dry lab resource binder--answer key - CIA-Biology-2011-2012
advertisement
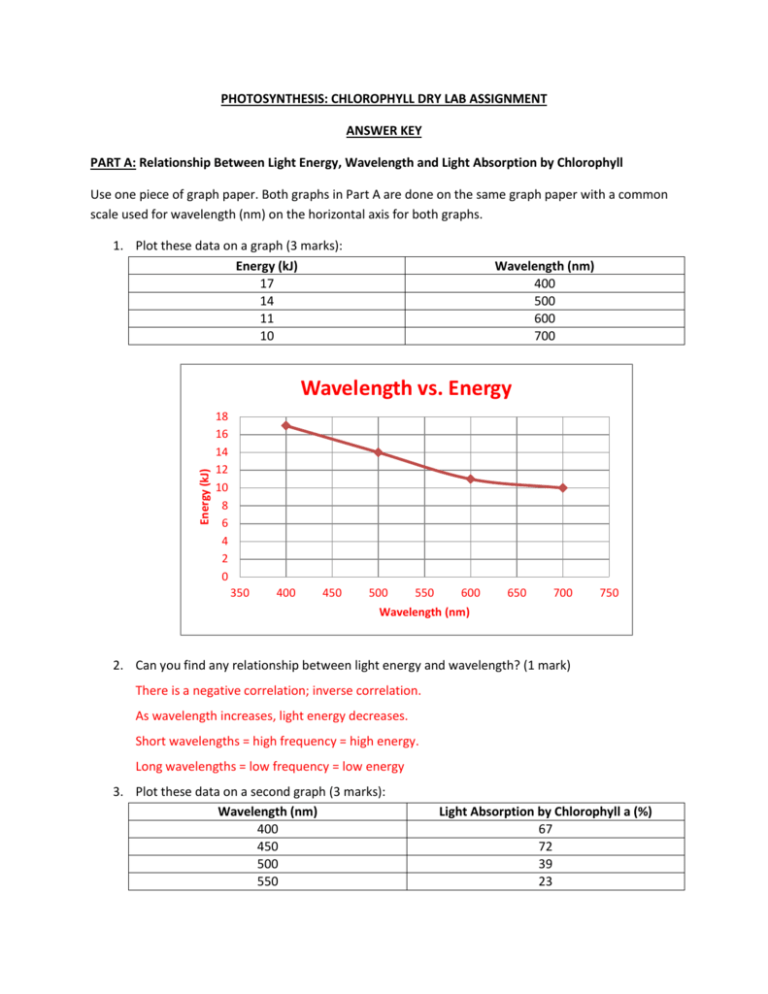
PHOTOSYNTHESIS: CHLOROPHYLL DRY LAB ASSIGNMENT ANSWER KEY PART A: Relationship Between Light Energy, Wavelength and Light Absorption by Chlorophyll Use one piece of graph paper. Both graphs in Part A are done on the same graph paper with a common scale used for wavelength (nm) on the horizontal axis for both graphs. 1. Plot these data on a graph (3 marks): Energy (kJ) 17 14 11 10 Wavelength (nm) 400 500 600 700 Energy (kJ) Wavelength vs. Energy 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 350 400 450 500 550 600 650 700 750 Wavelength (nm) 2. Can you find any relationship between light energy and wavelength? (1 mark) There is a negative correlation; inverse correlation. As wavelength increases, light energy decreases. Short wavelengths = high frequency = high energy. Long wavelengths = low frequency = low energy 3. Plot these data on a second graph (3 marks): Wavelength (nm) 400 450 500 550 Light Absorption by Chlorophyll a (%) 67 72 39 23 600 650 700 30 70 7 Wavelength vs. Light Absorption by Chlorophyll a Light Absorption by Chlorophyll a (%) 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 350 400 450 500 550 600 650 700 750 Wavelength (nm) 4. Which wavelength(s) does chlorophyll a absorb the most? The least? (2 marks) Most: 450 nm and 650 nm Least: 700 nm 5. What light energy does chlorophyll a absorb? (2 marks) 450 nm: 400 nm corresponds with 17 kJ and 500 nm corresponds with 14 kJ. Average energy: (17 kJ + 14 kJ)/2 = 15.5 kJ 15.5 kJ x 72% = 11.16 kJ 650 nm: 600 nm corresponds with 11 kJ and 700 nm corresponds with 10 kJ. Average energy: (11 kJ + 10 kJ)/2 = 10.5 kJ 10.5 kJ x 70% = 7.35 kJ Therefore chlorophyll a absorb at light energies of 11.16 kJ (450 nm) and 7.35 kJ (650 nm) 6. What colour(s) of artificial light would you see used to grow indoor plants successfully? (2 marks) Violet, blue, or red light; these colours are absorbed the most by the plant (chlorophyll) for photosynthesis. PART B: Absorption Spectrum of Spinach Leaf Pigments Wavelength (nm) 400 420 440 460 480 500 520 540 Absorption Spectrum of Spinach Leaf Pigments Absorbance (%) Wavelength (nm) 0.42 560 0.68 580 0.60 600 0.58 620 0.83 640 0.23 660 0.11 670 0.12 680 Absorbance (%) 0.12 0.15 0.17 0.25 0.40 0.32 0.56 0.24 1. Construct a line graph of the data with percent abundance along the vertical axis and wavelength along the horizontal axis. Indicate the colours of the visible spectrum corresponding to the wavelengths along the horizontal axis. (5 marks) Absorption Spectrum of Spinach Leaf Pigments 0.9 0.8 Absor bance (%) 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 350 400 450 500 550 600 650 Wavelenth (nm) 2. Which colours of an intact spinach leaf would be least visible? Why? (2 marks) Blue because the leaf absorb blue wavelengths the most. 3. What colours is absorbed the least by the pigment extract? Why? (2 marks) Green because it is the most reflected; spinach are green in colour. 700 4. Compare the graph to the absorption spectrum found below. Which pigment is most likely responsible for the peak at 670 nm? (1 mark) Chlorophyll a is responsible for 670 nm peak. 5. Why are there no peaks in the range of 500 nm-620 nm? (1 mark) There are no pigments that absorb light at those wavelengths. % absorbance is closer to 0. To absorb light at these wavelengths, accessory pigment phycoerythrin has to be present. 6. Which pigments are primarily responsible for absorption in the range of 400 nm-480 nm? (2 marks) Chlorophyll a, b, and carotenoids.