Chemical Bonds
advertisement
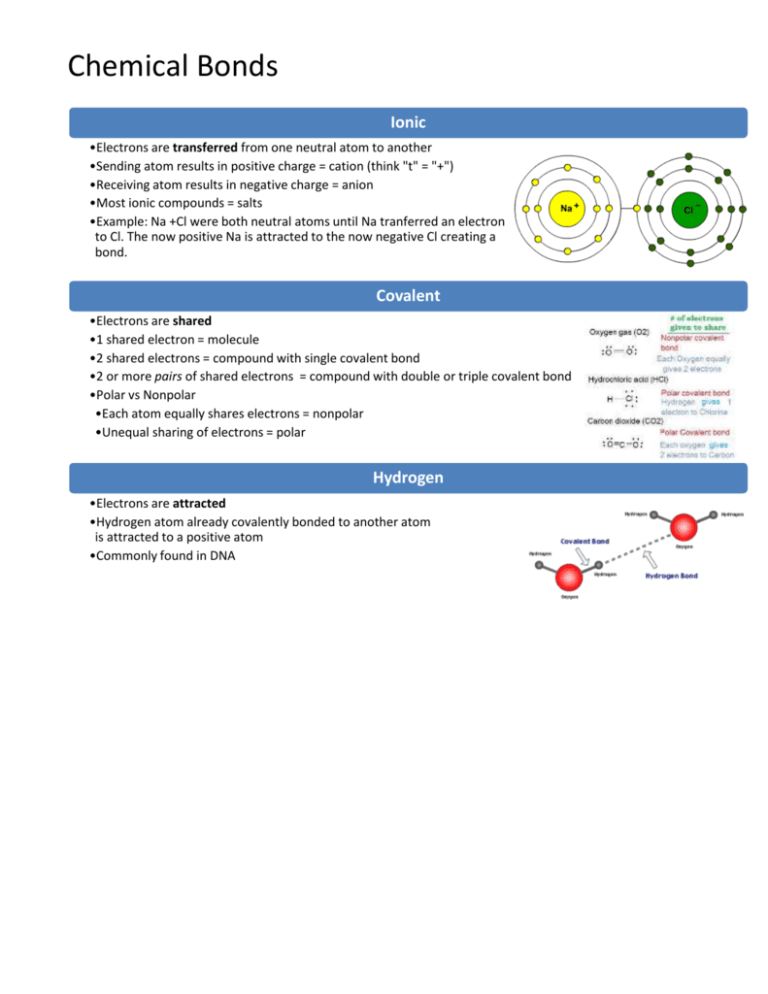
Chemical Bonds Ionic •Electrons are transferred from one neutral atom to another •Sending atom results in positive charge = cation (think "t" = "+") •Receiving atom results in negative charge = anion •Most ionic compounds = salts •Example: Na +Cl were both neutral atoms until Na tranferred an electron to Cl. The now positive Na is attracted to the now negative Cl creating a bond. Covalent •Electrons are shared •1 shared electron = molecule •2 shared electrons = compound with single covalent bond •2 or more pairs of shared electrons = compound with double or triple covalent bond •Polar vs Nonpolar •Each atom equally shares electrons = nonpolar •Unequal sharing of electrons = polar Hydrogen •Electrons are attracted •Hydrogen atom already covalently bonded to another atom is attracted to a positive atom •Commonly found in DNA