cell test #3 study guide
advertisement
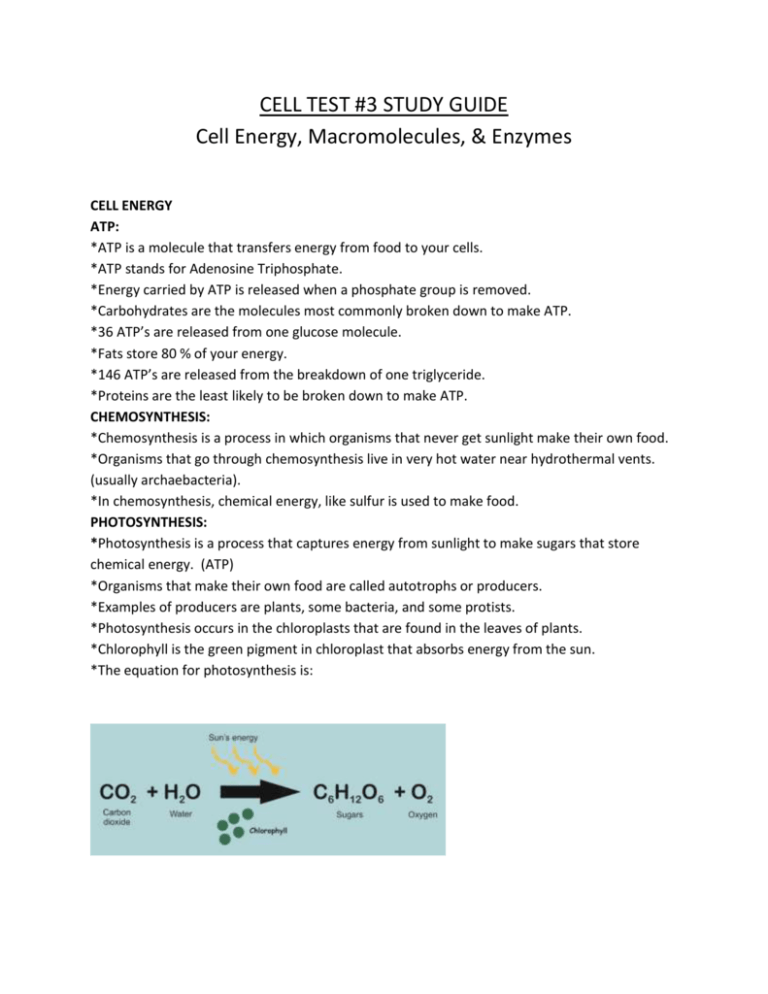
CELL TEST #3 STUDY GUIDE Cell Energy, Macromolecules, & Enzymes CELL ENERGY ATP: *ATP is a molecule that transfers energy from food to your cells. *ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. *Energy carried by ATP is released when a phosphate group is removed. *Carbohydrates are the molecules most commonly broken down to make ATP. *36 ATP’s are released from one glucose molecule. *Fats store 80 % of your energy. *146 ATP’s are released from the breakdown of one triglyceride. *Proteins are the least likely to be broken down to make ATP. CHEMOSYNTHESIS: *Chemosynthesis is a process in which organisms that never get sunlight make their own food. *Organisms that go through chemosynthesis live in very hot water near hydrothermal vents. (usually archaebacteria). *In chemosynthesis, chemical energy, like sulfur is used to make food. PHOTOSYNTHESIS: *Photosynthesis is a process that captures energy from sunlight to make sugars that store chemical energy. (ATP) *Organisms that make their own food are called autotrophs or producers. *Examples of producers are plants, some bacteria, and some protists. *Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts that are found in the leaves of plants. *Chlorophyll is the green pigment in chloroplast that absorbs energy from the sun. *The equation for photosynthesis is: *Photosynthesis is important because it makes sugars for the plants food source, aids in plant growth and development, removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, and gives us oxygen. CELLULAR RESPIRATION: *A heterotroph is an organism that obtains its energy and nutrients by eating other organisms. *All organisms go through cellular respiration to get ATP from food. *Cellular respiration is a process that releases chemical energy fromnsugars to make ATP when oxygen is present. *Any process that requires oxygen is aerobic. *Cellular respiration takes place in the mitochondria. *The formula for cellular respiration is: *Fermentation is an anaerobic process that allows glycolysis, the breaking down of glucose, to continue when oxygen is not present. *The term anaerobic means no oxygen. *Fermentation does not produce ATP. *The two types of fermentation are lactic acid and alcoholic. *Lactic acid fermentation produces lactic acid in your muscle cells, the cells of other vertebrates, and in the cells of some microorgansisms. *Alcoholic fermentation is used by yeasts and some bacteria. *Alcoholic fermentation produces and carbon dioxide and alcohol. *Fermentation is important in food production, digestion, and it is used to make alcoholic beverages. MACROMOLECULES: *The four types of carbon based molecules in organisms are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. Name of Examples Functions Elements Subunit (Made Macromolecule Present of?) Carbohydrate Sugars and Quick energy CHO in a 1:2:1 monosaccharides starches ration Lipid Fats, oils, waxes, Cell membranes, CHO in large 3 fatty acids and steroids protection, ratios 1 glycerol Protein Enzymes, collagen, hemoglobin, antibodies Nucleic Acid DNA and RNA insulation, stored energy Cell membranes, CHON speeds up chemical reactions, builds muscle… Genetic CHONPS information Amino acids nucleotides ENZYMES: *Enzymes are proteins that alter the rate of chemical reactions. *They act as catalysts by speeding up chemical reactions *Enzymes are not used up or changed during chemical reactions. The same enzyme can be used over and over. *The molecule with which an enzyme reacts is called the substrate. *A substrate is called a product when it is released after an enzymatic reaction. *The part of an enzyme molecule that binds with the substrate molecule is called the active site. *Enzymes always end in –ase. *Enzymes are not living things. They are proteins. *Enzymes can be denatured by an excess of heat, a high pH , or a low pH. *Enzymes speed up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy needed to start the reaction. *Activation energy is the energy needed to start a chemical reaction. *Enzymatic Reactions can be altered by: --decreasing activation energy. --increasing temperature. --increasing enzyme concentration.