STATION 1: Copy the information found below on mixtures and also
advertisement
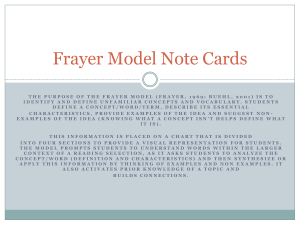
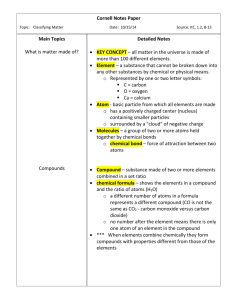
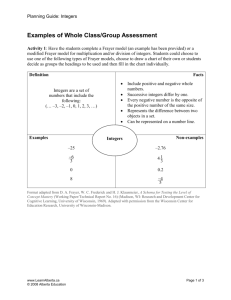
STATION 1: Copy the information found below on mixtures and also copy both Frayer Models. You will use the notes provided to fill in the information that is required from you. MIXTURES: Two or more substances that are not chemically combined with each other and can be separated by physical means. The substances in a mixture retain their individual properties. No chemical change takes place They can be separated physically Can further be classified as Heterogeneous or Homogeneous Mixtures FRAYER MODEL: Definition: Examples: Characteristics/Facts: HOMOGENEOUS MIXTURE Non-Examples: FRAYER MODEL: Definition: Examples: Characteristics/Facts: HETEROGENEOUS MIXTURE Non-Examples: STATION 2: Copy the information found below on Pure Substances and also copy both Frayer Models. You will use the notes provided to fill in the information that is required from you. Pure Substances A sample of matter, either an element or a compound, that consists of only one component with definite physical and chemical properties and a definite composition. FRAYER MODEL: Definition: Characteristics/Facts: Examples: ELEMENT Definition: Non- Examples FRAYER MODEL: Definition: Example: Characteristics/Facts: COMPOUND Non- Example STATION 3: Copy the information found below on Physical Separation Techniques. Copy the concept map and fill in the information that is required of you by using the notes provided. Physical Separation Techniques: When two or more substances, that do not react chemically, are blended together, the result is a mixture in which each component retains its individual identity and properties. Techniques used to separate mixtures rely on differences in the physical properties of the components. Definition and Picture CONCEPT MAP: Technique Physical Separation Techniques STATION 4: Analyze all the pictures that are on the cards found in the baggie. Place each card under the correct category so that you can identify each item on the pictures as being composed of an element, compound, or mixture. ELEMENT COMPOUND MIXTURE