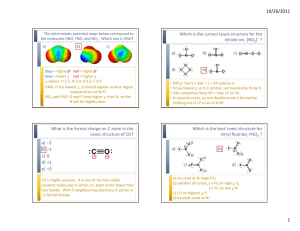
Bonding Theories: Molecular Geometry & VSEPR
advertisement
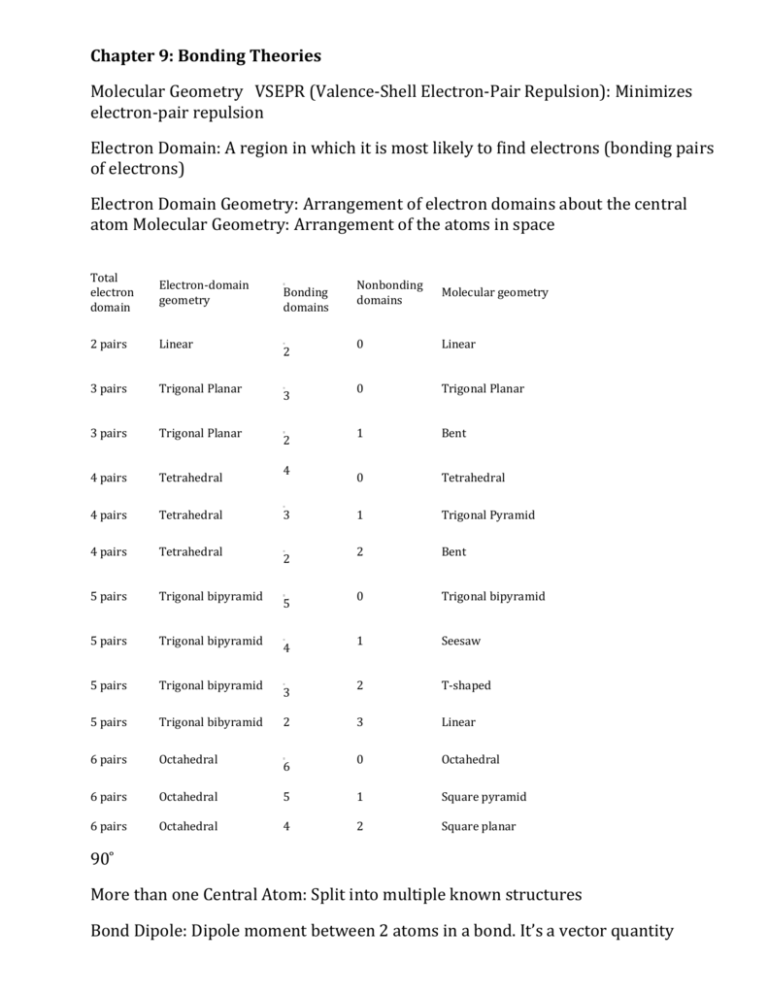
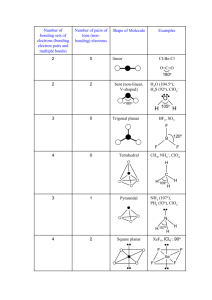
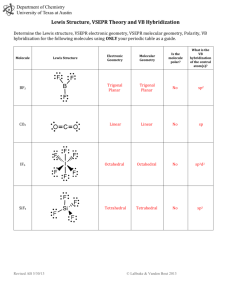
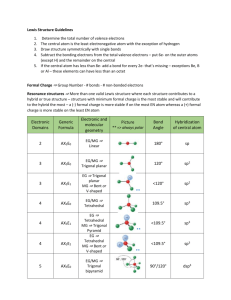
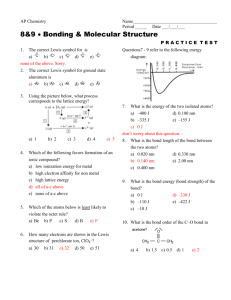
Chapter 9: Bonding Theories Molecular Geometry VSEPR (Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion): Minimizes electron-pair repulsion Electron Domain: A region in which it is most likely to find electrons (bonding pairs of electrons) Electron Domain Geometry: Arrangement of electron domains about the central atom Molecular Geometry: Arrangement of the atoms in space Total electron domain Electron-domain geometry 2 pairs Linear 3 pairs Trigonal Planar 3 pairs Trigonal Planar 4 pairs Tetrahedral 4 pairs Tetrahedral 4 pairs Tetrahedral 5 pairs Trigonal bipyramid 5 pairs Trigonal bipyramid 5 pairs Trigonal bipyramid 5 pairs Trigonal bibyramid 6 pairs Octahedral 6 pairs Octahedral 6 pairs Octahedral Nonbonding domains Molecular geometry 0 Linear 0 Trigonal Planar 1 Bent 0 Tetrahedral 1 Trigonal Pyramid 2 Bent 0 Trigonal bipyramid 1 Seesaw 2 T-shaped 3 Linear 0 Octahedral 5 1 Square pyramid 4 2 Square planar Bonding domains 2 3 2 4 3 2 5 4 3 2 6 90 ̊ More than one Central Atom: Split into multiple known structures Bond Dipole: Dipole moment between 2 atoms in a bond. It’s a vector quantity Hybridization: Orbitals formed by mixing two or more atomic orbitals on an atom Linear = sp hybrid Trigonal Planar = sp2 hybrid Tetrahedral = sp3 hybrid Trigonal bipyramid = sp3d hybrid Octahedral = sp3d2 hybrid Sigma Bond : Single bonds and lie on bond axis. Stronger than pi bonds. Pi Bond : 2 unhybridized P orbitals overlapping parallel to the bond axis. Pi bonds break first, and larger atoms form pi bonds less readily Will only form with sp and sp2 hybrids since it needs an unhybridized p orbital to be present Double and Triple bonds produce smaller bond lengths and produce more repulsion than singles Example: How many hybridized pairs on CO :C O: 2 pair on C, and 2 pair on O (don’t include pi bonds) Diamagnetic: No unpaired electrons Causes substances to be repelled from induced magnetic fields Paramagnetic: Having unpaired electrons Causes substances to be attracted into an induced magnetic field Electrons are not necessarily confined to bonds localized between 2 atoms The more unpaired electrons, the stronger the force of attraction is Delocalized Electrons: Molecules with resonance structures that have pi bonds that can extend over more than two bonded atoms Usually happens in molecules with pi bonds and more than one resonance structure Hybridization Quiz http://www.sciencegeek.net/Activities/structures/hybridization.html Bonding Quiz – Topic 8 http://www.adriandingleschemistrypages.com/apquiz.html Book Companion Site Mastering Chemistry http://masteringchemistry.com/ Tutorials http://www.kentchemistry.com/aplinks/chapters/9CovalOrbitals.htm Flashcards http://www.funnelbrain.com/sid-21-ap-chemistry.html - select Molecular Geometry