Atoms, Matter, & Properties Study Guide

Unit 7 Study Guide:
Atoms, Elements/Compounds/Mixtures, States of Matter, Physical and
Chemical Properties and Changes
1.
Famous scientists in the study of the atom: Name, dates, and contribution. See summary on page 203.
Date Contribution
Aristotle
Democritus
John Dalton
Joseph Priestly
Antoine Lavoisier
James Rutherford
J.J. Thomson
Niels Bohr
Gilbert Lewis
James Chadwick
2.
Using the Periodic Table to find the characteristics of an atom:
Consider Phosphorous P-15. See practice pages 211, 213, 218.
Atomic Symbol:
Model
Atomic Number:
Atomic Mass:
Protons:
Electrons:
Neutrons:
Group:
Period:
Electron Shells:
Valence Electrons:
Ionic State:
Type:
Most common Isotope:
______
______
______
______
______
______
______
______
______
______
______
______
______
Bohr Model Lewis
3.
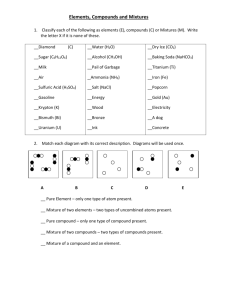
Classifying matter; mixture or pure substance, homogeneous or heterogeneous, and compound or element.
Substance mixture/pure substance homo/hetero/compound/element
Sand
Fruit punch
Magnesium
Baking Soda (NaHCO
3
)
4.
Properties of matter physical or chemical
Physical properties are ____________________,
____________________, ___________________, and can be
_______________ without _______________ the substance.
Chemical properties are _______________, or _______________.
They cannot be observed except in a _______________
_______________.
Characteristic
Smell
Bubbles
Color change
Length
Physical Chemical
Observation Physical Change
Alka Seltzer in water
A melting popsicle
Dissolving Kool-Aid in water
Frying French-fries
Chemical Change
5.
Knowing the relationship between the following terms:
Atom is to Element:
____________________________________________________
Molecule is to Compound :
______________________________________________
6.
An intensive property versus an extensive property
Intensive:
__________________________________________________________
Extensive:
__________________________________________________________
Characteristic
Length
Density
Melting Point
Mass
Intensive or Extensive
7.
Law of Conservation of Mass
___________________________________________________________
__________
8.
Kinetic Molecular Theory
___________________________________________________________
__________
9.
Using the L.O.C.M. to determine the mass of reactants or products
10.
18g of water are formed from 2 grams of hydrogen and ______g of Oxygen
11.
58g of NaCl are formed from ______g Na and ______g Cl.
12.
Separating Mixtures. How would you separate a mixture of sand, salt, and iron filings?
___________________________________________________________
__________
___________________________________________________________
__________
___________________________________________________________
__________
13.
Identifying state of matter, compounds, or mixtures looking at representative molecule models.
A
Salt in water ______
A solid ______
A Liquid
A Gas
______
______
A compound ______
A mixture ______
B
C D E F
14.
Kinetic Molecular Theory and the phases of matter. P.244
When energy is added, molecules __________ __________, and
__________ __________.
_______________ is the measurement of the relative kinetic energy of matter.
A solid remains at the same temperature as it melts or freezes because of its __________ __________ __________.
A liquid remains at the same temperature as it boils or condenses because of its __________ __________ __________.
15.
Be able to calculate density to the correct number of decimals
(limited to the fewest in the math), when D=M ÷ V
16.
Solutions: The lesser part of the mixture is the solute, the greater part of the mixture is the solvent.