5.2 Time and Geology
advertisement
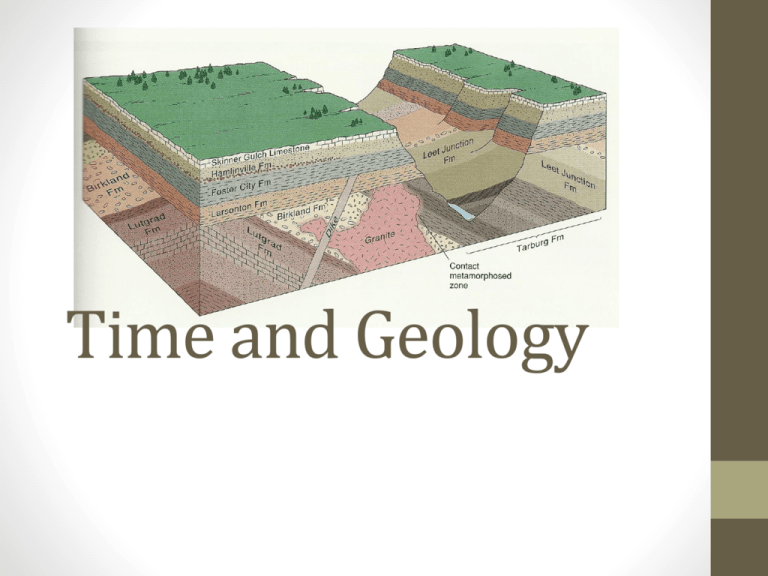
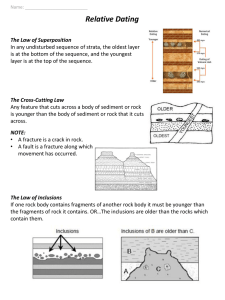
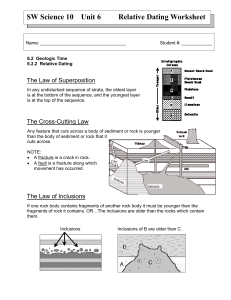
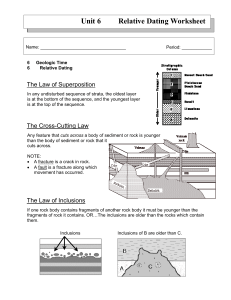
Time and Geology Relative Age Dating • In trying to understand the creation of the geology of an area prior to the 20th century techniques, a method referred to as Relative Age Dating was used. • Relative Age refers only to the order (i.e. older or younger) of particular events, not the actual age of an event. • Relative Age Dating is process involving the application of good observation skills and common sense to deduce the sequence of events in a particular area. True age is not relevant. Principle of Original Horizontality • This principle is based upon the observation that sediment usually accumulates or is deposited in horizontal layers • X Principle of Superposition • This states that in a layered sequence of sedimentary rocks, the oldest layer is on the bottom and become progressively younger toward the top. Principle of Lateral Continuity • This principle state that a layer of sedimentary rock or sediment extends laterally in all directions until it thins out or terminates Principle of Cross-Cutting Relationship • Any event (e.g. fault: intrusions) that cuts through a rock or another event must be younger that the event it cuts through. Principle of Inclusions • This states that inclusions (fragments of rock) of one rock found in another are always older than the rock they are found in. The Principle of Faunal Succession • This principle proposes that fossil assemblages (groups of fossils) succeed one another through time in a regular and predictable order, from least complex to most complex. So what has happened here? What is the oldest rock? What is the youngest rock? The end result