BIOLOGY MIDTERM REVIEW Mrs. Hicks : 2014.2015 *****KEEP IN
advertisement

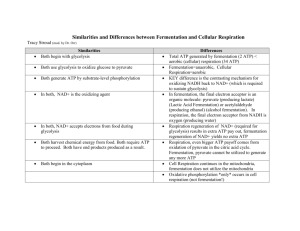
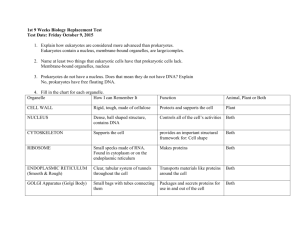
BIOLOGY MIDTERM REVIEW Mrs. Hicks : 2014.2015 *****KEEP IN MIND : THIS IS INTENDED FOR REMINDING YOU OF THINGS WE HAVE COVERED IN CLASS. IT IS NOT INCLUSIVE. LOOK OVER YOUR NOTEBOOK (OLD WORKSHEETS, NOTES, VOCAB SHEETS, TESTS AND QUIZZES AND LABS). ALL MATERIAL IS FAIR GAME FOR THE MIDTERM! For 15 Extra Points on your Midterm this review packet is due the day of the Midterm, completely filled out with no exceptions. CHAPTER 1: WHAT IS SCIENCE? (pp 2-33) What are the parts of the Scientific Method? Explain each. Explain each of the following parts of an experiment: Independent Variable Dependent Variable Constants Control Group Experimental Group Define the following terms: Hypothesis Scientific Theory Scientific Law Homeostasis Who were the scientists involved in biogenesis/abiogenesis (spontaneous generation)? What did they do? Who was for biogenesis? Who was for spontaneous generation? List at least 5 Lab Safety Rules: What are the 4 basic units of measurement in the Metric System (ex. Volume is ___________) Be able to convert between metric units. (ex kg to mg) Explain the 8 characteristics of living things we discussed in class (P 16). Identify and Define the 10 levels of organization we discussed in class (P 21): - BIOSHPERE - MOLECULES CHAPTER 19: VIRUSES AND BACTERIA (pp 470-491) How do we classify (2 kinds) and Identify (3 ways) Prokayotes? Name 3 ways to control bacteria. Draw and Label a Bacteria (Prokaryotic cell). DEFINE : Virus T4 Bacteriophage Lytic Cycle Lysogenic Cycle Capsid Retrovirus CHAPTER 18: CLASSIFICATION (pp 446-465) What are the 4 main reasons to classify living things? How did Linnaeus group organisms in his classification system? Which 2 Kingdoms did Linnaeus recognize? What is binomial nomenclature? Give an example. List the 8 levels of taxonomy (modern levels of classification). From LARGEST (least specific) to SMALLEST (most specific) Explain the modern ways of classifying (cladogram/molecular clocks) How many Kingdoms are there? How many Domains? What are the main characteristics of each of the Domain? The Kingdoms? Be able to use a dichotomous key and cladogram. List the characteristics of organisms in the Phylum Chordata ADDITIONAL VOCABULARY: taxonomy genus taxon evolutionary classification derived characteristics CHAPTER 2: THE NATURE OF MATTER (pp 35-57) What are the three subatomic particles of an atom? What are their characteristics? Where are they found in the atom? What are isotopes? What are ions? What are elements? What are compounds? How are ionic and covalent bonds similar? How are they different? What is a hydrogen bond? What are solutions/suspensions? Draw a molecule of water – H2O Define the properties of water that make it a unique molecule. Give an example of each. Capillary Action Cohesion Adhesion Surface Tension High Heat of Evaporation Solid form is less dense than liquid form Fill in the following chart : Organic Compound Monomer Polymer Carbohydrate Lipid Protein Nucleic Acid What is pH? What are acids? Bases? What is a buffer? What are enzymes? List 3 things that can affect/regulate enzyme activity. Function Example What is activation energy? What is an exergonic reaction? What is an endergonic reaction? ADDITIONAL VOCABULARY: Atom Atomic number Atomic mass Nucleus Cohesion Adhesion Mixture Solution Solvent Solute Suspension Reactant Product Catalyst Substrate CHAPTER 7: CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION (pp 168-197) What are the 3 parts of the Modern Cell Theory? What are the three parts of the Traditional cell theory? Who were the scientists involved in the development of the cell theory? What was their contribution? What are the four levels of organization in a living organism from smallest to largest? Define: tissue How do you determine total magnification of a microscope if you have an eyepiece of 10X, and objectives of 4X, 10X and 40X? What are those lenses named? What are the similarities and differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? What are the similarities and differences between plant cells and animal cells? What are the functions of the main organelles we studied? Cell membrane Cell wall Nucleus Cytoplasm Nucleolus Ribosomes Endoplasmic reticulum (rough and smooth) Golgi apparatus Lysososmes Vacuoles Chloroplasts Mitochondria Explain the 6 ways of getting things in/out of cells. What is unique about each one? (use chart from class) What are the different solutions (isotonic/hypertonic/hypotonic) and what happens to cells in those solutions? What is plasmolysis? What is cytolysis? CHAPTER 8: ENERGY AND LIFE (pp 200-219) What are autotrophs? What are heterotrophs? Give an example of both. What is ATP? How is energy stored in the cell? How is energy released in the cell? What is the equation for photosynthesis? Describe the 2 reactions (processes) of photosynthesis. Where does each process take place? CHAPTER 9: ENERGY AND LIFE (pp 220-239) What is the equation for cellular respiration? Explain/write out the reactants and products of Lactic Acid Fermentation Explain/write out the reactants and products of Alcoholic Fermentation *** Cellular Respiration results in the production of 36 ATP molecules Process ATP release Glycolysis Krebs or Citric Acid Cycle Electron Transport Chain Fermentation Total 36 Where in the cell? Need O2 Type of Respiration