5.2 Relative Time
advertisement

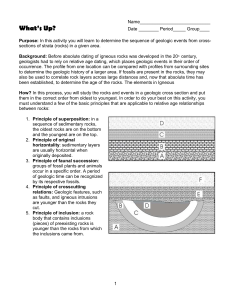
Relative Time Geo 12 Name _______________ 1. Fill in each blank with the appropriate word. The placing of geologic events in sequence from oldest to youngest is termed a) _____________ age dating. This technique uses several common-sense principles. A sequence of sedimentary rocks that is vertical was not formed that way, but was deposited in a horizontal manner. The Principle of b) ________________ ___________________ states this. The Principle of c) ___________________ states that the oldest layer of sedimentary sequence is on the bottom and the d) ________________ layer is on the top. Fragments of one rock found in another are termed e) ___________________ and can be used to determine that the source of the inclusion is f) ______________________ than the rock containing the inclusions. A fault that cuts through a series of rocks is always g) ___________________ than the series of rocks. This is determined using the Principle of h) ____________________________ ____________________. The Principle of i) __________________ ________________________ states that fossils (organisms) succeed one another in a definite and predictable order. A gap in the geological record indicates that j) ___________________ 2. a) Using the Principle of Superposition, place the following cards in sequence from the first (oldest) to the last (youngest) to be laid down. b) Were you able to place all of the cards in sequence? If not, Why? 3. Recall that an igneous dike is an igneous intrusion that cuts across (or is at an angle to) the rocks it intrudes. The following diagram depicts four dikes that intrude into a sequence of sedimentary rocks. a) Using the Principle of Cross-Cutting Relationships, place the dikes in order from oldest to youngest. b) Is the sequence of sedimentary rocks older or younger than the three dikes? Explain your reasoning. 4. The following diagrams depict granite in contact with a layer of sandstone. The geological history of each is quite different. For each cross-section, tell which is older, the granite or the sandstone. Explain your reasoning using the Principle of Inclusions. 5. Answer the following questions using the hypothetical cross-sections provided a) Which is older the dike or Unit C? How do you know? b) Is there an unconformity present? How do you know? c) Is there an unconformity present in this figure? How do you know? d) In this figure which is older – Unit E or Unit A? Which principle did you use in arriving at your answer? e) Is the fault older or younger than the sill? Which principle did you use to get your answer? e) On the next figure did the intrusion occur before or after the deposition of Units A, B, and C? How do you know? f) Did the folding of the Units A, B, C occur before or after the deposition of Units A, B, C? Which principle did you use to get your answer?