Bioenergetics
advertisement

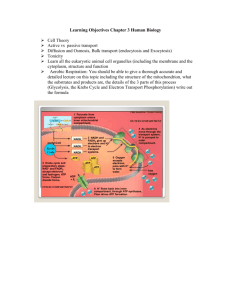
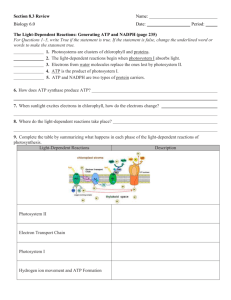
Bioenergetics The Big Picture - energy flows through - matter recycles Producers = Autotrophs - organisms which can make their food - plants, algae, some bacteria - most use photosynthesis Consumers = Heterotrophs - organisms which get their food from other organisms - animals, fungi, most protists - most use cellular respiration ATP = Adenosine triphosphate - normal molecule that cells use to store and release energy - used to power all cellular work - stores small amounts of usable energy - cells must recycle it quickly Photosynthesis - process by which plants use the energy of sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into high-energy carbohydrates (sugars + carbs) and oxygen (a waste product) 6CO2 + 6H2O --- light --> C6H12O6 + 6O2 carbon dioxide + water ---light--> sugars + oxygen - chlorophyll is the primary light-gathering pigment of plants - chlorophyll reflects green light See diagram page 209 in text Photosynthesis happens in mesophyll cells of a leaf. - contain chloroplasts which have thylakoids where reactions occur - two sets of reactions: 1. Light-dependent reactions 2. Light-independent reactions = Calvin cycle Light-dependent reactions - require light - happen in photosystems on thylakoid membranes - sunlight splits water into H+ and O2 - also forms ATP and NADPH -NADPH carries electrons (energy) to Calvin cycle - excited electrons from photosystems give energy to pump H+ into thylakoid spaces and then form ATP See diagram on page 211 of textbook. - a concentration gradient of H+ in thylakoids is balanced by diffusion through ATP synthase Light-Independent Reactions = Calvin Cycle - occur in the stroma of the chloroplast - use the ATP and NADPH from the light reactions to convert CO2 into C6H12O6 - six CO2 are needed to make one sugar molecule Cellular Respiration – Ch. 9 - the energy captured in photosynthesis is released by organisms by several chemical pathways - breaks down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen 6O2 + C6H12O6 Oxygen + glucose 6CO2 +6H2O + Energy carbon dioxide + water + energy - energy of food is measured in calories - food Calorie = 1 kilocalorie (1,000 calories) - energy of food must be released slowly and captured in the bonds of ATP See page 222 in textbook Glycolysis - breaks a molecle of glucose into two pyruvic acids - occurs in the cytoplasm of all cells with or without oxygen - net gain of 2 ATP – not much, but very fast - also produces 2 NADH’s which carry electrons and H+ to other reactions in the cell Fermentation - when oxygen is not available fermentation occurs - yeasts and a few other organisms form alcohol - in our muscles fermentation forms lactic acid Kreb’s Cycle = Citric Acid Cycle (pg. 227) Krebs Cycle = Citric Acid Cycle - in the presence of oxygen, pyruvic acids are modified and taken into the mitochondria - capture energy from bonds of pyruvates to form ATP, NADH, and FADH2 - occurs in mitochondrial matrix - releases CO2 Electron Transport Chain (pg. 228) - NADH and FADH2 from glycolysis and Krebs Cycle carry electrons (energy) to electron transport chains on inner membrane of mitochondria - movement of electrons through E.T.C. pumps H+ into outer compartment of mitochondria to establish a concentration difference - H+ can only diffuse out through ATP synthase and the energy of their diffusion is used to form ATPs See page 228 Summary of ATP production in Cellular Respiration