Ppt teacher notes for thermo ppt
advertisement

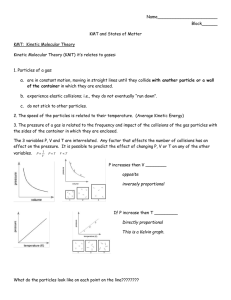
Ppt teacher notes for thermo ppt 1. nothing 2. The amount of randomness in a container of gas is large or the entropy is high The amount of randomness in a container of ice is small or the entropy is low. 3. First page of students notes As is probably obvious, this term is extremely vague because it covers a huge number of processes that take place in the world. To get an understanding of what this really means, we need to start where we usually do… at the beginning. Some terms and ideas you need for studying thermodynamics: As with everything, thermodynamics has specialized terms to describe the things that go on in the real world. Before moving on to seeing how energy behaves, we need to first understand the terms that are used to describe it. (i.e. objects that are waiting to fall off of a shelf, energy stored in chemical bonds, etc). KMT is kinetic molecular theory We know this from the KMT, which says that the amount of energy is proportional to the temperature (in K). The more the particles in an object move around, the higher the temperature 4. One of the main laws that describe how energy behaves in the world is called the law of conservation of energy (also known as the “first law of thermodynamics”): This means that you can change kinetic energy to potential (and vice-versa), but you can never make the amount of energy go away. Examples: You can take the stored gravitational energy of a book on a shelf and make it into the kinetic energy of the book moving through the air. You can use the potential energy of the bonds in gasoline in your car to make your car move. You can use the energy of moving turbines (kinetic) to charge a battery (potential) 5. The energy can be any kind. Electricity, heat, or nuclear. Can you think of another form of energy? 6. it’s not enough that a reaction be spontaneous – in order to be useful a reaction has to take place at a useful rate. Kinetics is the study of chemical reaction rates, but it is also KMT that describes how a gas behaves with its container. 7. it’s not enough that a reaction be spontaneous – in order to be useful a reaction has to take place at a useful rate. Kinetics is the study of chemical reaction rates, but it is also KMT that describes how a gas behaves with its container. 8. Initially, you have several reactants that you are trying to make react with one another. If the reactant particles hit each other with enough energy to react (called the “activation energy”, ∆E) and if the particles hit with just the right orientation, they form the “activated complex” (also called a “transition state”). The transition state is the halfway point in the chemical reaction – the reactant particles are halfway to forming products. From the transition state, the reaction progresses toward the desired products. 9. Similar to exothermic except now the products have more energy than the reactants 10. Rusting in florida is spontaneous Students second page 11. The more energy you need to get to the activated complex, the slower the reaction No matter how exothermic a reaction is, the reaction simply will not take place unless enough energy is added to reach the transition state. Example: Combustion. By adding energy to the system, you’re making it more likely that the reactants will collide with enough force to form the transition state and react. 12. Remember, collision theory says that, in order to have a chemical reaction, the reactant particles have to hit each other with enough energy and in the right orientation to form the transition state! 13. Very unstable reactants tend to be very reactive. These include reagents like halogens and alkali metals (which will tend to react as much as possible to gain the same number of valence electrons as the nearest noble gas). Demonstration: Place both magnesium and calcium in water – the calcium will react more quickly because it is more reactive than magnesium. As we’ve already seen, adding energy to the reagents in a chemical reaction allows them to better overcome the activation energy of the reaction (if necessary, reshow energy diagrams and show what this looks like). Demonstration: Show a slice of bread that was left out in the hood for a week and another one that was left in the refrigerator for a week. If your reagent has a high surface area, there will be more space over which it can come into contact with other reagents. This increases the rate of reaction. Demonstration: Steel wool vs. chunk steel burning. When you increase the concentration of a solution, you increase the number of particles that can run into one another. Because increasing the number of collisions increases the chances that the molecules will hit in just the right way to react, this increases the rate of reaction. Demonstration: Iron nail in very dilute and very concentrated nitric acid. Catalyst: Anything that increases the rate of a reaction without being consumed during the reaction. 14. How a catalyst works: It generates a new reaction pathway with a lower activation energy than the uncatalyzed reaction. As a result, the reaction happens more quickly 15. Catalytic converters…phase such as solid liquid and gas The homo and hetero are catalyst that speed up a reaction Paint, salt, food preservatives 16. . It is commonly used for Nuclear reactions. When we study thermo more in the next unit we will go into ΔH of fusion Fusion is the combining of materials more.