Cardiac Physiology Anatomy guided notes
advertisement
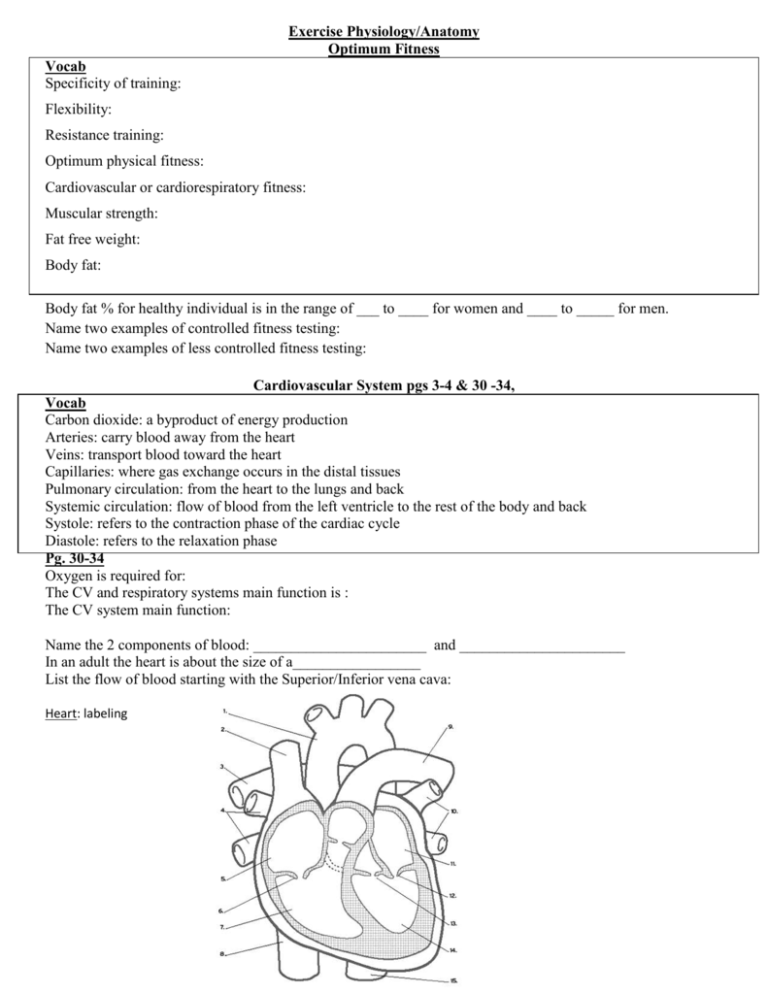
Exercise Physiology/Anatomy Optimum Fitness Vocab Specificity of training: Flexibility: Resistance training: Optimum physical fitness: Cardiovascular or cardiorespiratory fitness: Muscular strength: Fat free weight: Body fat: Body fat % for healthy individual is in the range of ___ to ____ for women and ____ to _____ for men. Name two examples of controlled fitness testing: Name two examples of less controlled fitness testing: Cardiovascular System pgs 3-4 & 30 -34, Vocab Carbon dioxide: a byproduct of energy production Arteries: carry blood away from the heart Veins: transport blood toward the heart Capillaries: where gas exchange occurs in the distal tissues Pulmonary circulation: from the heart to the lungs and back Systemic circulation: flow of blood from the left ventricle to the rest of the body and back Systole: refers to the contraction phase of the cardiac cycle Diastole: refers to the relaxation phase Pg. 30-34 Oxygen is required for: The CV and respiratory systems main function is : The CV system main function: Name the 2 components of blood: _______________________ and ______________________ In an adult the heart is about the size of a_________________ List the flow of blood starting with the Superior/Inferior vena cava: Heart: labeling Heart Basics: - R side = - Myocardium contracts sends blood to lungs - Blood picks up - Oxygenated blood to ______ side - While ____ side contracts _____ side contracts and sends blood through the ______ to rest of body 2 main circulatory patterns: - Pulmonary: o - Systemic: o - Cardiac cycle: Cardiac Output: - Factors - Stroke volume Equation: Ejection Fraction: Oxygen Extraction at the Muscle: Energy Production in Cells Vocab Aerobic: Mitochondria: Anaerobic: Ischemia: Angina Pectoris: ATP - Stroke: Anaerobic Threshold: Glycogen: Creatine Phosphate: Enzymes: Supply of energy (ATP) comes from 1 of 3 pathways: Aerobic energy system Anaerobic energy system Creatine Phosphate system Enzymes: - Aerobic Capacity Maximal Oxygen Consumption VoO2 max: Depends on 2 factors: Formula: MET: To determine VO2 Equivalent: VO2 Max increases with: Therefore: The Aerobically trained client can perform more intense activities than the untrained person. Cardiovascular/Cardiopulmonary Responses to Exercise Changes in Oxygen Delivery - - Increase in o WHY? o HOW? SBP during exercise: - Diastolic pressure during exercise: - Why do we want these changes? Changes in Cardiac Output In response to aerobic training: - Increased aerobic capacity causes: o 1. o 4. o 2. o 5. o 3. o 6. Changes in Oxygen Extraction - 1. New capillaries: o - - Importance? 2. Increase in: o Which increases o Which increases Increased maximum _______________________________ + increased ___________________ = o 1. o 2. o Ability to produce ATP = Submaximal exercises changes: Guidelines for Cardiovascular Fitness Overload Principle: Maximizing overload: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Type of Exercise: Principle of Specificity of Training: Large Muscle Groups: Rhythmic: Intensity of exercise: - If too great: - - range should be: - Or range should be: - Higher the level of fitness = - Improvement will show at: Duration of Exercise: Monitoring Intensity: - 1. -2 - 3. - 4. -5. -Research indicates: - explain the inverse relationship and its equation - Interval Training exercise: * 1. * 2. Frequency of Exercise: Warm up and cool down - - - - Benefits of Regular Aerobic Exercise: warm up : Cool down: - 4 primary risk factors for coronary artery disease: - 1. - 2. - 3. - weightbearing exercises: 4. - Diabetes: - Minimizing CAD risks: - 1. - 2. 3.