Unit 2 Test Review and Study Guide

Date______________ Physical Science – Mr. Lewis Name__________________
Unit 2 Test Review and Study Guide
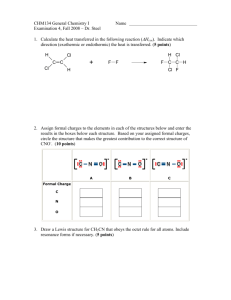
1. Draw Lewis Diagrams for the following elements: a. Te b. In c. Ge d. Br e. Rb f. Kr g. Li h. Sr
2. Ionic Bonding: Use Lewis Diagrams to show how these elements will bond. Be sure to show the charges. a. K and Br b. K and O c. Be and O d. Be and P e. Al and Cl
3. Covalent Bonding problems: Use Lewis Diagrams to show how these elements will bond. a. I and I b. H and Br c. H and O d. C and O
4. Why do all of the elements in Question 2 form Ionic Bonds?
5. What is the difference in how polar covalent bonds and non-polar covalent bonds share electrons?
6. Which covalent bond in Question 3 is certainly non-polar? Explain how you know that?
7. What is meant by the term “lattice” in metallic bonds?
8. How do electrons behave (how do they move) in metallic bonds?
Date______________ Physical Science – Mr. Lewis Name__________________
9. Metals are good conductors of electricity (electricity = the movement of electrons). Explain why, based on your answer to question 8
10. Metals are generally malleable. Based on the way metallic bonds form, explain why this is true.
11. Comparing Ionic, Polar Covalent, and Non-polar Covalent Bonds: (use the comparison table we worked on in class and a guide): a. How does each bond form? b. Which type of bond is the weakest? c. Which type of bond is the strongest? d. Which types of bonds normally makes gases? e. Which types of bonds form compounds that normally have very high melting and boiling points? f. Which type of bond forms brittle compounds? g. Which type of bond has no charge?
12. What is an ion?
13. Cations a. Have what charge? b. Are formed by __________ electrons c. Are typically metals / non-metals / metalloids (circle correct answer)
14. Anions a. Have what charge? b. Are formed by __________ electrons c. Are typically metals / non-metals / metalloids (circle correct answer)
15. Ionization energy trends (use the graph we worked on in class as a guide): a. As you go DOWN a GROUP, the ionization energy tends to increase / decrease / remain constant (circle correct answer) b. Explain WHY this is the case c. As you go ACROSS a PERIOD, the ionization energy tends to increase / decrease / remain constant (circle correct answer)
Date______________ Physical Science – Mr. Lewis Name__________________
16. Atomic radii (atom size) trends (use the figure we worked on in class as a guide): a. As you go DOWN a GROUP, the atomic radius tends to increase / decrease / remain constant (circle correct answer) b. Explain WHY this happens c. As you go ACROSS a PERIOD, the atomic radius tends to increase / decrease / remain constant (circle correct answer) d. Explain WHY this happens
17. For METALS, as you go DOWN a GROUP, the reactivity will: increase / decrease / remain constant (circle correct answer) a. Explain WHY this happens
18. For NON-METALS, as you go DOWN a GROUP, the reactivity will: increase / decrease / remain constant (circle correct answer) a. Explain WHY this happens
19. The Noble Gases are Group 8. Explain why these elements are the least reactive in the periodic table.
20. The name of the MOST REACTIVE NON-METAL in Group 7A is_____________
21. The name of the MOST REACTIVE METAL in Group 1A is________________
22. Group 1A is also known as the _______________________
23. Group 2A is also known as the _______________________
24. Group 7A is also known as the _______________________