1st 9 Weeks Biology Replacement test Key
advertisement
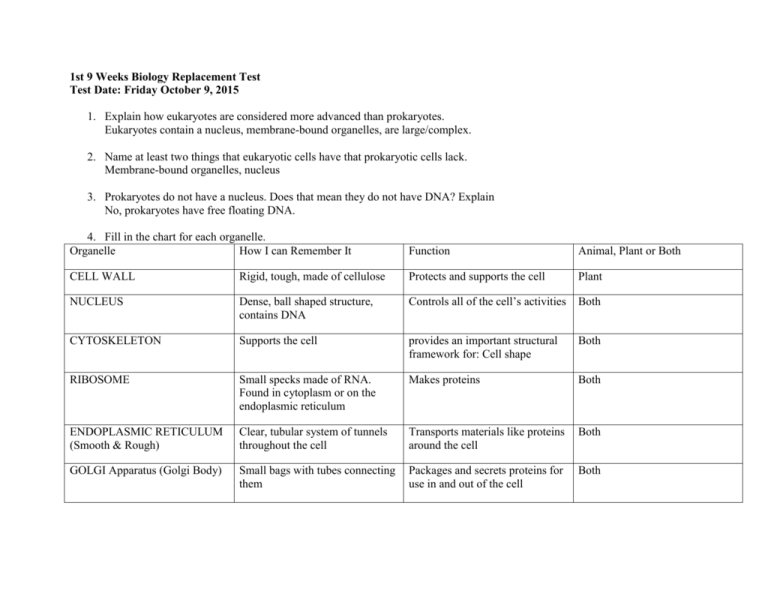
1st 9 Weeks Biology Replacement Test Test Date: Friday October 9, 2015 1. Explain how eukaryotes are considered more advanced than prokaryotes. Eukaryotes contain a nucleus, membrane-bound organelles, are large/complex. 2. Name at least two things that eukaryotic cells have that prokaryotic cells lack. Membrane-bound organelles, nucleus 3. Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus. Does that mean they do not have DNA? Explain No, prokaryotes have free floating DNA. 4. Fill in the chart for each organelle. Organelle How I can Remember It Function Animal, Plant or Both CELL WALL Rigid, tough, made of cellulose Protects and supports the cell Plant NUCLEUS Dense, ball shaped structure, contains DNA Controls all of the cell’s activities Both CYTOSKELETON Supports the cell provides an important structural framework for: Cell shape Both RIBOSOME Small specks made of RNA. Found in cytoplasm or on the endoplasmic reticulum Makes proteins Both ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (Smooth & Rough) Clear, tubular system of tunnels throughout the cell Transports materials like proteins around the cell Both GOLGI Apparatus (Golgi Body) Small bags with tubes connecting them Packages and secrets proteins for use in and out of the cell Both LYOSOME Small, round structures, containing enzymes Digests older cell parts, food or other objects Animal VACUOLE Large open storage area, smaller in animal cells Storage tank for food, water, wastes or enzymes Both CHLOROPLAST Green structures that contain chlorophyll Captures sunlight and uses it to produce food through photosynthesis Plant MITOCHONDRIA Location in the cytoplasm, bean shaped Supplies energy or ATP for the cell through cell respiration using glucose and oxygen Both CELL MEMBRANE Thin, covering, protects cells Protects the cell, performs active transport and passive transport, moves materials in and out of the cell, communication Both 5. Why does water move from a hypotonic solution to a hypertonic solution across a selectively permeable membrane? Because water goes from an area of high concentration gradient to an area of low concentration gradient. 6. What makes faciliated diffusion different from normal diffusion? Faciliated diffusion transports larger molecules using a channel protein while simple diffusion transport smaller molecules across the cell membrane. 7. How are active and passive transport different? Active transport requires energy to transport molecules across the cell membrane, passive transport does not. 8. Explain how endocytosis and exocytosis help maintain homeostasis in single-celled and multi-cellular organisms. Exocytosis is important in expulsion of waste materials out of the cell and in the secretion of cellular products such as digestive enzymes or hormones. Endocytosis is the process by which materials move into the cell. 9. Which group of macromolecules do each of the following belong to: Monosaccharide-------------------Carbohydrate DNA--------------------------------Nucleic Acid Enzymes---------------------------Protein Steroid-----------------------------Lipid 10. Give the macromolecule that best describes each of the following: A sequence of multiple simple sugars-------------------------------------Carbohydrates A set of 3 fatty acids attached to a molecule of glycerol----------------Lipid A chain of amino acids folded and twisted into a molecule------------Protein A sequence of nucleotides--------------------------------------------------Nucleic Acids 11. Which macromolecules are the main sources of energy for living things? What is different about the type of energy they store? Carbohydrates is short term energy, lipids is long term energy 12. Describe how an enzyme attaches to a substrate. Enzymes contain an active site. The substrate binds to the enzyme at the active site forming the Enzyme-Substrate Complex. Once the product has been formed from the Enzyme-Substrate Complex, the enzyme is ready to bind with another substrate. They work together like a Lock and Key Mechanism. 13. What are the three examples you were given of lipids? Fat, Steriods, Wax, Oils 14. Are lipids water soluble? Why is the important to cells? No they are not water soluble, because without Lipids the cell membrane would collapse. 15. Enzymes (speed up, slow down) a chemical reaction. They do this while (changing, not changing) the products and the temperature of the reaction. Enzymes are a type of catalyst that help essential biochemical reactions occur fast enough to maintain homeostasis. Catalysts affect chemical reactions by lowering its activation energy. Enzymes (change, do not change) during a chemical reaction. Temperature, pH, and Concentration Solutions are factors that can alter enzyme activity. 16. In terms of function, reactants, and products, explain why cellular respiration is considered to be the opposite of photosynthesis. THEY ARE BASICALLY THE SAME FORMULA BUT MIRROR IMAGES OF EACH OTHER. WHAT GOES INTO ONE PROCESS IS WHAT COMES OUT OF THE OTHER. WATER & CARBON DIOXIDE GO INTO PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND WATER AND CARBON DIOXIDE COME OUT OF CELLULAR RESPIRATION. 17. Where, in a cell, does photosynthesis occur? List the Reactants and Products of each Stage. Stage 1: Light Dependant Reaction: Occurs in the Thylakoids: LIGHT & H2O LIGHT SPLITS H2O KEEPING THE HYRDOGENS -------------- O2 IS RELEASED & THE HYDROGENS ARE TAKEN TO THE NEXT STEP Stage 2: Light Independant Reaction (Calvin Cycle): Occurs in the Stroma: HYDROGENS + CO2---Glucose 18. Where, in a cell, does cellular respiration occur? List the Reactants and Products of each Stage. Stage 1: Glycolsis: Occurs in the Cytoplasm: Glucose------------ Pyruvate acid and ATP (2) Stage 2: Kreb Cycle: Occurs in the Mitochondria: Pyruvate and ATP------6 CO2 , 2 ATP, 2 FADH, 8 NADPH Stage 3: Electron transport Chain: Occurs in the Mitochondria: Glucose----34 ATP, CO2 , H2 O 19. How are autotrophs and heterotrophs different? Give examples of each. Autotrophs make the own food while heterotrophs ingest their food. Autotroph: Plant Heterotroph: Animal 20. Explain and draw a diagram showing how energy is released from ATP. ATP IS THE ENERGY STORING MOLECULE. THE ENERGY IS STORED IN THE BONDS OF THE 2ND & 3RD PHOSPHATE. WHEN THE BOND IN BROKEN BETWEEN THE 2ND & 3RD PHOSPHATE ENERGY IS RELEASED. ATP IS NOW ADP. T O GET BACK TO ATP ALL THAT HAS TO HAPPEN IS THAT A PHOSPHATE IS BONDED TO THE 2ND PHOSPHATE ON ADP 21. What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration? Aerobic Respiration involves oxygen while anaerobic respiration does not involve oxygen 22. Compare and contrast the two main types of fermentation: lactic acid fermentation and alcoholic fermentation. Lactic Acid Fermentation breaks pyruvate down into lactic acid, commonly found in muscles of animals after over use. Alcoholic Fermentation breaks pyruvate down into Ethel Alcohol and Carbon Dioxide.