________________________________ 5. DNA that does not exist naturally, but is created artificially by combining a gene taken from one organism and attaching it to the DNA of another organism is called as ____________________. 6. What is a transgenic organism? __________________________________________________________________________________ 14