Chapter 9 紫外光谱
advertisement

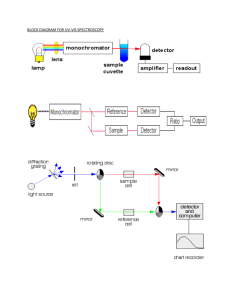
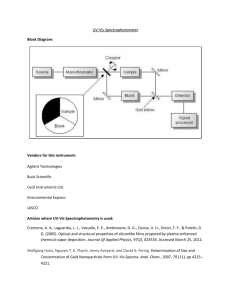
Ultraviolet Spectroscopy 紫外光谱 9.1 Basics of Ultraviolet Spectroscopy The UV involves the absorption of ultraviolet light by a molecule causing the promotion of an electron from a ground electronic state to an excited electronic state. The transitions are generally between a bonding or lone-pair orbital and an unfilled non-bonding or anti-bonding orbital. The wavelength of the absorption is then a measure of the separation of the energy levels of the orbitals concerned. UV UV-Vis * > n* > * > n* <200nm 200 to 800 nm 9.2 The UV-Vis spectrum and Beer’ laws The UV-Vis spectrum typically represents the absorption of light as a plot (Figure 3.2) of energy (as wavelength, λ , in nanometers, from E = hc/λ) versus the intensity of absorption (as absorbance, A, or molar extinction coefficient, ε). Quantitative measurement (定量测定) (IR, UV-vis, AAS, etc.) 9.3 Instrumentation Instrument: spectrophotometer(分光光度计) Stimulus: monochromatic light energy(单色光) Analytical response: light absorption Transducer(传感器): photocell Data: electrical current Data processor处理器: current meter(测流计) Readout: meter scale(仪表) photocell Light Intensity Current Meter Current Scale 动画(部件), P246 闪耀光栅 准直透镜 P247 动画grating and monochromator 仪器进展: 透镜 传感器、检测器 动画PMT 动画pee 动画(紫外) single beam (SB) double-beam (DB) double beam 9.4 Charge transfer transitions (P250) 电荷转移跃迁(荷移吸收光谱 ) 电荷转移跃迁本质上属于分子内氧化还 原反应,因此呈现荷移光谱的必要条件是构 成分子的二组分,一个为电子给予体,另一 个应为电子接受体。 2+ + Fe2+ 3 N N N N 3 Fe2+ A + D hv D +A - (受电子体)(给电子体) [Fe3+ SCN-] +h = 黄色 无色 O 四氯苯醌 血红色;490nm [Fe2+SCN ]2+ Cl Cl Cl Cl O 深红色 六甲基苯 9.5 Applications:Foundamental variables • The wavelength (or energy) of the radiation. (辐射的波长;定性) ☆不同的物质只对不同的、特定波长的光有较强 的吸收或发射。(other wavelength, transparent) • The amount of the radiation at .(辐射的强 度;定量)☆同一物质(溶液)不同浓度的吸 收曲线 c3 > c2 > c1 B A c3 c2 c1 λa λb a Example 1(P7); Example 2 Potassium dichromate(重铬酸盐) and potassium permanganate have overlapping absorption spectra in 1 M H2SO4. K2Cr2O7 has an absorption maximum at 440 nm, and KMnO4 has a band at 545 nm (the maximum is actually at 525 nm, but the longer wavelength is generally used where interference from K2Cr2O7 is less). A mixture is analyzed by measuring the absorbance at these two wavelengths with the following results: A440 = 0.405, A545 = 0.712 in a 1-cm cell (approximate; exact length not known). The absorbances of pure solutions of K2Cr2O7 (1.00 10-3 M) and KMnO4 (2.00 10-4 M) in 1 M H2SO4, using the same cell gave the following results: ACr,440 = 0.374, ACr,545 = 0.009, AMn,440 = 0.019, AMn,545 = 0.475. Calculate the concentrations of dichromate and permanganate in the sample solution. Interferences(干扰、影响因素) Spectral interference(光谱干扰) matrix 基体,基质,样品; component 组成,组分 assay 特定的测定方法 Chemical interference(化学干扰) Instrument interference(仪器干扰) 定性分析(qualitative analysis确定未知 化合物) 缺点:吸收峰少 定性鉴别的依据→吸收光谱的特征(反映结构 中生色团和助色团的特性,不完全反映分 子特性;甲苯与乙苯:谱图基本相同;) 吸收光谱的形状、吸收峰的数目、吸收峰的位 置(波长)、吸收峰的强度、相应的吸光 系数max;(比较法、标准谱图库) 借助经验规则计算吸收峰波长; 1.比较下列化合物(a, b, c)的最大吸收波长 2.IR表明化合物C9H10O分别含有一个苯环、羰 基、亚甲基、甲基,但无法确定羰基的位置。 UV 显 示 有 三 个 吸 收 带 254nm(lgmax=4.1); 280nm(lgmax=3.1);320nm (lgmax =1.9)。化合物结构是? 3. 某化合物在200-400nm范围内没吸收,该化合 物是芳香族;含共轭双键;醛;酮;羧酸 4. 某化合物分子式C5H8O,在UV图上有两个 吸收带(224,9750;314,38),结构是 CH3CH=CHCOCH3;CH2=CHCH2COCH3 CH3CH=CHCH2CHO;CH2=CH(CH2)2CHO 5. 某羰基化合物在近紫外和可见光区只产生 一个204nm (60)的弱吸收带。该化合物 可能是酯;醛酮;,-不饱和醛酮;, -不饱和酯; 在下列化合物中同时含有*、 n*跃迁的化合物是 三氯甲烷、丙酮、丁二烯、二甲苯 在下列化合物中,那一个化合物能吸 收波长较长的辐射( ) 苯、二甲苯、对氯代甲苯、萘 某化合物分子式为C9H10O, 其图如右,指出发色团。 ~320nm 230nm 270nm 360nm