Phase Changes
advertisement

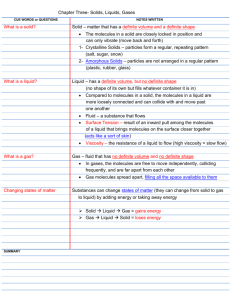
PHASE CHANGES KINETIC THEORY OF MATTER Matter is made up of particles which are in continual random motion. WHAT ARE THE 4 STATES OF MATTER? Solid Plasma Liquid Gas SOLIDS: • Solids have a definite shape and volume • usually organized, crystalline solid • Softer solids will have no pattern, amorphous solid. • packed tightly together • Vibrate in place • Liquids have a definite volume • Liquids take the shape of their container. • Liquids are a fluid • Far enough apart to slide over one another • Energy level is greater than in solids PARTICLES IN LIQUIDS: • No definite volume or shape. • Gasses spread out to fill the entire space given. • Can be squeezed together • Particles are very far apart and move freely • Collide frequently • Have LOTS of energy PARTICLES IN GASES: PARTICLES IN PLASMA: • Plasma is a lot like a gas, but the particles are electrically charged. • Have indefinite shape and volume. • EXTREMELY energetic • Lightning is a plasma. • Used in fluorescent light bulbs and Neon lights. STATES OF MATTER SOLID Tightly packed, in a regular pattern Vibrate, but do not move from place to place LIQUID Close together with no regular arrangement. Vibrate, move about, and slide past each other GAS Well separated with no regular arrangement. Vibrate and move freely at high speeds PLASMA Has no definite volume or shape and is composed of electrical charged particles WHAT IS A PHASE CHANGE? • A change from one state of matter to another • Phase changes are physical changes because they do not affect the chemical make up of a substance. WHAT HAPPENS DURING A PHASE CHANGE? • During a phase change heat energy is either absorbed or released • Heat energy is released as molecules slow down and move closer togetherexothermic • Heat energy is absorbed as molecules speed up and expand-endothermic MELTING • Phase change from a solid to a liquid • Molecules speed up, move farther apart, and absorb heat energy FREEZING • Phase Change from a liquid to a solid • Molecule slow down, move closer together and release heat energy. VAPORIZATION (BOILING) • Phase change from a liquid to gas. It occurs at the boiling point of matter. • Molecules speed up, move farther apart, and absorb heat energy. EVAPORATION • Phase change from a liquid to a gas on the surface of a liquid (type of vaporization). • Molecules speed up, move farther apart, and absorb heat energy. CONDENSATION • Phase change from a gas to a liquid. • Molecule slow down, move closer together and release heat energy. SUBLIMATION • Phase change from a solid to a gas. • Molecules speed up, move farther apart, and absorb heat energy. DEPOSITION • Phase change from a gas to a solid. • Molecules slow down, move closer together and release heat energy. PHASE CHANGE OF WATER 1. Why is there no change in temperature during a phase change? 2. Define melting and boiling point. 3. What is the melting and boiling point of water? 4. At what temperature does water freeze and become a solid?