Writing Chemical Formulas for Transition Metals
advertisement

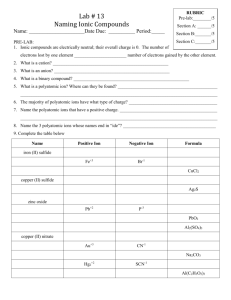
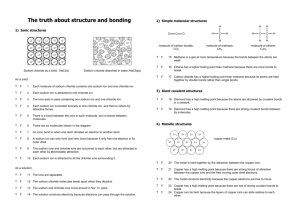
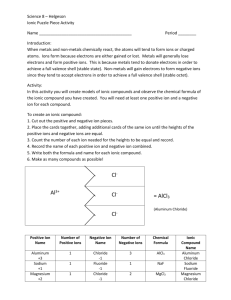
How to Write Chemical Formulas for Transition Metals Transition metals are the elements written in columns 3 through 12 of the periodic table, and they are metallic elements that serve as a bridge between the elements on the left side of the table and those on the right side. Writing chemical formulas for transition metals is a simple task that involves identifying the correct charge of an ion and balancing that charge with the valence of other ions present in a compound. Identifying the Symbols When handed the task of writing chemical formulas, you typically have the name of a compound, such as “copper chloride.” In general, compounds involving transition metals are comprised of cations, or positively charged ions, and anions, or negatively charged ions; the transition metal is the cation, and the non-metal component is the anion. To begin writing the chemical formula of such a compound, you need to identify the symbol of the cation and anion. The symbol for copper is Cu, and the symbol for chloride is Cl. Determining the Valence Finding the valence, or charge, of each ion is essential to writing the correct chemical formula. As cations, the transition metal will be a positive ion, but transition metals commonly have more than one valence. The valence of a transition metal must be notated with a Roman numeral in parentheses following its name. For example, you will see “iron(II)” to denote iron with a positive +2 charge. If no Roman numeral is present, you should be given the transition metal name with a specific suffix. The suffix “-ic” indicates a higher charge than “-ous”; for example, ferric chloride, or FeCl3, indicates a charge of +3 for iron, while ferrous chloride, or FeCl2, indicates a +2 charge. The periodic table will show you the valences of the anions. Group 17 elements, or those elements listed in column 17 of the table, have a -1 charge, Group 16 elements have a -2 charge and Group 15 elements have a -3 charge. Use the charge of polyatomic ions when present. Balancing Charges All compounds must have a total charge of zero, so sometimes you must use subscripts to balance the charges of the cations and anions. Take “copper(II) chloride” for example. Copper has a charge of +2, indicated by the Roman numeral. Chloride, which is located in Group 17 of the periodic table, has a charge of -1. To balance these ions, you need two chloride ions per one copper ion. You would write “2” as a subscript on the chloride symbol to indicate two ions. Writing the Chemical Formula When writing chemical formulas for compounds with transition metals, the transition metal will always come first. For the copper(II) chloride example, you first write “Cu” for copper, followed by “Cl” for chloride. Since you determined you need two chloride ions when you balanced the compound, the complete chemical formula should read “CuCl2.” If you have a transition metal in a compound with a polyatomic ion, the polyatomic ion needs to go in parentheses. For example, chromium(II) bicarbonate’s formula is “Cr(HCO3)2.” Notice the subscript for the polyatomic ion is located outside of the parentheses. by Cara Batema, Demand Media